* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Toxicology - Madison County EMD
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
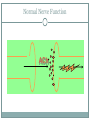
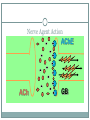
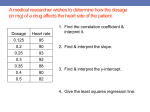
Toxicology MADISON COUNTY EMD ANDREW SCORDATO EMT-P Toxic Exposure 10% of ED visits and EMS responses involve toxic exposures. 70% of accidental poisonings occur in children under 6 years old. Drug Abuse In 2010 22.6 million 4.6 million ED visits 46% involved abuse o Mortality-100,000- 1 in 4 o Cost ½ trillion dollars o Common Rx’s=Alcohol, Stimulants, Hallucinogens, Prescription medications Routes of Exposure Inhalation Example-Huffing-paint, gasoline, nitrous oxide, Carbon monoxide, ammonia, chlorine, Tear gas, Freon, methyl chloride, Carbon tetrachloride A&P- Capillary exchange Assessment-Evaluate the scene and respiratory, CNS, cardiac systems Management-Safety, Remove Pt. from environment, Poison Control Routes Ingestion Examples-prescription medications, Household/Cleaning agents , Petroleum-based agents, Cosmetics, plants, or foods A&P- absorption in stomach and small intestine AssessmentWhat, When and How much? Did you drink any alcohol? Have you attempted to treat yourself? Have you been under psychiatric care? Why? Weight Physical exam Management-ABC use AEIOUTIPS Routes Surface Absorption Examples-Poison ivy, Organophosphates, drug patches=fentanyl, nitro A&P-Drug and patient dependent Assessment-Respiratory, Neurologic Management-Safety, Removal of drug Routes Injection Examples-IV drug abuse-Heroin/Steroid users A&P-Intravenous VS. Intramuscular Assessment-Physical findings- Sites? Management-ABC treat with Antidote if possible Watch for anaphylactic reactions Poison Control Centers Provide detailed information 24hr staffed Id pills and toxicity Effects Toxidromes Similar toxins typically have similar signs and symptoms. In some cases it may be difficult to identify a specific toxin. Types Anticholinergic Cholinergic Hallucinogenic Opiate/Narcotic Sedative/Hypnotic Sympathomimetic Anticholinergic Signs and Symptoms Delirium, Flushed Skin, Dilated Pupils, Urinary Retention, Decreased Bowel Sounds, Memory Loss, SZR, Hyperthermia, HTN, Tachycardia Causes Antihistamines Scopolamine Jimson Weed Angel Trumpet Benztropine CyclicAntidepressants Atropine “Hot as a Hare, Dry as a Bone, Red as a Beet, Blind as a Bat” Cholinergic Signs and Symptoms Confusion, Weakness, Salivation, Lacrimation, Defecation, Emesis, Diaphoresis, Muscle Fasciculations , Miosis , SZR, Bradycardia, Hypothermia, Tachypnea Causes Organophosphates Carbamates Mushrooms SLUDGE MM Hallucinogenic Signs and Symptoms Disorientation, Hallucinations, Visual Illusions, Panic Reaction, Moist Skin, Hyperactive Bowel Sounds, SZR, Tachycardia, Tachypnea, HTN Causes Amphetamines Cannabinoids Cocaine Phencyclidine (PCP) Sedative/Hypnotic Signs and Symptoms Coma, Stupor, Confusion, Sedation, Progressive Deterioration of CNS Function, Apnea Causes Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Ethanol Anticonvulsants Opiate/Narcotic Signs and Symptoms Altered Mental Status, Unresponsiveness, Miosis, Shock, Shallow & Slow Respiratory Rate, Bradycardia, Hypothermia, Hypotension Causes Opiates Propoxyphene Dextromethorphan Sympathomimetic Signs and Symptoms Delusions, Paranoia, Diaphoresis, Piloerection, Mydriasis, Hyperreflexia, SZR, Anxiety , Tachycardia, Bradycardia (if pure alpha agonist)HTN Causes Cocaine Amphetamines Methamphetamine Phenylpropanolamine Ephedrine Pseudoephedrine Albuterol Ma huang Inhaled Toxins Carbon Monoxide Inhaled colorless, odorless gas Poorly ventilated heating systems Confined spaces Signs and Symptoms Headache N&V altered mental status Tachypnea Management Prev. discussed Initiate supportive measures. High-flow, high-concentration oxygen Hyperbaric therapy Inhaled Hydrocarbons Compounds of Carbon and Hydrogen May be ingested, inhaled, or adsorbed Signs and Symptoms Burns due to local contact Wheezing, dyspnea, hypoxia, pneumonitis Headache, dizziness, slurred speech, ataxia, ALOC, cardiac dysrhythmias Foot and wrist drop with numbness and tingling