* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar Basics - Valencia College
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
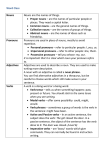
GRAMMAR BASICS Some Terms WHY LEARN GRAMMAR? Knowing grammar will help you learn how to put sentences together. Knowing how to put sentences together will help you become a better writer. Becoming a better writer will help you express yourself better as well as get better grades. FYI Different kinds of words are called… parts of speech NOUN def: nouns can be people, places, and things ex. dog, homework, Abraham Lincoln, love VERB def: a word that shows action, state, or occurrence ex. walk, will eat, am playing, is ADJECTIVE def: a word that describes a noun ex. happy, beautiful, tired QUICK QUIZ What part of speech is the underlined word? The dog ran after the cat. noun PRONOUN def: a word that takes the place of a noun ex. Josh likes to watch TV. He prefers sports shows. ADVERB def: a word or phrase that modifies an adjective, verb, or another adverb (modify: to describe or limit) ex. I am very happy PREPOSITION def: a word used to tell direction, location or time; usually contains a noun and gives more information about something else in the sentence ex. in, at, for, to, with The man is in the grocery store. SUBJECT def: who or what the sentence is about (will be a noun or noun phrase) ex. Jessica, the book, returning clothes Tim plays the guitar. OBJECT def: a noun/pronoun that receives an action of a verb ex. I sent a letter. ARTICLE (DEFINITE & INDEFINITE) definite (specific): the indefinite (general): a/an ex. I bought the car. (a specific car my reader/listener already knew about) ex. I played a game. (general, not specific) INFINITIVE def: to + base form of verb ex. to eat, to sleep, to cry SUBJECT-VERB-OBJECT (SVO) def: in English, clauses tend to follow a subject – verb – object pattern ex. The company fired the employees. PHRASE def: a group of words ex. falling on the floor, in the moonlight CLAUSE def: a group of words with a subject & a verb ex. …while I was watching a movie. I took a shower. INDEPENDENT CLAUSE def: a clause that can be a complete sentence (can have a period) ex. I opened the door. DEPENDENT CLAUSE def: a clause that cannot be a complete sentence by itself; it needs an independent clause ex. When I was playing basketball yesterday, I sprained my ankle. SENTENCE / “COMPLETE SENTENCE” def: a group of words with at least 1 independent clause ex. Teachers are crazy. COMPOUND SENTENCE def: more than 1 independent clause, but no dependent clause ex. I workout at home, and I play video games at home. COMPLEX SENTENCE def: one independent clause, and at least 1 dependent clause ex. My parents washed my car while I was on vacation. COMPOUND-COMPLEX SENTENCE def: more than 1 independent clause, and at least 1 dependent clause. ex. After I get home from school, I clean my room, and my mom makes dinner. FRAGMENT def: a group of words with a period at the end, but is not a complete sentence (it is missing either a subject or a verb) ex. Waiting at the store. (who was waiting? There’s no subject.) FUSED SENTENCE / RUN-ON def: when two complete sentences (independent clauses) are connected without punctuation or a connecting word ex. Kelly is on the track team she is very good. COMMA SPLICE def: when two complete sentences (independent clauses) are connected with a comma ex. Kelly is on the track team, she is very good. CONJUNCTION def: a word that joins or connects 2 parts of a sentence ex. Birds can fly and lay eggs. COORDINATING CONJUNCTION def: a word that joins or connects 2 independent clauses; these are often called “fanboys” for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so ex. Birds can fly, but dogs can only run. SUBORDINATING CONJUNCTION def: a word that makes one clause in the sentence dependent ex. If I go to the store, I will buy milk. GERUND def: a ”verb” ending in –ing that is used as a noun ex. eating, swimming, biking I love swimming. PARTICIPLE def: a verb ending in –ing that is part of a “complete” verb in a specific verb tense ex. Joel is taking his test. PARALLELISM / PARALLEL STRUCTURE def: when you use the same “kinds” of words or phrases in a sentence or list ex. Tom is happy, rich, and going to college. Tom is happy, rich, and smart. (all adjectives) ONE LAST THING… There are many more grammar terms. You can find them online or on the grammar boot camp website. It is possible for a word or phrase to be more than one of the grammar terms at the same time. ex. Paul threw a ball. (ball is a noun, and