* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metrology of Electrical Quantities
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
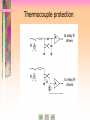
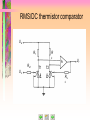
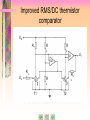
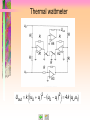
Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 Athens Athens Programme Programme 2008 2008 Metrology of Electrical Quantities Laboratory of Legal Metrology Department of Measurements Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague Responsible professor: Prof. Ing. Jaroslav Bohacek, DrSc. Phone +420 22435 2220 E-mail [email protected] http://measure.feld.cvut.cz/... Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 I often say that when you can measure what you are speaking about, and express it in numbers, you know something about it … … but when you cannot measure it, when you cannot express it in numbers, your knowledge is of a meagre and unsatisfactory kind. William Thomson, Lord Kelvin Athens 2008 Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Far from being a dull area of science, high-precision measurements are an increasingly exciting area in which to work, for they push theory and experiment to the very limits of which they are capable… If we recall that the rich oil deposits under the North Sea remained unknown until the advent of the very precise geophysical measurements, or that the spin of the electron was inferred from precise spectroscopic measurements, we see more clearly the class of discoveries which can come from precise measurement. Brian W. Petley Athens 2008 Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Laboratory visits Course objectives Lectures What is metrology? Previous intro Laboratory demonstrations Please, select some topic above to continue Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Laboratory demonstrations 1. Thompson-Lampard's capacitance standard 2. Frequency performance of resistance standards 3. Calibration of capacitance boxes Athens 2008 Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 Course objectives: to present an overview of modern and perspective methods for precision measurements of electrical quantities, to demonstrate various techniques used in calibrations of electrical measurement instruments and standards. Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Lectures Lecture 1 Introduction Measurement units and measurement standards Quantum standards of voltage and resistance Thompson-Lampard's capacitance standard Equivalent circuits of standard resistors, capacitors and inductors Resistors with calculable frequency performance Transfer standards Athens 2008 Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 Lectures Lecture 2 Voltage and current inductive ratio devices and optimization of their metrological parameters. Athens 2008 Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Lectures Lecture 3 Methods for precision measurement of dc current and dc voltage Modern potentiometers Measurement of voltage, power and energy in audiofrequency range Sample lecture Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 Lectures Lecture 4 Bridges for dc and ac measurements of resistance Transformer and current-comparator-based capacitance bridges Metrological applications of the quantum Hall effect (QHE) Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 What is Metrology? Metrology is the science of measurement. Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 What is Metrology? Metrology covers three main activities: 1. The definition of internationally accepted units of measurement, e.g. the metre. 2. The realization of units of measurement by scientific methods, e.g. the realization of a metre through the use of lasers. 3. The establishment of traceability chains by determining and documenting the value and accuracy of a measurement and disseminating that knowledge, e.g. the documented relationship between the micrometer screw in a precision engineering workshop and a primary laboratory for optical length metrology. Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 What is Metrology? Metrology is considered in three categories with different levels of complexity and accuracy: 1. Scientific metrology deals with the organisation and development of measurement standards and with their maintenance (highest level). 2. Industrial metrology has to ensure the adequate functioning of measurement instruments used in industry as well as in production and testing processes. 3. Legal metrology is concerned with measurements where these influence the transparency of economic transactions, health and safety. Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 Systematic measurement with known degrees of uncertainty is one of the foundations of industrial quality control and, generally speaking, in most modern industries the costs bound up in taking measurements constitute 10 -15% of production costs. Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU in Prague Athens 2008 Laboratory visits: Czech Metrology Institue www.cmi.cz Calibration of digital multimeters Quantum Hall effect based calibrations of resistance standards Laboratory of Legal Metrology, CTU Prague in Prague See you in Prague! 2008 Athens 2006 TOPIC 3 Current balance IC1 = IC2 = IC3 = I C1 C2 C3 IC1 enters C1 at the bottom and leaves it at the top, IC2 enters C2 at the top and leaves it at the bottom. Electromagnetic forces on the suspended coil, produced by these two currents, are of the same sense. Current balance F13 IC1 IC3 M13 2 I f13 z 0 4 d 1 d 3 a13 M13 C1 C3 (Neumann´s formula) Current balance F23 M23 2 IC2 IC3 I f23 z From symmetry, f13 f23 f Resulting electromagnetic force on C3 is F F13 F23 2 f I 2 Current balance operation • The mass of the suspended coil plus the vertical electromagnetic force exerted on it are counterbalanced by means of a mass m on the left scale pan. • After reversing the current in the suspended coil, the change m of this mass, necessary to offset the change F of the acting electromagnetic force, is determined. 1 Δm g ΔF 4 f I Δm g I 2 f 2 Current balance operation A separate moving experiment makes it possible to avoid the troublesome calculation of f from the dimensions of the coils: Coil C3, which is threaded by the magnetic flux produced by the current I flowing in C1 and C2, is moved with a constant velocity v in the vertical direction, a voltage u(t) being induced in it: Current balance operation If a voltage drop U = R I is produced by the current I on a known resistance R and if a velocity v is choosen for which u t U in the moment of passage of the scale beam through its equilibrium position, M13 R f z 2v Electronic kilogram In case that quantum standards of voltage and resistance are used to measure the current I flowing in the coils in course of the weighing experiment, a current balance with a known value of f can be used to produce known values of electromagnetic force and to monitor variations of masses which are used to counterbalance it. Voltage balance is an apparatus based on counterbalancing the attractive force between electrodes of a capacitor. 1 2 C Fz U 2 z DC comparator potentiometer I I s p Slave PS R Constant current PS Ux, Ue N n N s s p PD Ns = 1000 turns ns = 11 turns in steps of 10-4 turns OSC Np 2000 turns, steps of 10-4 turns Realization of the equivalent of fractional turns SPS Is ... 500 50 Ω Ω 5.625 Ω 1turn / step 1000 turns R Primary voltage standard system with closed-cycle refrigerator Primary voltage standard system with closed-cycle refrigerator • 100 nV calibration accuracy • -11 V to 11 V range available from 10-V system • typically 1 hour stability time at 10 V for 10-V system • automatic voltage calibration in minutes • automatic calibration of DVMs • complete system diagnostics RMS/DC thermocouple comparator 1 2 S1 Rs1 Ux TE1 S2 R Rs2 TE2 Ur Automatic RMS/DC thermocouple comparator Ux Ur Rs1 TE1 Rs2 TE2 Thermocouple protection A to relay R drives A to relay R drives R R RMS/DC thermistor comparator Ua R1 R 2 Rs1 Ux Ur A T1 T2 Rs 2 Improved RMS/DC thermistor comparator Ua R1 R R 3 2 A1 A2 Rs Ux 1 Rs R 2 4 T1 T2 Ur Electrodynamic method of measurement of AC power moving coil ic1 ic1 dM Inst. torque i c1 i c2 d dM mean torque i c1 i c2 d T ic2 i c1 i c2 fixed coils 1 i c1 i c2 dt T 0 ic1 = i1 + I1 ic2 = i2 - I2 i1 i 2 I1 I2 mean torque 0 0 Electrodynamic method of measurement of AC power Uout Ur I2 Control circuit R I1 ic1 electrodynamometer ic2 R uU R R i2 i1 uI i1 A2 A1 fixed coils moving coil Thermal wattmeter uU Uout R R R R A4 R A2 A1 R uI R R A3 Uout k uU uI 2 uU uI 2 4 k uU uI