Management Standard emergency procedures Ingested toxins Alcohol Physiologic Effects CNS depressant Alcoholism Susceptible to methanol or ethylene glycol ingestion Peripheral vasodilation, diuresis General Alcoholic Profile Drinks early in the day, alone, or secretly Binges, blackouts, GI problems, “green tongue syndrome,” chronic flushing of face and palms Cigarette burns, tremulousness, and odor of alcohol Ingested Alcohol cont Chronic Alcohol Ingestion Poor nutrition Alcohol hepatitis Liver cirrhosis, pancreatitis Sensory loss in hands/feet Loss of balance and coordination Upper GI hemorrhage Hypoglycemia Falls (fractures and subdural hematoma) Ingested Withdrawal Delirium Tremens (DTs)- “Shaking Frenzy” Signs and Symptoms Tremor of hands, tongue, eyelids N&V, general weakness, anxiety Tachycardia, sweating, hypertension, hallucinations, irritability or depressed mood, poor sleep Increased sympathetic tone, orthostatic hypotension TX ABC/O2,IV,EKG. Determine if other drugs are involved. Consider medications. 25g D50W if hypoglycemic 100mg thiamine IV or IM Benzos for DT’s Ingested Medications Commonly due to dosage errors Example-Beta Blocker overdose Signs and Symptoms Nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, confusion Profound hypotension, cardiac dysrhythmias Bronchospasm, pulmonary edema Management Standard procedure BB/TCA-Sodium , Calcium, Glucagon Surface absorbed poisons Caustic Substances Typically occurs by ingestion or surface absorption. Acids Cause significant damage at sites of exposure. Are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream. Alkalis Slower onset of symptoms allows for longer contact and more extensive tissue damage Signs and Symptoms Facial burns Pain in the lips, tongue, throat, or gums Drooling, trouble swallowing Hoarseness, stridor, or shortness of breath Shock Manage-Airway Surface Example Hydrofluoric Acid Toxic; used to clean and etch glass. Signs and Symptoms Burning at site of contact. Confusion, palpitations, muscle cramps. Management standard toxicologic emergency procedures. Irrigate and immerse the affected area. Specific Drugs AND DRUG ABUSE Definitions Drug abuse-nontherapeutic Overdose-in excess Addiction-overwhelming need Tolerance-larger doses Withdrawal-psychological/physical effects Why? Pleasurable Social Anxiety Performance enhancing Curiosity Specific Drugs Hallucinogens Mind altering/CNS Common agents-LSD, PCP, Mescaline Example-Jimson Weed Anticholinergic effects Atropine Effects 24-48 hours Assessment-Hallucinations, Hyperthermia, Photophobia Tx-ABC, Rapid transport, beware of Seizures and Violent Behavior Specific Sympathomimetic Examples-Cocaine, Bath Salts, Khat, AlphaPVP and Gravel IPOD cleaner Effects-extreme sympathetic arousal Assessment-Cocaine=Chest pain/Bath Salts=Delusions, Paranoia/Khat=Anxious-----Excited Delirium? Treatment-Safety, Sedation?, Calm Bath Salts Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bKbTbRqXVFg Specific Amphetamines Example-Crystal Meth, Contains- Ephedrine/Pseudoephedrine Assessment-rapid speech, violence and paranoia, Meth mouth Treatment-ABC, treat signs and Symptoms-----Excited Delirium Methamphetamine Specific Cannabis compounds Example- K2 and SPICE “Ear Wax” More potent hard to control dosages Assessment-Loss of Control, Decreased pain response, delusions Treatment-Safety, Supportive Brands “Ear Wax” Specific Club/Rave Drugs Examples-Ecstasy, Roofies (rohypnol) Effects-Ecstasy=Reduces inhibitions and eliminates anxiety/Roofies=Relaxation and drowsiness, Dangerous when consumed with alcohol (Date Rape Drug) Assessment-Ecstasy=Constant motion, Excessive talking/Roofies=If mixed with alcohol coma Decreased HR and RR Treatment-Ecstasy-monitor temperature/hydration. Roofies=SANE capable hosp. Specific Prescription and OTC medications Examples-Robotussin, Corcidin, Krocodill, Skittles Parties Effects-Dextromethorphan long acting anesthetic and depressant/Krocodil=tissue necrosis/Skittles Parties=Clean out the medicine cabinets. Assessment-Loss of motor control(like they are intoxicated) Seizures Treatment-ABC- Supportive-treat signs and symptoms, PCC Krocodil tissue damage