* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Second Book: Student´s Reference Book ……
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
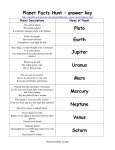
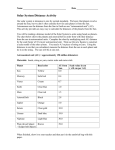
Eudoxos Project 2003 Second Book: Student’s Reference Book ...or how the student can get themselves out of a state of forgetfulness or ignorance. © C.P.R. Campiña de Tarifa. Cádiz. Spain. 2003. 1 Eudoxos Project 2003 Main Concepts Galaxy, enormous group of hundreds or thousands of millions of stars, all together and orbiting around a common centre. All the stars we see from our planet belong to our galaxy. Solar System, system formed by the Sun, nine planets and their satellites, asteroids, comets and meteorites, dust and interplanetary gas. The dimensions of this system are expressed in terms of the average distance of the Earth from the Sun. The nine planets are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. Milky Way, also called the Galaxy, a group of stars in the shape of a saucer, which include the Sun and its Solar System. For an observer on Earth, the Galaxy appears as a faint band of light which can be seen at night extending across the sky, especially on clear summer nights with no moon. Structure: It has been discovered that the Milky Way is a large, spiral galaxy with several spiral arms which are coiled around a central nucleus. Constellation, any of the 88 groups of stars that appear in the celestial sphere and take their names from religious or mythological figures, animals or objects. Eclipse, is the disappearance of a heavenly body caused by the positioning of a second body between the first and the observer or between the heavenly body and the star that illuminates it. Luna Eclipse: Disappearance of the moon into the shadow of the Earth. This takes place when the earth is found between the sun and the moon and its shadow obscures the moon. Partial Eclipse: One which only hides a part. Total Eclipse: Complete disappearance of a heavenly body. Eclipse of the Sun: Disappearance of the sun caused by the positioning of the moon between the sun and the earth. This is produced when the moon is found between the sun and the earth and its shadow is projected onto the earth’s surface. © C.P.R. Campiña de Tarifa. Cádiz. Spain. 2003. 2 Eudoxos Project 2003 Transits and Occultation, are astronomical phenomena similar to eclipses and due to small celestial bodies which come between the earth and a bright heavenly body. Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun. It’s found at a distance of approximately 58 million km, it has a diameter or 4,875 km, its volume and mass are similar to Earth’s and its average density is approximately the same as the Earth’s. Mercury orbits around the Sun every 88 days (planet year). Radar studies of the planet show that it turns on its axis once every 58.7 days. Given that its surface is porous and of dark rock, Mercury is a bad reflector of sunlight. Venus, second planet from the Sun. It is the brightest object in the sky after the Sun and the Earth. This planet is called the Morning Star when it appears in the East at dawn and the Evening Star when it is in the West at dusk. Due to the distances of the orbits of Venus and the Earth from the Sun, Venus is visible for no more than three hours before dawn and three hours after dusk. Earth, third planet from the Sun and third largest in size of the nine main planets. The average distance of the Earth from the Sun is 149,503,000 km. It is the only planet known to have life, although some of the other planets have atmospheres and contain water. The Earth isn’t a perfect sphere but the shape of an orange. This planet has a satellite, the Moon. Just like the whole Solar System, the Earth moves in space. Its movements are: revolution and rotation. Rotation means that the Earth turns on its own axis and revolution means that the Earth moves around the Sun. Mars, planet that takes its name from the Roman god of war. The fourth from the Sun and the seventh greatest in mass. Mars has two small satellites with craters: Phobos and Deimos which some astronomers believe are asteroids captured by the planet early in its history. Phobos measures 21km in diameter and Deimos only 12km. Jupiter, fifth planet from the Sun and the biggest in the Solar System. Jupiter is 1,400 times bigger than the Earth, but its mass is only 318 times that of our planet. The average density of Jupiter is about a quarter of the density of the Earth, showing that this enormous planet must be composed of gases more than metals and rocks like the Earth and other planets. Saturn, sixth planet from the Sun and the second biggest in the Solar System. Saturn is best-known for being surrounded by a system of rings, discovered in 1610 by Galileo using one of the first telescopes. More than 20 satellites have been discovered in Saturn’s orbit. © C.P.R. Campiña de Tarifa. Cádiz. Spain. 2003. 3 Eudoxos Project 2003 Uranus, seventh planet in distance from the Sun, that revolves outside Saturn’s orbit and inside Neptune’s. In addition to its rings, Uranus has 15 satellites. All of them revolve around its equator and move in the same direction as the planet. Neptune, is the fourth biggest planet and the eighth in distance from the Sun. The average distance of Neptune from the Sun is 4,500 million km and its average lineal diameter is approximately 49,400 km or nearly 3.8 times that of Earth. Its volume is approximately 72 times, its mass 17 times and its average density 0.31 that of the Earth or 1.7 times that of water. Eight satellites are known to revolve around Neptune, two of which can be seen from the Earth. Pluto, ninth planet in the Solar System; it’s the furthest planet from the Sun that we know of. This planet has a satellite. Light Year: This is a unit of measurement used in astronomy to measure large distances. It is equal to the distance travelled by light in an average solar year. Taking the speed of light to be 300,000 km/sec, a light year is equivalent, in round figures, to 9,461,000,000,000 km. © C.P.R. Campiña de Tarifa. Cádiz. Spain. 2003. 4