* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1-STD,gonorrheanimer-mansour (1)
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Hookworm infection wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Candidiasis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
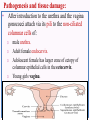
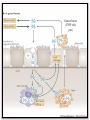
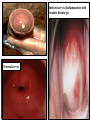
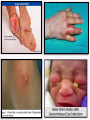
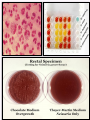
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Epidemiology: USA: • More than 110 million are living with STD. 20 million will become infected every year. • 50% of the new cases are teenagers. WHO: • More than 1 million people acquire a sexually transmitted infection (STI) every day. • The majority of STIs are present without symptoms. • Some STIs can increase the risk of HIV acquisition three-fold or more. Currently, more than 30 diseases are known to spread through sexual activity: o Bacterial: gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydial infection, chancroid, bacterial vaginosis. o Viral: Genital herpes, warts, HIV. o Parasitic: Trichomoniasis. o Fungal: Candidiasis. Entry, Spread, Damage and Complications: Entry: Most of the STD-causing agents enter the body through the mucosal or squamous epithelial layers of the urethra, vagina, cervix, rectum or oral pharynx. * Some agents may spread by blood products, transplacental,……… Reservoir: Asymptomatic human carriers. Damage: Acute manifestations of STDs are classified into: • Mucopurulent discharge (urethritis and cervicitis): Example: Gonorrhea and chlamydial infection. • Genital ulcer disease: Example: Syphilis, chancroid and genital herpes. N Consequences of STDs include: Most complications are experienced by women: • Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). • Infertility, ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion and premature delivery. • Congenital and neonatal infections. • Increased risk of acquiring HIV. • Anogenital or cervical cancer. • Tertiary syphilis &recurrent herpes infection (chronicity). Gonorrhea Gonorrhea is an infection that involves mucous membranes, and epithelial layers of the urethra and the cervix, resulting in a copious- purulent discharge. • Causative agent: Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Gram negative diplococci. • Reservoir: • Humans are the only reservoir. • Asymptomatic carriage is greater among women. Pathogenesis and tissue damage: • After introduction to the urethra and the vagina gonococci attach via its pili to the non-ciliated columnar cells of: o male urethra. o Adult female endocervix. o Adolescent female has larger zone of ectopy of columnar epithelial cells in the ectocervix. o Young girls vagina. N Factors of multiplication and inflammation: • IgA Protease: Escape humoral response. • Phase variation: Turning on /off genes of surface adherence components: escape neutrophil killing and antibodies protection. • The microbial lipooligosaccharide (LOS): o Polyclonal B lymphocyte activator. o Death of ciliated-epithelia: TNF-α production from the macrophages. • The result is urethritis in males and cervicitis in females and vulvovaginitis in adolescent females. Summary o Attachment to non ciliated cells by the pili. o Evade immune response by IgA protease and phase variation mechanism. o Multiply within the non ciliated cells. o Death of ciliated cells by the LOS and TNFα. o Outcome: • Copious purulent discharge (pus) in most male and some female patients. • Subclinical infection in 30% of females. • Pelvic inflammatory disease. • Systemic dissemination. Gonorrhoeae (PMN rich pus) Infected cervix (Inflammation with exudate discharge) Normal cervix N Neisseria gonorrhoeae, other pathogens and vaginal flora can ascend to female upper reproductive tract due to: - Loss of endocervix mucus production. - End of menses (menstrual cycle; loss of mucus). The ascending infection results in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Endometritis: Endometrium infection (columnar). Salpingitis : Fallopian tubes infection. Ovaritis (oophoritis). DGI: septic arthritis, tenosynovitis, skin pustules, bacteremia (rare) and endocarditis (rare). N Other causative agents of STDs and PID: - Chlamydia trachomatis. - Mycoplasma hominis. - Mycoplasma genitalium. - Ureaplasma urealyticum. - Endogenous E. coli. Late complications: infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain. N Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection in male: Urethritis: • Dysuria, redness, pain, and thick copious(greenish- yellow) discharge of pus. • The infection could be disseminated to the epididymis (epididymitis), prostate gland (prostatitis), testicular tissue (orchitis). • DGI. Diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection: Clinical specimens: Urethral discharge, cervical swab, rectal swab, vaginal discharge, pharyngeal swab. Laboratory tests: microscopic examination, culture, PCR . Microscopic examination: (gram stain): Intracellular gram negative diplococci (inside the polymorphnuclear leukocytes). N • Culture: Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a fastidious bacteria it needs: • NADP and Hematin (X and V factor): so the bacteria grow best on: Chocolate agar or the selective medium: Thayer-Martin agar which contains antibiotics (vancomycin, colistin, and nystatin). • 5-10% CO2 for primary isolation. • All species are oxidase positive. • Sugar fermentation to differentiae it from other neisseriae: N. gonorrhoeae ferments only glucose. N PCR: Detection of microbial genetic material in the clinical specimen. Antibiotic sensitivity test: • More than 20% of current isolates are resistant to penicillin due to Beta-Lactamase plasmids. • Penicillinase producing N. gonorrhoeae (PPNG) strains are sensitive to third generation cephalosporin. • Add antichlamydial antibiotic (co-infection is very common) • Treat the partner.