Prescription Antidepressants TCA Include amitriptyline, amoxapine, doxepin, nortriptyline, imipramine, clomipramine. TCAs have a narrow therapeutic index. Assessment Dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention, constipation, Confusion, hallucinations, hyperthermia, Respiratory depression, SZR, hypotension, cardiac dysrhythmias. Tx Monitor and treat cardiac dysrhythmias. Avoid use of flumazenil, which may precipitate seizures. Prescription MAO Inhibit the activity of Monoamine Oxidase which breaks down neurotransmitters like epinieprhine, seritonin, and dopamine. Infrequently Prescribed Antidepressant Only if TCA or SSRI don’t work High mortality with overdose because of drug’s action Signs and Symptoms Headache, Nausea, agitation, restlessness, tremor, hyperthermia Palpitations, severe hypertension and tachycardia Progresses to bradycardia, hypotension, coma, and death Tx Standard Prescription Trazodone, Bupropion, and SSRIs Signs and Symptoms Drowsiness, tremor, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia Serotonin syndrome Triggered by increasing the dose or by adding selected drugs Marked by agitation, anxiety, confusion, insomnia, headache, coma, salivation, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, “goose bumps”, flushed skin, hyperthermia, rigidity, shivering, incoordination, and myoclonic jerks Tx Standard OTC ASA Common Overdose Drug Includes aspirin, oil of wintergreen Signs and Symptoms Tachypnea, hyperthermia, confusion, lethargy, coma, cardiac failure, and dysrhythmias, Abdominal pain, vomiting, pulmonary edema, ARDS Tx Activated charcoal indicated Tylenol, Acetometophin Common OTC Antipyretic and Analgesic ASA/Tylenol Tylenol cont’d OTC NSAIDS Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Include ibuprofen, keterolac, naproxen sodium Signs and Symptoms Headache, tinnitus, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, drowsiness, Dyspnea, wheezing, pulmonary edema, swelling of extremities, rash, itching Specific Plants Decorative Plants Common source of accidental poisoning in children Signs and Symptoms Excessive salivation, lacrimation, diaphoresis, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and altered mental status Examples- Intentional-Salvia Divinorium aka Magic Mint, Sally-D Effect-Hallucinogenic, users report it is just intense as Mescaline. Not controlled by DEA. Assessment-Hallucinations, Delusion Sally-D Opiates Heroin Names-smack, skag, horse, brown, black, tar Origin-Heroin is an opiate drug that is synthesized from morphine, a naturally occurring substance extracted from the seed pod of the Asian opium poppy plant Action-Works on opiate receptor in the brain specifically mu, kappa, and delta receptors in the central nervous system Onset-Intravenous heroin peaks in the serum in less than 1 minute while intranasal and intramuscular heroin peaks in 3 to 5 minutes Routes-injected, snorted/sniffed, or smoked Problems Heroin's lipid solubility 7 times more toxic than morphine when IV Concurrent Rx use Heroin Effect Poppies Herbals Complimentry medicine Herbal-used to treat illness or disease, considered safe Supplements-Product used to supplement the diet, may also contain herbs Often used for conditions such as Arthritis, Asthma,Diabetes Common herbals-Ginseng, Garlic Common supplements-Fish oil, Glucosaimine Herbals What to expect Patient is often taking many of these Herb/Supp Side effect of these medication-Cardiac, Fluid loss Locate and take with you to Hospital Example-Cascara Sagrada Used for Constipation, Indigestion Adverse effects-Vomiting, Dysrhythmias Treat for Fluid loss monitor EKG Chondroitin Use-joint damage Adverse effect-Nausea and Diarrhea can enhance the effect of blood thinners General Management Scene Size-Up What is the call Be alert to the potential for violence. Restraints Look for signs of hazardous material/Drugs/suspicious material Pill bottles Meth equipment Resources Suicidal Patients and Protective Custody Involve law enforcement/medical direction. Know local laws and procedures General Management Primary Assessment ABC Transport decision Secondary Obtain Hx Rapid head to toe