* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Storage Aware Protocols For heterogeneous networks
Telecommunications in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Windows Vista networking technologies wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
PSTN network topology wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
Streaming television wikipedia , lookup
Content delivery network interconnection wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
STORAGE AWARE ROUTING
FOR CONTENT DELIVERY
APPLICATIONS
Shweta Jain
Assistant Professor
Mathematics and Computer Science
York College CUNY
Outline
• Background and Motivation
• Protocols for Content Delivery Applications
• Storage Aware Protocols
• Some Results
• Current Work: End to End Transport for SAP
• Future Directions and Wish list
BACKGROUND AND
MOTIVATION
Why storage aware protocol stack?
Internet Evolution
• Number: Handful of nodes in ARPANET to billions today
• Application: Text based conversation to real time and
stored content delivery
• Interface: Mainly wired to mostly wireless
• Mobility: Fixed to mobile (going toward highly mobile)
Some Statistics
• Mobile broadband users worldwide
• 1.2 billion estimated by the ITU in 2011
• Growth rate 45% annually over last 4 years
• Mobile broadband subscriptions outnumber fixed subscriptions 2:1
• Top Mobile broadband Usage (survey 2010 by
Keynote/Adobe)
• Media and entertainment
• Social networking (76%), local information (73%), news (68%), music
(63%), games (61%), video (56%)
• Travel
• Maps (81%), Research travel (47%)
Key Issues
• Internet has evolved
• Support for mobility and content are required for future Killer apps
• Sensors, IoT, VANET are now being promoted by utilities
and services company
• Support for seamless communication across these networks and
the wired network is a major requirement and challenge
• Proposal: Storage and Content awareness built into the
network design
• Intuitions:
• Caching content near the consumer improves network performance
• Temporary storage and history based routing for interoperability
between networks
PROTOCOLS FOR CONTENT
DELIVERY APPLICATIONS
Storage aware Network, Transport and Application
Idea: State of a connection need not be
binary
• Route states at the network layer are:
available, unavailable and in-repair
• Mobility triggers new route discover
• Sensor networks re-configure routes to avoid to energy depletion
• Cognitive radios transmission interrupted by primary user
• Congestion related delay in the network
The network is still trying to keep the
connection alive:
Idea: State of a connection need not be
binary
• Similarly application and transport layer connection states
could be:
Available
Repairing
Unavailable
An App to connect the disconnected
• Consider a commuter in an underground train
• Normally no network connectivity is available
• Consider a train with storage capable routers
• Commuter turns on his tablet
• Starts an app
• The app automatically searches and
connects to one of the storage routers
• Storage routers have cached content such as news, movies,
songs, even personal files.
• Caches refresh in an on-demand basis at the train station.
• Commuter gets the illusion of being connected to the Internet!
Requirements:
• The App accepts cached content, initiates search for
content
• The content routing feature in the network layer, finds the
best proxy cache for content
• Uses destination routing to retrieve content along the best path
• The transport layer reliably retrieves the content
• Maintains state for extended period of time if the end-user gets
disconnected
Extend the commuter scenario
everywhere!
• Why not use the same architecture at home?
• Cable, Optical and other network providers maintain proxy cache
• Could be the ONT, customers’ DVR, some routers in the service
provider network
• App searches for content proxy
• Perhaps finds the content in neighbor’s DVR!
• Transport and Network layers optimize the network
performance by using “special/efficient” techniques
• Find the best route
13
STORAGE AWARE
PROTOCOLS
Work done so far… in collaboration with Prof Dipankar
Raychaudhuri at WINLAB Rutgers University
14
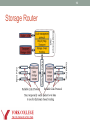
Components of SAP
• Storage Aware Routing (STAR)
• Use history based routing metric
• Use storage to delay data delivery while the network searches for
“better” paths
Better ϵ {Energy efficient, most storage, fastest, higher probability of success,…}
• Content caching based transport
• End-to-end transport with ability to create and use intermediate
cache
• Hop by Hop Transport
STAR: Storage Aware Routing
• Compute multiple paths to the destination using the hop count based routing
metric- breadth first topology search
• Maintain long and short term “expected link rates” to describe the
temporal/variable cost component of the routes
• Choose to store when the best path is
• Worse than usual or
• Downstream routers have low available storage (network layer
backpressure flow control)
(Future routers will have storage space for caching and temporary storage)
(storage is getting cheaper by the year)
Forwarding Algorithm
16
Storage Router
Applicable to all networks?
