* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. VanderLeest AP Psychology Class
Factitious disorder imposed on another wikipedia , lookup
Victor Skumin wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental health professional wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Moral treatment wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological evaluation wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
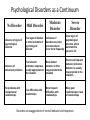
Abnormal Psychology What is a psychological Disorder? • Psychological disorders are persistently harmful thoughts, feelings and actions. – When behavior is deviant, distressful and dysfunctional, psychologists label it a disorder. • The more extreme a disorder is, the more easily it is detected. When trying to diagnose a patient, doctors look for three classic symptoms of sever psychopathology: • Hallucinations-false sensory experiences. • Delusions-extreme disorders that involve persistent false beliefs. • Affect (emotion)-characteristically depressed, anxious, manic, or no emotional response. What was once believed to cause mental disorders? Perceived Causes movements of sun or moon lunacy--full moon evil spirits Ancient Treatments exorcism, caged like animals, beaten, burned, castrated, mutilated, blood replaced with animal’s blood Early Theories • Music or singing was often used to chase away spirits. • In some cases trephening was used: – Cutting a hole in the head of the afflicted to let out the evil spirit. Psychological Disorders as a Continuum No Disorder Mild Disorder Moderate Disorder Severe Disorder Absence of signs of psychological disorder Few signs of distress or other indicators of psychological disorder Indicators of disorders are more pronounced and occur more frequently Clear signs of psychological disorder, which dominate the person’s life Absence of behavioral problems Few behavior problems; responses usually appropriate to the situation More distinct behavior is often inappropriate to the situation Severe and frequent behavior problems; behavior is usually inappropriate to the situation No problems with interpersonal relationships Few difficulties with relationships More frequent difficulties with relationships Many poor relationships or lack of relationships Disorders are exaggerations of normal behavior and responses. DSM- Diagnostic and Statistic Manual of Mental Disorders. -Primary reference for making diagnostic judgments Indicators of Abnormality • While psychologists look for the three classical symptoms, not all disorders have such sever symptoms. A few others are: – Distress: Does the individual show unusual or prolonged levels of anxiety? – Maladaptiveness: Does the person act in ways that make others fearful? – Irrationality: Does the person act or talk in ways that are irrational or incomprehensible to others? – Unpredictability: Does the individual behave erratically and inconsistently at different times? – Unconventional/undesirable behavior: Does the person act in ways that are statistically rare and violate social norms? The More the Better • Clinicians are more confident in labeling behavior as “abnormal” when two or more of the indicators are present. – Extremes and prevalence = greater confidence in diagnosis Rates of Psychological Disorders The Medical Model • In the late 18th century, the “disease view” reemerged. • The result was the medical model, a view that mental disorders are diseases of the mind that, like ordinary physical diseases, have objective causes and require specific treatment. butt ** Medical Model in Practice • The medical model led to mental hospitals or “asylums.” In this supportive atmosphere, many patients actually improved, even thrived, on rest, contemplation and simple but useful work. Problems with the Medical Model • Despite its success, modern psychologists find fault with relying solely on the medical model. • They suggest that treating the disorder as a “disease” leads to a doctor-knows-best approach in which the therapist takes all the responsibility for diagnosing and correcting the problem. • In this model, the patient becomes a passive recipient of medication and advice. Psychologists vs. Psychiatrists • The other problem psychologists have with the medical model (doctor-knows-best), is that it takes responsibility away from psychologists and gives it to psychiatrists. – According to our authors, it assigns psychologists to second-class professional status. The Cognitive Approach • The cognitive approach to depression points out that negative thinking styles are learned and modifiable. *Think classical and operant conditioning. Social-Cognitive-Behavioral Approach • As psychology has evolved, theories which were originally at odds, have now been combined to offer more thorough explanations, for example, cognitive psychology and behaviorism. • Cognitive psychology looks inward, emphasizing mental processes. Behaviorism looks outward and emphasizes the influences of the environment. • Psychologist from these perspectives see these two as complementary, and add that cognitions and behavior usually happen in social context, requiring social perspective. Combining Perspectives • The behavioral perspective tells us that abnormal behaviors can be acquired in the same fashion as healthy behaviors-through behavioral learning. • The cognitive perspective suggests that we must consider how people think about themselves and their relations with other people. • Social-cognitive-behavioral approach, then, is an alternative to the medical model combining all three of psychology’s major perspectives. Rosenhan Experiment • Rosenhan suspected that some strange behaviors seen in mental patients might originate in the abnormal atmosphere mental hospitals, rather than in the patients themselves. • To test these theories, Rosenhan and seven collogues conducted the Rosenhan Experiment in the early 1970s. David Rosenhan Explaining Rosenhan • Rosenhan said that the mistaken diagnosis were most likely a result of the lack of time the doctors spent with the patients. • Surprisingly, the other hospital patients readily detected the experiment. The pseudo-patients reported that the other patients regularly voiced their suspicions. – Watch Rosenhan discuss his experiment – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j6bmZ8cVB4o After the Experiment • All of the people who served in the original study were eventually discharged from the hospital with the label of "schizophrenic in remission." • To put it another way, they were still considered schizophrenic, but they were temporarily free of symptoms. Psychological Disorders and Courtrooms The Insanity Plea: Breaking the myths – Does not mean a person gets away with a crime without circumstance – Not easy to be considered not guilty by reason of insanity; less than 1% – If deemed not guilty by reason of insanity individuals don’t go home, they are assigned to go to a mental institution until they are deemed mentally stable; could be longer than a prison sentence. Court Confidentiality Problem- Psychologist are required to maintain patient confidentiality and not expose what they a patient told them in private. However, a judge may require that a psychologist give a testimony as to the psychological state of an individual, divulging confidential details. In a court of law, a judge may issue a subpoena that requires a psychologists full cooperation.