* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Biomedical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Miltenyi Biotec wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
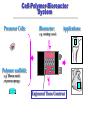
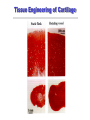
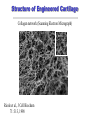
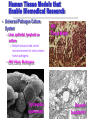
Tissue Engineering in Microgravity Neal R. Pellis, Ph.D. Chief, Biological Systems Office NASA Johnson Space Center Houston, TX 77058 [email protected] Why Tissue Engineering? • Millions suffer tissue or organ loss from diseases and accidents every year – Yearly cost of treatment exceeds $400 billion • Major medical treatment is transplantation – Shortages of replacement tissue and organs • Development of alternative sources for transplantations by engineering tissue • In vitro tissue models may allow better understanding of disease pathology to avoid organ failure Biomedical Applications of Tissue Engineering • In vitro Growth of Tissues for Implantation – Replacement of Diseased or Damaged Tissues » Skin replacement for treatment of serious burns • Extracorporeal Support – External Devices Containing Tissue that Replace the Function of Internal Organ » Artificial liver • Human Disease Models – Differentiated Tissues for Pathogen Propagation » Models for HIV, Cyclospora – Three-Dimensional Cancer Models » Prostate, Colon Biomedical Applications of Tissue Engineering • Drug Testing and Development – New Tissue models for drug development » Renal Toxicity, Heart • Biomaterial-guided Tissue Regeneration – Implantation of Biomaterials to Induce Tissue Regeneration » Absorbable collagen matrix for guiding tissue regeneration in periodontal surgery. Immune System Problems • Immunosuppressive Drugs – Serious Complications • Autologous – Use the person’s cells – Best approach if possible • Encapsulation: Immunoisolation – Biopolymer coating to keep immune system out • Future: Genetically Modified Cells – Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) genes – Stem Cells Current Commercial Products • Human Skin Equivalent with Cells – Autologous » Genzyme (Epicel): Epidermal Grafts, 16 Days to make » Organogenesis (Apligraf) - Two layer preparation – Neonatal foreskin » Used for skin ulcers » Stimulates the host tissue to regenerate • Cell-based Procedure to Repair Knee Injuries – Autologous » Genzyme (Carticel) » Inject chondrocytes under periosteal flap Microgravity: Tissue Engineering in 5 Steps Assembly 3-Dimensional Growth Matrix Formation Differentiation Vascularization Microgravity Cell Culture Analog Solid Body Fluid Rotation • Fluid rotates with the cylinder • Results in particle suspension without stirring • Cells are in near continuous suspension • Fluid shear is minimal • Suspension is possible for tissue assemblies ~0.5-1.0 cm NASA Rotating Bioreactor Licensed to Synthecon, Inc. Microgravity Analog Culture: Advantages • • • • Suspension with minimal mechanical shear Low hydrodynamic shear Promotes tissue morphogenesis Sufficient mass transfer to support cell metabolism and growth • May share some characteristics with space flight culture Cell-Polymer-Bioreactor System Precursor Cells: Bioreactor: Applications: e.g. rotating vessel Polymer scaffold: e.g. fibrous mesh or porous sponge Engineered Tissue Construct Tissue Engineering of Cartilage Structure of Engineered Cartilage Collagen network (Scanning Electron Micrograph) native Riesle et al., J Cell Biochem 71: 313, 1998 Engineered Heart Tissue Compared with monolayer cultures, 3-D multilayer cultures more closely resemble intact cardiac tissue Human Tissue Models that Enable Biomedical Research • Universal Pathogen Culture System – Liver, epithelial, lymphoid coculture HIV Tissue Model » Multiple tissue provide correct microenvironment for most common human pathogens – EBV, Ebola, Monkeypox Cyclospora sporozoites Borrelia burgdorferi Summary • Microgravity offers a unique environment that re-orders the forces exerted on cells • Cells unloaded from gravity may perform to our advantage in tissue morphogenesis • The response of cells to the re-ordering provides novel insights into cellular mechanisms