* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HW 2 - Marriott School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
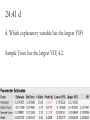
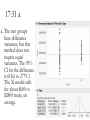
HW 23 Key 24:41 Promotion. These data describe promotional spending by a pharmaceutical company for a cholesterol-lowering drug. The data cover 39 consecutive weeks and isolate the area around Boston. The variables in this collection are shares. Marketing research often describes the level of promotion in terms of voice. In place of he level of spending, voice is the share of advertising devoted to a specific product. The column Market Share is sales of this product divided by total sales for such drugs in the Boston area. The column Detail Voice is the ratio of detailing for this drug to the amount of detailing for all cholesterol-lowering drugs in Boston. Detailing counts the number of promotional visits made by representatives of a pharmaceutical company to doctors’ offices. Similarly, Sample Voice is the share of samples in this market that are from this manufacturer. 24:41 a a. Do any of these variables have linear patterns over time? Use timeplots of each one to see (scatterplot matrix). Do any weeks stand out as unusual? Week is most linear with Sample Voice, barely for Detail Voice, and not really for Market Share. 24:41 b b. Fit the multiple regression of Market Share on three explanatory variables: Detail Voice, Sample Voice, and Week (which is a simple time trend, numbering the weeks of the study from 1 to 39). Does the multiple regression, taken as a whole, explain statistically significant variation in the response? 24:41 b b. The slopes are all not 0. 23% of the variation in Market Share is explained by the model. F = 4.9 24:41 c c. Does collinearity affect the estimated effects of these explanatory variables in the estimated equation? In particular, do the partial effects create a different sense of importance from what is suggested by marginal effects? The VIFs do not suggest collinearity. The slopes aren’t even all the same direction. 24:41 c c. The marginal and partial effects for Sample Voice and Week are fairly close. Detail Voice is rather different. 24:41 d d. Which explanatory variable has the largest VIF? Sample Voice has the largest VIF, 4.2. 24:41 e e. What is your substantive interpretation of the fitted equation? Take into account collinearity and statistical significance. There aren’t any real collinearity concerns. To have a real affect on Market Shares, there needs to be many visits, but it may not have an actual impact. Sample voice is the only thing that really contributes. 24:41 f f. Should both of the explanatory variables that are not statistically significant be removed from the model at the same time? Explain why doing this would not be such a good idea, in general (are they collinear?). Probably not. They may not explain much, but they are not collinear. Two insignificant variables might be highly correlated with each other, but not here. 17:31 Used Cars. Prices of 155 used BMW. Some have 4 wheel drive (xi type) and other 2 wheel drive (i type). 17:31 a a. 17:31 a a. 17:31 a a. 17:31 a a. The two groups have difference variances, but this method does not require equal variances. The 95% CI for the difference is 618.6 to 2779.3. The Xi model sells for about $600 to $2800 more, on average. 17:31 b b. No. The average age of the cars in the two groups is identical. Age has not confounded the comparison in “a”. 17:31 b b.

















![1 Full model [35] - UC Davis Plant Sciences](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005851071_1-e12c4cdfc7a07f0144ab735094259dac-150x150.png)








