* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review - Anemias/WBCs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
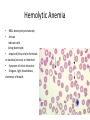
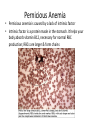
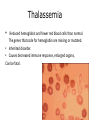
Review - Anemias/WBCs Hemolytic Anemia • • RBCs destroyed prematurely. Arrows indicate cells being destroyed; • Acquired (thru ertain chemicals or bacteria/viruses) or inherited. • Symptom of other disorders. • Fatigues, light-headedness, shortness of breath. Pernicious Anemia • Pernicious anemia is caused by a lack of intrinsic factor • Intrinsic factor is a protein made in the stomach. It helps your body absorb vitamin B12, necessary for normal RBC production; RBCs are larger & form chains Aplastic Anemia • Aplastic anemia develops when damage occurs to your bone marrow, slowing or shutting down the production of healthy RBCs • May be from radiation, toxic chemicals or certain drugs • Causes dizziness, fatigue, headache Thalassemia • Reduced hemoglobin and fewer red blood cells than normal. The genes that code for hemoglobin are missing or mutated. • Inherited disorder. • Causes decreased immune response, enlarged organs, Can be fatal. Polycythemia • The overproduction of red blood cells; may be 6 to 9 million erythrocytes per cubic millimeter of blood • Can be inherited or a symptom of another condition. • Causes increased blood clots, increased bleeding, bone and joint pain. Sickle Cell anemia • Genetic mutation • Erythrocytes are Formed misshapen And die early. • Causes lack of O2 And can lead to stroke Iron Deficiency Anemia • Caused by diet, blood loss, pregnancy. • Leads to extreme fatigue, weakness, light headedness.