the object) NOUNS Woohoo! WHAT ARE NOUNS AGAIN? def: a person, place or thing What are the nouns in the sentence? John owns a bike, two cats, and 6 shoes. John owns a bike, two cats, and 6 shoes. DIFFERENT KINDS OF NOUNS Nouns Concrete Nouns Common Nouns Abstract Nouns Proper Nouns DIFFERENT KINDS OF NOUNS Concrete: nouns that can interact with out senses (you can see, taste, touch, hear, and smell them) ex. airplane, sandwich, key DIFFERENT KINDS OF NOUNS Proper nouns: names of people, places or things; ex. George Bush, Canada, The Matrix What is special about these nouns? They use capital letters. DIFFERENT KINDS OF NOUNS Abstract nouns: these are nouns we cannot experience with our 5 senses; they are ideas Ex: love, death, religion, success I cannot smell, taste, touch, hear, or see these things, but I can experience them. DIFFERENT KINDS OF NOUNS Count nouns: count nouns are nouns that I can…count; they can be made plural ex. 1 paper, 2 papers, 3 papers DIFFERENT KINDS OF NOUNS Noncount nouns: nouns that are group or collective nouns, and cannot be counted or pluralized ex. homework, research, happiness, popcorn I have 2 homeworks. I have some homework. DIFFERENT KINDS OF NOUNS Sometimes you will see people ”pluralize” noncount nouns, but it’s a trick. See below: I want 2 coffees, please. What are they really saying? I want 2 cups of coffee, please. *Coffee is a noncount noun.* HOW CAN I FIND A NOUN? First, try to decide if it’s a person place or thing. After that, you can try adding an article (a/an, the) before it. If the article “fits” it is probably a noun. a cat the pool a eat the happy HOW CAN I FIND A NOUN? You can also try to make the noun a subject and put a verb with it- if it make sense, it’s probably a noun. ex. try adding “is good” to a word Love is good. Happily is good. PRONOUNS YAY! WHAT ARE PRONOUNS AGAIN? def: a word that takes the place of a noun ex. he, she, I, who, this The chickens are eating. They like worms a lot. DIFFERENT KINDS OF PRONOUNS Subject pronouns: these pronouns are used as subjects in a sentence ex. We are hungry. Subject Pronouns I, you, he, she, it, we, they DIFFERENT KINDS OF PRONOUNS Object pronouns: these pronouns are used as objects in a sentence ex. They threw me the ball. Object Pronouns me, you, him, her, it, us, them DIFFERENT KINDS OF PRONOUNS Relative pronouns: these pronouns are used to connect a clause or phrase to a noun/pronoun ex. Tiffany, who is a teacher, made ice cream. Relative Pronouns who, whom, whoever, whomever, which, whichever, that DIFFERENT KINDS OF PRONOUNS Reflexive pronouns: these pronouns refer back to the subject of a sentence within the same sentence ex. Terry cut down the tree himself. Reflexive Pronouns myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves DIFFERENT KINDS OF PRONOUNS See the handouts or the grammar boot camp website for more pronouns. VERBS Whoa! WHAT ARE VERBS AGAIN? def: a word that shows action, state, or occurrence What is the verb in the sentence? John owns a bike, two cats, and 6 shoes. John owns a bike, two cats, and 6 shoes. HOW CAN I FIND A VERB? Look for a word that does an action. ex. People help other people. Look for a word that shows a state of being ex. Jimmy is happy. THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS Verbs show tense (time) past | present | future Yesterday, I walked to school. Today, I go to homeroom. Tomorrow, I will see my friends. THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS Verbs can be more than one word ex. The students are doing their homework. I turned in my homework. THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS Verbs can show action or a state Action: The horse ran through the gate. State of being: The spaghetti is hot. THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS An –ing verb is never by itself (don’t confuse with a gerund) ex. I camping today. I am camping today. THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS What are helping verbs? Helping verbs are verbs that “help” the main verb. ex. may, might, are, do, did, was I might go to the party. THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS What are the “be / to be” verbs? am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS What are the “do” verbs? do, does, did, doing, done THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS What are the “have” verbs? have, has, had, having THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS What are modal verbs? Modal verbs (modals) show us degree can, could, might, have to, must, should, would, ought to These verbs can’t be