* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
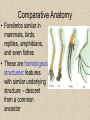
Evidence for Evolution •Fossils •Comparative Anatomy •Vestigial organs •Distribution of Plants and Animals •Related Species •Genetic code is universal Fossils • Allows us to infer lines of evolution • Older fossils are in deeper strata • Radioactive dating is used to determine the age of fossils – Radioisotope has it’s own unique rate of decay – Half-life = amount of time it takes for half of the radioisotope to decay Fossils Continued • Bias in the fossil record – some organisms less/more likely to fossilize • Aquatic organisms become covered by sediment, while terrestrial organisms often decay quickly or destroyed by scavengers • Shells and bones make the best fossils Comparative Anatomy • Forelimbs similar in mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and even fishes • These are homologous structures: features with similar underlying structure – descent from a common ancestor • Analogous Structures: Similar in function/appearance but not in origin or development • Arise from Convergent evolution (evolution that is similar, but species do not share common ancestor) Vestigial Organs • Remnants of organs that were previously used but no longer are Biogeography • Def: The study of the distribution of plants and animals • Evolution of each species occurs only once • The place where the evolution of an organism occurred is called center of origin • Not a single point, but a range of the population • Each species spreads out until stopped by a barrier Similar Patterns of Development of Species • Evolution is conservative: natural selection builds upon what the organism already has Genetic Code is Universal • ALL organisms use the same genetic code • “UUU” codes for the same amino acid in every organism to examined to date (plants, insects, bacteria, animals, etc) Other Points of Evidence • Organisms that are remotely related, such as humans, oak trees, and E-Coli have some of the same proteins (cytochrome c) – There are differences in the amino acid sequences for cytochrome c – Organisms more closely related have less differences Other Points of Evidence Cont. • Can use DNA sequencing (determining the order of nucleotide bases in DNA) • Greater similarities in nucleotide sequences = closer relationship See book pg. 315 Evolution in New Zealand • No native terrestrial mammals (have bats) • No mammals to prey on birds • Many species of birds that have filled the niches of mammals and remain unprotected against introduced mammals Tree Fossils Glacier Moa • Extinct giant flightless bird of New Zealand • 15 different species • Hunted by humans Takahe • a large flightless rail, became the sheep of New Zealand, browsing grasslands. Weka Kea Bush Wrens • Scurry about on the forest floor, mice-like, in pursuit of insects. Kokako • weakly flighted wattlebirds, behave like squirrels, hopping through branches after fruit. Paradise Ducks Kiwi • • • • Blind and flightless Nocturnal Has Whiskers Nostrils at end of beak (used to find food in the ground) • Has bone marrow