* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Assisted Conception
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
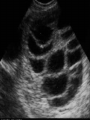
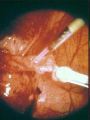
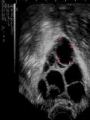
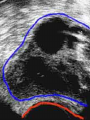
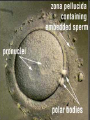
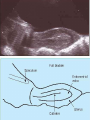
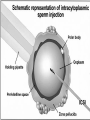
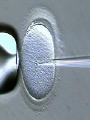
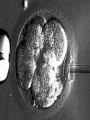
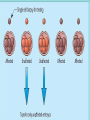
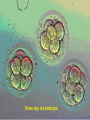
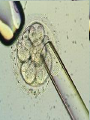
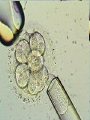
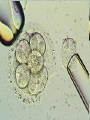
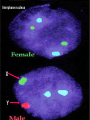
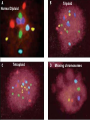
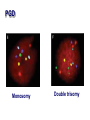
Assisted Conception Dr. ZEINAB ABOTALIB MRCOG, DGO, Associate Professor & Consultant Obs/Gyna Infertility & IVF Assisted Conception • • • • • • IUI: intrauterine insemination IVF: in vitro fertilization ICSI: intracytoplasmic sperm injection GIFT: gamete intrafallopian transfer ZIFT: zygote intrafallopian transfer PESA: percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration Assisted Conception • • • • ET: embryo transfer TESE: testicular sperm extraction SUZI: subzonal sperm injection PGD: preimplantation genetic diagnosis Assisted Conception • Objective – To bring sperm and oocyte close to each other to promote chances of fertilization and, ultimately, achieve a pregnancy Assisted Conception • Main types: – IUI: intrauterine insemination – IVF: in vitro fertilization – ICSI: intracytoplasmic sperm injection Assisted Conception • Required procedures – Superovulation – Sperm preparation – Assisted fertilization Superovulation • Hormonal manipulation to enhance ovulation and release multiple oocytes during ovulatory cycle Superovulation • Drugs used: • Human menopausal gonadotropin – Taken from urine of postmenopausal women – Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) activity • Recombinant FSH • Recombinant LH Superovulation- protocol • Gonadotropin for 9-11 days • Monitoring follicular development by transvaginal ultrasound • Follicles 16 -18 mm in diameter – 10,000 IU hCG • Oocytes maturation • Ovulation Sperm Preparation • Select PMNS • Remove seminal plasma, WBC, and bacteria • Sperm capacitation – Coating of sperm with seminal plasma proteins – Allow sperm to become fertile – In vivo or in test tube Intrauterine insemination • Sperm sample deposited in uterus just before release of an oocyte (s) in a natural or stimulated cycle • Soft catheter • Give hCG at injection or up to 24 hrs later • Sperm volume: 0.2-0.3 ml • Pregnancy rates – Around 15% per cycle Gamete intrafallopian transfer • Laparoscopic technique in which oocyte and sperm placed in fallopian tube, allowing in vivo fertilization • Procedure – Superovulation – US guided transvaginal oocyte retrieval • 0.1-0.2 mil sperm with 2-3 oocytes In vitro fertilization - IVF • Taking oocytes from woman • Fertilizing them in lab with her partner's sperm • Transferring resulting embryos back to her uterus 3 or 5 days later IVF • Procedure – Superovulation – Insemination – Embryo transfer – Luteal support IVF - Superovulation • • • • Gonadotropin stimulation Monitoring follicular development US guided transvaginal oocyte retrieval Oocyte fertilization with sperm IVF - Insemination • Containers used – Test tubes, Petri dishes, multi-well dishes • Each oocyte inseminated with 0.5-1.0 mil PMNS • Fertilization detected 12-20 hrs later by presence of – 2 pronuclei in oocyte cytoplasm – 2 polar bodies in perivitelline space IVF - Insemination • Syngamy (combination of maternal and paternal pronuclei 24 hrs after insemination • Further cleavages occur at 24 hr intervals IVF - Embryo transfer • Embryos transferred to uterus on 2nd or 3rd day after in vitro insemination • 4-8 cells embryos • 2-3 embryos transferred in 20 µl of culture