assessment Identify the toxin and length of exposure Monitor vital signs closely Hx from Family members/Poison control General Management Drug removal Reduce intake/Remove the individual from the toxic environment. Reduce absorption of toxins in the body. NG tube and activated charcoal. Enhance elimination of the toxin Antidotes Drugs for treatment Names-naloxone, Narcan Action-Narcotic Antagonist, competes for opiate receptors in the brain. It also displaces narcotic molecules from receptors IV Narcan has an onset of 1-2 minutes and a duration of 45-90 minutes. Indications-For reversal of depression cause by the following (MSO4, Demerol, Heroin, Dilaudid, codeine, Percodan, Fentanyl, Methadone. Tx of coma of unknown origin Dose and Route- 1 to 2 mg SIVP, IM, and SQ. 2mg IN Contraindications/Precautions/Side-effect-Hypersensitivity, Narcan should be admin cautiously to patient who are known to be physically dependent on narcotics Drugs Names- Sodium Bicarbonate, Bicarb Action-Alkanlinizing agent, salt that provides bicarbonate to buffer metabolic acidosis Indication-TCA overdose Dosage and Route-1meq/kg initial followed by .5 meq/kg q 10 min IV for persistent or prolonged QRS Contraindications/Precaution-None in TCA overdose, do not admin with calcium chloride. Weight important when calculating doses Drug Calcuim Chloride Name Action-Reverse symptoms of Calcium Channel blockers Indications-Calcuim Channel od, Hydrofluroic acid exposure with cardiac arrest or Tetany(Overactive neurological reflexes, cramping.) Dosage and Route-1,000mg IV, hydrofluoric 400mg iv Contraindications- renal-cardiac disease no arrest, hypercalcemia, Precatuions/Side-effects-hypotension, watch for inflitration, sodium bicarbonate and calcium precipitate Drugs Names-GlucaGen Action-Glucagon has direct myocardial action and has been investigated as an inotrope in both ischemic and non-ischemic heart failure Indications-Calcium Channel Blocker and Beta Blocker OD Dosage and Route-1mg IV or IM Contraindications-Allergies to Protein Drugs Names-Romazicon Action-Benzo. Antagonist, inhibits action on GABA/Benzo. Complex. Reverses sedation Indication-Complete and partial reversal of CNS and respiratory depression. From the following agents Valium , Versed, Ativan, Restoril, Ambien, Klonopin, Xanax Dosage and Route-.2mg up 1.0mg Contraindication-TCA overdoses or people with a hx of szr. Precaution-Causes szr. Drugs Benadryl Names-diphenhydramine Actions –blocks histamine receptors Indications-Extrapyramidal reactions Dosage and route-50mg iv or IM Contraindications-MAO, Nursing mothers, Newborns Precautions/Side effects-drowiness,hypotension,palpations use with caution in patients with Asthma Nerve Agents Affect nerve impulse conduction Examples GB (sarin) VX GD (soman) GA (tabun) Organophosphates General Characteristics Military Tabun (GA), Sarin (GB), Soman (GD), VX Commercial Parathion, Sevin Therapeutic Drugs Antilirium® Prostigmine ® Mestinon ® Normal Nerve Function ACh Nerve Agent Action AChE ACh GB Nerve Agents Absorption or inhalation Assessment: SLUDGE MM Management Atropine Pralidoxime chloride Agent Release Possible cloud, puddle strange or unusual odor Dead or damaged plants and/or animals Potential targets Key: manifestation of common signs and symptoms occurring rapidly among a large group of individuals Protect yourself Approach from uphill. Maintain distance. Evacuate. Decontaminate. Provide appropriate medical treatment Drugs Atropine Name Action-Anticholinergic Indication-symptomatic bradycardia or Organophosphate poisoning/nerve agent Dosage and Route-.5mg up to 3 for brady iv. For poisoning 2mg q IV,IO, or IM until lungs are clear. Contraindications- obstructive disease of the GI tract, neuropathy, glaucoma Precaution/Side effects-paradoxical bradycardia when pushed to slowly. Drugs 2-pam Names-Pralidoxime Action-reactivates cholinesterase after poisoning with anticholinesterase agents, reverse muscle paralysis Indications-to be used after atropine in nerve agent posioning Dosage and Route-600mg IM auto-injector Contraindications Precautions/side effects-use in caution with pregnant female or those nursing THE END