* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download mesoderm
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
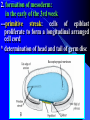
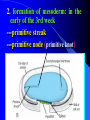
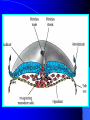
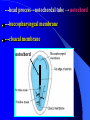
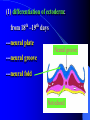
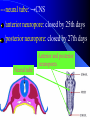
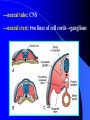
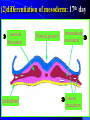
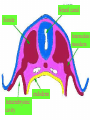
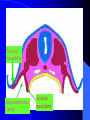
组织胚胎学课件 中国医科大学 基础医学院 组胚—英文教学组 HUMAN EMBRYOLOGY Department of Histology and Embryology China Medical University Chapter 4 Further Development of Embryo Formation and differentiation of trilaminar germ disc 1. formation of epiblast and hypoblast : By the 8th day, the inner cell mass differentiates into two layers of cells epiblast (columnar) bilaminar germ disc hypoblast (cuboidal) Amnionic cavity epiblast hypoblast Bilaminar germ disc ---epiblast: primary ectoderm amniotic cavity: amniotic fluid roof: amniogenic cells floor: epiblast --- hypoblast: primary endoderm hypoblast →Heuser’s →primary yolk sac membrane Amnionic cavity epiblast Bilaminar hypoblast germ disc Extra-embryonic mesoderm Primary yolk sac secondary yolk sac Body stalk Extra-embryonic cavity Extra-embryonic mesoderm Primary yolk sac extra-embryonic mesoderm → extra-embryonic cavity (chorionic cavity) --visceral layer --parietal layer /secondary yolk sac: yolk sac ---body stalk (connecting stalk): formed by extra-embryonic mesoderm 2. formation of mesoderm: in the early of the 3rd week ---primitive streak: cells of epiblast proliferate to form a longitudinal arranged cell cord * determination of head and tail of germ disc 2. formation of mesoderm: in the early of the 3rd week ---primitive streak ---primitive node (primitive knot) 2. formation of mesoderm: in the early of the 3rd week ---primitive streak: ---primitive node (primitive knot) ---primitive pit (blastopore) ---mesoderm: intra-embryonic mesoderm ---endoderm: hypoblast cells are replaced by epiblast cells ---ectoderm: epiblast changed the name into ectoderm by the end of the 3rd week trilaminar germ disc: endoderm + mesoderm + ectoderm ---head process→notochordal tube → notochord ---buccopharyngeal membrane ---cloacal membrane notochord 3.differentiation of trilaminar germ disc 4th –8th weeks ---differentiation: same cells which are primordial and inmuture differentiate into different cells which have specific structure and function ---induction: some tissues effect the differentiation, and determine the differentiating orientation of another tissue (1) differentiation of ectoderm: from 18th –19th days ---neural plate: neuro-epithelium (neural ectoderm): pseudostratified columnar epi. neural plate Notochord (1) differentiation of ectoderm: from 18th –19th days ---neural plate Neural groove ---neural groove ---neural fold Notochord ---neural tube: →CNS /anterior neuropore: closed by 25th days /posterior neuropore: closed by 27th days Neural tube Anterior and posterior neuropores Spina bifida anencephaly ---neural tube: CNS ---neural crest: two lines of cell cords→ganglions (2)differentiation of mesoderm: 17th day paraxial Mesoderm endoderm Neural groove Intermediate mesoderm Lateral mesoderm ---paraxial mesoderm somite: 20th days, 3 pairs/per day, 42-44 pairs by the end of 5th weeks -sclerotome: →bone, cartilage -dermatome: → dermis and hypodermis -myotome: →skeletal muscle Neural canal Somite Intermediate mesoderm endoderm Intraembryonic cavity ---intermediate mesoderm: →kidney and reproductive system ---lateral mesoderm: Intra-embryonic coelom: →body cavity parietal or somatic mesoderm: →muscle, CT, parietal layer of pleura, peritoneum and pericardium visceral or splanchnic mesoderm: →muscle, CT of digestive tract, visceral layer of pleura, peritoneum and pericardium Parietal mesoderm Intra-embryonic cavity visceral mesoderm 3. differentiation of endoderm: primitive gut: →digestive, respiratory and urinary system foregut midgut oropharyngeal membrane hindgut Cloacal membrane 1. Embryonic period is B A. from fertilization to the end of week 2 B. from fertilization to the end of week 8 C. from week 3 to the end of week 8 D. from week 5 to the end of week 8 E. from week 9 until birth 2. How long will an individual stay in the uterus of its mother? C A. 18 weeks B. 28 weeks C. 38 weeks D. 48 weeks E. 58 weeks 3. What is penetrated by a spermatozoon during the process of fertilization C A. oogonium B. primary oocyte C. secondary oocyte D. primary follicle E. primordial follicle 4. Which protein is receptor of spermatozoa on the zona pellucida? C A. ZP1 B. ZP2 C. ZP3 D. ZP4 E. ZP5 5. The time of implantation is C A. from 1st-2nd day to 7th-8th day B. from 3rd-4th day to 9th-10th day C. from 5th-6th day to 11th-12th day D. from 7th-8th day to 13th-14th day E. from 9th-10th day to 15th-16th day 6. Which structure is not belong to early blastocyst ? E A. trophoblast B. zona pellucida C. inner cell mass D. blastocoele E. endoderm 7. Which is not correct about implantation D A. blastocyst will be imbedded in the endomytrium B. zona pellucida disappears C. polar trophoblast secretes proteinase D. endomytrium is in proliferative phase E. there is a corpus luteum of pregnancy in the ovary 8. The most common position of implantation is E A. mucus of uterine tube B. mucus of ampullary portion of uterine tube C. ovary D. mucus of cervix of uteru E. mucus of body of uterus Chapter 4 Further Development of Embryo Question s 1. Describe the formation of bilaminar germ disc and its associated structures. 2. Describe the formation of trilaminar germ disc and its associated structures. 3. Describe the differentiation of three germ layers briefly. 4. Preview fetal membrane and placenta.