• Applicability:
• Long term cost: Time scale of variation depends upon the
network type
• Storage space: Indicates congestion in wired, wireless, DTN
(Available storage space is a measure of congestion)
• Storage aware routing concept for all networks
• Unifies and generalizes the routing scheme across
networks
• Support for mobility
• Allows policy and price based store or forward
• Avoid expensive 3G
• Store if the Wi-Fi data rate is lower than usual
Transport layer consideration
• Network layer store event may lead to
• end-to-end transport layer timeout
• Out of order data delivery at the destination
• Storage aware routing was evaluated with a hop-by-hop
transport
• Divide large content into smaller batches
• Send each batch using hop by hop reliability
• Exchange end-to-end acknowledgements to maintain states at
source and destination --- with higher tolerance for delay
• Perform content caching based on popularity, pricing etc.
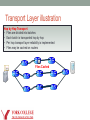
Transport Layer illustration
Hop by Hop Transport
• Files are divided into batches
• Each batch is transported hop by hop
• Per hop transport layer reliability is implemented
• Files may be cached on routers
Files Cached
Network Layer illustration
Storage Aware Routing
• Transmit when the link is average or better than average
• Store upon disconnection or when the link is worse than
average
Weaker link
detected! Store data locally
EVALUATION AND
RESULTS
Orbit testbed and NS2 simulation
Evaluation Topologies
Testbed topologies
Simulation Topologies
Truncated Levy Walk
Mesh network
Disconnected
Network
Access Point
Topology
Linear Topology with
varying link packet
loss rate
Mesh network
connectivity graph
Testbed Results
• In mesh topology: STAR
is as much as 2 times
better
• Access point topology:
• Linear topology with link
outage: SAP is an order of
magnitude more efficient
compared to current state
of the art
Mesh network
Access Point
Topology
• SAP also works in
disconnected networks
Disconnected
Network
Linear Topology with
varying link packet
loss rate
Simulation Results
•Levy Walk Topology:
•Many more files delivered
with lower delay
•Higher throughput
•Mesh topology with
exponential arrival rate:
•30% more files delivered with
delay less than 1 minute
•33% higher throughput
Publications
• Shweta Jain, Sneha Gopinath, Dipankar Raychaudhuri. "STAR: STorage Aware
Routing for Generalized Delay Tolerant Networks." IEEE International Symposium
on a World of Wireless Mobile and Multimedia Networks 2011
• Ryoichi Shinkuma, Shweta Jain, Roy Yates. "In-network Caching Mechanisms for
Intermittently Connected Mobile Users." 34th IEEE Sarnoff Symposium 2011
• Sneha Gopinath, Shweta Jain, Shivesh Makharia, Dipankar Raychaudhuri,. "An
Experimental Study of the Cache-and-Forward Network Architecture in Multi-hop
Wireless Scenarios." 17th IEEE Workshop on Local and Metropolitan Area
Networks (LANMAN) 2010, Best Paper Award.
• Shweta Jain, Ayesha Saleem, Hongbo Liu, Yanyong Zhang, Dipankar
Raychaudhuri,. "Design of Link and Routing Protocols for Cache-and-Forward
Networks." 32nd IEEE Sarnoff Symposium 2009
• Ryochi Shinkuma, Shweta Jain, Roy Yates. "Network Caching Strategies for
Intermittently Connected Mobile Users." 20th Commemorative Personal, Indoor
and Mobile Radio Communications Symposium (PIMRC) 2009
CURRENT WORK
Ongoing…
27
End to End Transport Proposal
• Send feedback to sender or sender’s agent when data
forwarding is interrupted
• Sender keeps the route alive by sending 1 byte packets– similar to
flow control in TCP
• Data is stored at the last router that detected disconnection
• If route becomes available, transmission resumes
• If it takes too long….
• The end host will need to retry
Practical Caching
• Cache personal and popular content at routers, access
points, other key junctions in the network
• Brings content closer to the consumer
• Intercept and redirect requests to serve content from the
cache
• Cross layer protocols to enable interception of requests
• Authentication to ensure requestor is authorized to receive content
29
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
30
Future Directions
• Tying the lose ends
• How much state to maintain?
• Where should proxies be placed?
• How long and how much to store?
• Implementation and evaluation
• Simulation and emulation of network and transport on various
topologies
• Design the mobile app for testbed/proof-of-concept
deployment
• Implementation phase—needs industry interest and support
Future Directions (Wish List)
• Case Studies:
• Deployment in underground transportation system
• Internet connectivity is available only at stations
• Routers available on the trains to cache content
• Goal: Improve productivity during commute
• Deployment in fiber to the home networks
• Cache on demand movies on home DVRs and/or ONT
• Use P2P network principles to deliver cached content between
customers
• Goal: Reduce load on the core network, improve service to customer
THANK YOU
Questions and Suggestions?