fluid • Transabdominal US to see fluid placed in uterus • Cryopreserve excess embryos IVF - Luteal support • Progesterone (P4) necessary for pregnancy maintenance • Premature luteolysis in some superovulatory regimens • P4 supplementation until menses occur or woman has positive pregnancy test Intracytoplasmic sperm injection - ICSI • Injection of single sperm into single oocyte in order to get fertilization • Procedure – Superovulation – US guided transvaginal oocyte retrieval – IVF • Oocytes injected with sperm using special microscopes, needles and micromanipulation equipment ICSI - Indications • Low sperm concentration, motility, abnormal morphology • Antisperm antibodies • Fertilization failure after conventional IVF • Ejaculatory disorders • absence of vas deferens or obstruction of ejaculatory ducts Assisted Hatching • Indications – Couples having IVF with • Female partner's age over 37 • Poor quality embryos –Excessive fragmentation –Slow rates of cell division Assisted Hatching – Procedure • Embryo held with a specialized holding pipette • A needle used to expel an acidic solution against ZP • A small hole made in ZP • Embryo washed and put back in culture in incubator • ET shortly after hatching procedure – Hope for the best Further Advances And Uses Of Assisted Conception Technology • Cryopreservation of – Sperm – Embryo – Oocyte – Ovarian tissue • Growth of human follicles and oocytes in vitro • In vitro maturation and transplantation of human spermatozoa Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) Dr. Abdelsalam Talafha American Board Certified, Comparative Veterinary Obstetrics and Gynecology ART • Infertility – Inability to conceive after 1 year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse • Primary infertility – Couples have never had children • Secondary infertility – Couples initiated conception in the past and then had difficulty ART • Infertility – Female partner: 35% – Male partner: 35% – Both partners: 20% – Unknown cause: 10% • Infertility more common with increasing age ART • USA women infertility rate – Ages 20-24: 4.1% – Ages 25-29: 5.5% – Ages 30-34: 9.4% – Ages 35-39: 19.7% • 80% of infertility cases can be diagnosed • 85% of cases can be successfully treated ART • Female infertility – Disorders of ovulation: 27% – Fallopian tube disorders: 22% – Pelvic adhesions: 12% – Endometriosis: 5% to 15% – Hyperprolactinemia: 7% ART • Male infertility – Abnormal semen parameters • Count, motility, morphology • Infertility treatment – Correcting underlying abnormality – ART ART • Main techniques – IUI – IVF - embryo transfer – ICSI – Assisted hatching Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) • Identify genetic conditions in embryo before ET – Hemophilia – Cystic fibrosis – Aneuploidy PGD • Hemophilia – Hereditary bleeding disorder – Absence of a blood protein essential for clotting – Types A: lack of factor VIII – Type B: lack of factor IX PGD • Cystic fibrosis – Genetic disease – Defective gene causes body to produce abnormally thick, sticky mucus that obstruct • Lungs • Pancreas PGD • Aneuploidy – Having less than or more than normal diploid number of chromosomes • Monosomy • Trisomy • Triploidy PGD • Performed with IVF • 8-cell stage (3 days old) embryo biopsy • Obtain 1-2 blastomeres for genetic Three day old embryos PGD • Genetic analysis – Multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) – Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) FISH • Detects – Number of chromosomes – Sexing embryos – Sex chromosome aneuploidy – Whole-chromosome paints for detection of rearrangements and identification of marker chromosomes – Analyze polar bodies FISH • Fuorescent probes that bind to specific chromosomes are labeled with biotin for detection by specific fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies under a fluorescent microscope Interphase nucleus X Y Triploid Normal Diploid Tetraploid Missing chromosomes PGD Monosomy Double trisomy