* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Non-Contact Forces Test: Tuesday, October 20, 2015 Non
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Aristotelian physics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
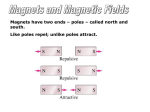
Non-Contact Forces Test: Tuesday, October 20, 2015 Non-Contact Forces What do all not-contact forces have in common? Gravitational Force What two factors affect the strength of gravity between two objects? Explain the difference between mass and weight. Know what would happen to each if you went to another planet or the moon. (Short answer question!) How does gravity affect the motion of objects? Why do objects in space orbit one another? (What force is involved?) Explain the “acceleration due to gravity” picture (apple falling from the tree or rock being dropped off the ledge) Magnetic Force What happens to magnetic force if you increase/decrease the distance between two magnetic objects? Where is a magnet the strongest? Where is it the weakest? Recognize the magnetic field diagrams for opposite poles and for like poles What happens when two like poles interact? What happens when opposite poles interact? Between what kinds of objects can magnetic force be exerted? Electrical Force What happens to electrical force if you increase or decrease the distance between charged particles? Recognize the electrical field diagrams for opposite charges and for like charges How do objects become charged? What happens to the number of electrons? What happens when 2 like charges interact? What happens when opposite charges interact? Between what kinds of objects can electrical force be exerted? Non-Contact Forces Test: Tuesday, October 20, 2015 Non-Contact Forces What do all not-contact forces have in common? Gravitational Force What two factors affect the strength of gravity between two objects? Explain the difference between mass and weight. Know what would happen to each if you went to another planet or the moon. (Short answer question!) How does gravity affect the motion of objects? Why do objects in space orbit one another? (What force is involved?) Explain the “acceleration due to gravity” picture (apple falling from the tree or rock being dropped off the ledge) Magnetic Force What happens to magnetic force if you increase/decrease the distance between two magnetic objects? Where is a magnet the strongest? Where is it the weakest? Recognize the magnetic field diagrams for opposite poles and for like poles What happens when two like poles interact? What happens when opposite poles interact? Between what kinds of objects can magnetic force be exerted? Electrical Force What happens to electrical force if you increase or decrease the distance between charged particles? Recognize the electrical field diagrams for opposite charges and for like charges How do objects become charged? What happens to the number of electrons? What happens when 2 like charges interact? What happens when opposite charges interact? Between what kinds of objects can electrical force be exerted? Essential Vocabulary: (This is not a vocabulary test, but you should understand the following terms and be able to apply them!) Magnitude Force Newton Net Force Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces Gravitational Force (Gravity) Air Resistance/Drag Magnetic Force (Magnetism) Poles: North and South Attract Repel Electrical Force Static Electricity Charge: Positive and Negative Electrons/Protons Contact Force Non-Contact Force Mass Weight Field Distance Gravitational Field Magnetic Field Electric Field Essential Vocabulary: (This is not a vocabulary test, but you should understand the following terms and be able to apply them!) Magnitude Force Newton Net Force Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces Gravitational Force (Gravity) Air Resistance/Drag Magnetic Force (Magnetism) Poles: North and South Attract Repel Electrical Force Static Electricity Charge: Positive and Negative Electrons/Protons Contact Force Non-Contact Force Mass Weight Field Distance Gravitational Field Magnetic Field Electric Field