conjugated. They connect with a main verb. THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT VERBS What are phrasal verbs? Phrasal verbs are verbs that include a verb and another word like an adverb or preposition ex. break down, fit in, break out VERB TENSES There are 12 different verb tenses in English. Keep in mind that some verbs are “irregular.” That means that they don’t follow normal rules of conjugation. VERB TENSES- SIMPLE Simple Present: base form of verb | -s/-es We play soccer. He/she/it plays soccer. Used when… talking about an action that is a fact, habit, or a regular action ex. Everyday, I eat dinner at 5PM. VERB TENSES- SIMPLE Simple Past: base form of verb + -ed I walked. They ran (irregular). You cut (irregular). Used when… talking about an action that happened in the past and is done VERB TENSES- SIMPLE Simple Future: will + base form of verb I will go to school. Used when… doing a future voluntary action, or when giving a promise VERB TENSES- CONTINUOUS / PROGRESSIVE Present continuous: ”to be” + verb + -ing We are playing soccer. Used when… talking about an action that is happening right now VERB TENSES- CONTINUOUS / PROGRESSIVE Past continuous: past “to be” + verb + -ing We were playing soccer. Used when… talking about an action that was done for a period of time in the past VERB TENSES- CONTINUOUS / PROGRESSIVE Future continuous: will + be + verb + -ing I will be playing soccer. Used when… talking about an action that will be happening during a certain time in the future. VERB TENSES- PERFECT Present perfect: have/has + past participle She has received a degree. Used for… an unspecified time before now ex. I have been to Mexico. (when?) an action that started in the past but continues until now ex. She has been a teacher for 5 years. (and still is) VERB TENSES- PERFECT Past perfect: past had + past participle She had received a degree. Used for… a completed action that came before another past action ex. She understood the movie because she had read the book. VERB TENSES- PERFECT Future perfect: will + have + past participle She will have received a degree. Used for… a completed action that will come before another future action ex. By tomorrow, I will have gained 3 pounds. VERB TENSES- PERFECT CONTINUOUS (PROGRESSIVE) Present perfect continuous: have/has + been + verb + -ing The dog has been chasing the cat. Used for… duration from past until now ex. He has been talking for the past hour. recently, lately ex. Recently, I have been feeling a little tired VERB TENSES- PERFECT CONTINUOUS (PROGRESSIVE) Past perfect continuous: had + been + verb + -ing The dog had been chasing the cat. Used for… duration before something in the past ex. They had been talking 3 hours before the sun rose. cause of something in the past ex. He gained weight because he had been overeating. VERB TENSES- PERFECT CONTINUOUS (PROGRESSIVE) Future perfect continuous: will + have + been + verb + -ing The dog will have been chasing the cat. Used for… duration before something in the future ex. They will have been talking for over an hour by the time Jenny arrives. VERB TENSES- PERFECT CONTINUOUS (PROGRESSIVE) Future perfect continuous (continued) Used for… cause of something in the future ex. James will be tired when he gets home because he will have been swimming. VERB TENSES- PERFECT CONTINUOUS (PROGRESSIVE) Future perfect continuous (using going to) is/are + going to + have + been + verb + -ing The dog is going to have been chasing the cat for 3 hours before mom gets home. THE END Finally! VERB TENSES- SIMPLE Simple Present: base form of verb | -s/-es We play soccer. He/she/it plays soccer. Simple Past: base form of verb + -ed I walked. They ran (irregular). You cut (irregular). Simple Future: will + base form of verb I will go to school. VERB TENSES- CONTINUOUS / PROGRESSIVE Present continuous: ”to be” + verb + -ing We are playing soccer. Past continuous: past “to be” + verb + -ing We were playing soccer. Future continuous: will + be + verb + -ing I will be playing soccer. VERB TENSES- PERFECT Present perfect: have/has + past participle She has received a degree. Past perfect: past had + past participle She had received a degree. Future perfect: will + have + past participle She will have received a degree. VERB TENSES- PERFECT CONTINUOUS (PROGRESSIVE) Present perfect continuous: have/has + been + verb + -ing The dog has been chasing the cat. Past perfect continuous: had + been + verb + -ing The dog had been chasing the cat. Future perfect continuous: will + have + been + verb + -ing The dog will have been chasing the cat.