* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DETERMINING THE CONCENTRATION OF A SOLUTION:
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
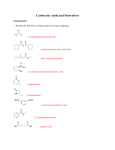
Name(s): ______________________________________________________________________ Signature(s): ___________________________________________________________________ ESTERS OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS BACKGROUND Did you know that the aromas of bananas, strawberries, other fruits, flowers, and perfumes are the result of organic chemistry? Many of these flavor additives are esters. An ester is an organic compound that is produced when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol. They are probably the most pleasant and delicious organic compounds one can study. A functional group is a specific arrangement of atoms in an organic compound that is capable of characteristic chemical reactions. The chemistry of an organic compound is determined by its functional group. R is any carbon chain/ring attached to the functional group (in red). The general equation for this reaction is: O R 1 C 2 OH R OH R1COOH + R2OH carboxylic acid alcohol reactants R1COOR2 ester + H2O water products The name of the ester formed is derived from the names of the alcohol and the carboxylic acid. For example, the ester formed from ethyl alcohol and acetic acid is called ethyl acetate. The first part of the name comes from the alcohol and the second part comes from the acid (Figure 1). Figure 1: Ethyl Acetate In this laboratory, you will synthesize and identify several esters. Sulfuric acid will be used as a catalyst for the esterification reactions. OBJECTIVES: When you have completed this activity, you will be able to: 1. Describe the structure of an ester and how it is formed 2. Synthesize several esters 3. Research and describe how esters are used in society …in order to illustrate the usefulness of organic compounds.. MATERIALS alcohols amyl (1-pentanol) methanol carboxylic Acids glacial acetic acid salicylic acid (solid) 18 M sulfuric acid (concentrated) (in fume hood) distilled water china marker hot plate thermometer beaker (400 mL) 2 Dropper Pipettes graduated Cylinders (10.0 mL) test tube rack 2 test tubes (16 x 100 mm) test tube holder balance weigh boat timer PROCEDURE CAUTION: You will be working with concentrated acids. Wear goggles, lab aprons, and closed-toe shoes. 1. _____ Prepare a water bath by adding 175 mL of tap water to a 400 mL beaker. Place the beaker on a hot plate and heat the water until the temperature is between 50 - 60C. 2. _____ Number 2 test tubes toward the top of the tube with a china marker. Into each of two numbered test tubes, put 20 drops of alcohol (1.0 mL) and 10 drops of carboxylic acid (0.5 mL). For salicylic acid, add 0.50 g of the carboxylic acid. See Table 1. Test Tube 1 2 Table 1 1.0 mL Alcohol 0.5 mL Carboxylic Acid amyl alcohol glacial acetic acid methyl alcohol salicylic acid (0.5g) 3. _____ Carefully add 2 - 3 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to each test tube. CAUTION: Handle concentrated sulfuric acid carefully. If the acid spills on your skin or clothing, immediately rinse the affected area with water and inform your teacher. 4. _____ Stir each mixture slightly by tapping the bottom of the tube with your finger. 5. _____ Place the test tubes in the hot water bath (50 - 60C) for 10 minutes. While you are waiting, complete “Structure of Hydrocarbons” attached. 6. _____ Using a test tube holder, remove the test tubes from the water bath and place them in a test tube rack. 7. _____ Add 5.0 mL of dI water to each test tube and mix. Esters are insoluble in water and appear as colorless liquid layers on top of the water. 8. _____ Immediately note the odor of the esters formed by wafting the fumes toward your nose with your hand. Try to relate each odor to a familiar, specific scent. Record your observations in the “Observations and Conclusions” Table. DATA Table 2: Observations and Conclusions Test Tube 1 2 Alcohol amyl alcohol Carboxylic Acid Ester formed glacial acetic acid amyl acetate salicylic acid methyl salicylate methyl alcohol Odor ANALYSIS: 1. Below are the equations for each of the esterification reactions performed in this experiment. Use 1a as an example to complete the formula for the ester in questions 1b and 1c. a. CH3OH + methyl alcohol C6H13COOH heptanoic acid CH3COOC6H13 + methyl heptanoate H2O water b. C5H11OH + amyl alcohol CH3COOH acetic acid _______COO______ + amyl acetate H2O water c. CH3OH + C6H4OHCOOH amyl alcohol salicylic acid ______COO_______ + methyl salicylate H2O water 2. A banana scented candle could contain this additive ester: a. Amyl acetate b. Methyl salicylate c. Methyl heptanoate 3. A wintergreen scented car freshener could contain this additive ester: a. Amyl acetate b. Methyl salicylate c. Methyl heptanoate 4. An ester is formed by reacting: a. alcohol with water b. carboxylic acid with water c. carboxylic acid with alcohol 5. The functional group for an alcohol is a. R b. –OH c. H2O d. –COOH 6. Amyl acetate is an inorganic compound. a. True b. False 7. Esterification is often classified as a dehydration reaction because… a. water is produced in the reaction b. water is used as a reactant in the reaction 8. Why was sulfuric acid added to the reaction? a. To speed up the rate of the reaction b. To keep the rate of reaction constant c. To make the reaction more dangerous and exciting for chemistry students d. To slow down the rate of the reaction so the ester could be smelled for longer periods of time 9. Esters are soluble in water. a. True b. False 10. According to the IUPAC naming system, the name of this hydrocarbon is: a. Butane b. Butene c. Butyne d. Propane e. Propene f. Propyne Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Period: _______ Page: ______ PRE-LAB: ESTERS OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Read the introduction and procedure to the lab activity, highlighting key information as you read. Use the information in the introduction, procedure, and your class notes to answer the following questions. 1. Write the general formula for the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Identify each reactant and product. 2. Name the ester formed from each of the carboxylic acids and alcohols. For the alcohol, remove the –anol ending and replace it with –yl. Alcohol octanol propanol 2 – pentanol ethanol Carboxylic Acid acetic acid butanoic acid benzoic acid acetic acid Ester octyl acetate 3. What safety precautions relate specifically to this lab? 4. What is the role of a catalyst in a reaction? 5. Why is water added to the test tubes after the esters are formed? STRUCTURE OF HYDROCARBONS Hydrocarbons are the simplest organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The two simplest hydrocarbons are methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6). IUPAC Rules for naming straight chain hydrocarbons: 1. Find the longest chain of carbons. 2. Count how many carbons are in that longest chain and use the correct prefix # carbons example prefix # carbons example prefix CH methC H hex1 6 4 6 14 C2H6 ethC7H16 hept2 7 C3H8 propC8H18 oct3 8 C4H10 butC9H20 non4 9 C5H12 pentC10H22 dec5 10 3. The suffix reflects whether the hydrocarbon is an alkane, alkene, and alkyne. only single covalent bonds -ane One or more carbon-carbon double covalent bond -ene One or more carbon-carbon triple covalent bond -yne Name the following structures: Write the correct name in the box for each hydrocarbon Options: butane, butene, ethane, ethyne, propane, propene, propyne 1. 5. 2. 3. 6. 4. 7.