* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Notes TC – 5: Isosceles Triangle Theorem Angle
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
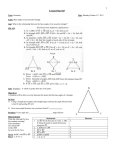
Geometry Notes TC – 5: Isosceles Triangle Theorem Angle Bisectors (review) Definition: An angle bisector Postulate: Every angle has Isosceles Triangle Theorem We wish to prove: If two sides of a triangle are congruent, the angles opposite those sides are also congruent. Complete the Given and Prove below and draw a suitable diagram. Given: Prove: The plan is to bisect the vertex angle of the given triangle and then prove the two new triangles are congruent. Fill in missing statements and reasons (including the blanks in statement 2) to complete the proof below. Statement Reason 1. Given 1. 2. Let point be on base such that 2. is the angle bisector of vertex angle 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. 6. 6. Ex: Draw a suitable diagram, then give an appropriate conclusion and reason: Given: In RAT, RA AT Conclusion: Reason: Ex: CAT, shown at right, has perimeter 52. A a. Find the value of x. 2y + 3z 2 x 5x z C 5y + 30 T 2x + 8 b. Find the values of y and z. The converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem is also true. (Proof is on a later HW). Write the converse: Ex: Determine which two sides of HUG are congruent. U 2x + 42 H 3x + 12 5x + 6 G Geometry HW: Triangle Congruence - 5 1. In ABC, if AB BC and mB = 80 find mC. 2. Each of the congruent angles of an isosceles triangle measures 9 less than 4 times the vertex angle. Find the measures of all three angles of the triangle. Find the value of x in each of the diagrams below. 3. A 130 D 50 D C A x C AD BD , BDC mADC = 130 AD DE , AB CB , ACD and BCE (2x) (5x) l1 7. y l1 || l1 y l2 (2x) 55 50 C E Find the values of x and y in each of the diagrams below. 6. B 5. x = mABD x B B 4. A (3x) D 8. In ABC, A C, AB = 5x + 6, BC = 3x + 14, and AC = 6x – 1. Find the lengths of all three sides of the triangle. 9. Prove the following: In an isosceles triangle, the median from the vertex, the altitude from the vertex and the angle bisector of the vertex are all the same. Given: Isosceles triangle ABC with AC BC , CP bisects ACB a. Prove (in statement – reason format) that CP is a median. b. Explain (in paragraph format) why CP is an altitude. 10. Given: Isosceles ABC with AC BC , M is the midpoint of AB , AME BMF Prove: CE CF C E A 11. In the diagram at right, MS is both an angle bisector and an altitude of BMW. Find the values of x, y and z. F B M M (2x + 14) 7 x + 8 3 B (5x) y z –7 2 S 3z + 3 W