* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Project Rubrics
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
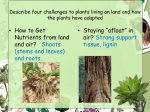
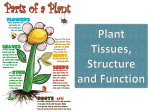
Plant Project Rubrics Create a power point, prezi, or a booklet. Include information on the following topics. Add pictures and diagrams. Basic plant characteristics Autotrophs Multicellular Don’t move around Have cell walls Have life cycles with two phases (alternation of generations---a sporophyte phase and a gametophyte phase) What plants need for survival: Sunlight Water Carbon dioxide Minerals Plant Adaptations to land: Reproduction without water (by using seeds) Prevent water loss by (cuticles) 5 Main groups of plants: (Make a separate slide for each group.) For each group, include the following information: 1. Green Algae (nonvascular, seedless) earliest plants: Where they are found---around water so plant won’t dry out Way of transporting materials---no roots, stems, or leaves so absorb water and nutrients directly from their surroundings. Process of sexual reproduction---water needed for sperm to swim to egg 2. Bryophytes (Mosses & Liverworts) (nonvascular plants) Where they are found---live in moist environments Small in size (because no vascular tissue) Way of transporting materials---no true roots, stems, or leaves; root-like structures called rhizoids absorb water and minerals and anchor the plant Process of sexual reproduction---water needed for sperm to swim to egg 3. Ferns, horsetails, and club mosses (vascular seedless plants) Where they are found---live in moist environments Way of transporting materials---have vascular tissue Plants can grow bigger xylem transports water to all plant parts phloem transports food and nutrients to all plant parts Process of sexual reproduction---water needed for sperm to swim to egg 4. Gymnosperms (vascular seed plants with cones) Naked seeds—seeds are on the cones, not covered Where they are found---everywhere, can live in dry places Way of transporting materials---have vascular tissue Plants can grow bigger xylem transports water to all plant parts phloem transports food and nutrients to all plant parts Process of sexual reproduction---pollen from pollen cones (male) is carried by the wind to female cones; no water is needed 5. Angiosperms (vascular seed plants with flowers) Enclosed seeds—seeds are inside the fruit Where they are found---everywhere, can live in dry places Way of transporting materials---have vascular tissue Plants can grow bigger xylem transports water to all plant parts phloem transports food and nutrients to all plant parts Process of sexual reproduction---(reproductive structure is the flower) Pollen (sperm) is carried by the wind or by animals to the ovule (egg) inside the ovary The ovary ripens and turns into fruit 6. 2 groups of Angiosperms A. Monocots Seeds---Single cotyledon Leaves---parallel veins Flowers---petals in multiples of 3 Stems---scattered vascular bundles Roots---fibrous roots--many B. Dicots Seeds---Two cotyledon Leaves---branched veins Flowers---petals in multiples of 4 or 5 Stems---vascular bundles in a ring Roots---tap root---one main root 7. Plant Structures & functions: A. Roots B. Stems C. Leaves 8. How plants are useful in everyday life: (3-5 ways)