* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Soil Review Soil – Soil is a mixture of weathered rock, decayed
Agroecology wikipedia , lookup
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
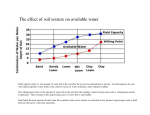
Soil Review Soil – Soil is a mixture of weathered rock, decayed organic matter, mineral fragments, water, and air Formation of Soil – can take thousands of years – is influenced by 1. Climate 2. Slope of the land 3. Type of Rock 4. Types of vegetation 5. Length of time that rock has been weathered Composition of Soil – the ingredients that make up soil Clay (smallest particles), Silt (medium particles), and Sand (largest particles) are all small particles of sediments Decaying, dark-colored plant and animal material is called humus Small spaces between soil particles may be filled with air or water Good soil has an equal mix of sand, silt, and clay called loam Soil Profile – Horizons are the different layers of soil O Horizon: Organic material A Horizon: the top soil layer of soil, usually covered with litter, or leaves, twigs, and other organic material B Horizon: the subsoil layer. Lighter in color due to less humus and is less fertile. C Horizon: the parent material. Mostly weathered rock and is bottom of the soil profile. It is most like the bedrock. Leaching – the removal of minerals (from the organic material-humus) that have been dissolved in water When it rains the water picks up minerals and nutrients and carries them to Horizon B Soil Types Parent rock affects soil formation Climate affects soil development Time affects soil development Weathered Rock – broken up rock in the form of sand, silt, and clay Bacteria and Fungi – agents that help break down organic matter (decaying plants and animals)