* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biotechnology - Jamaica Clearing
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
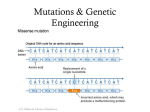
Biotechnology Sean Townsend Senior Research OfficerJamaica Clearing-House Mechanism Natural History Division Institute of Jamaica What is Biotechnology? • The term ‘biotechnology’ refers to any technological application that uses biological systems, living organisms, or derivatives thereof, to make or modify products or processes for a specific use. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) • Nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and some viruses. • The main role of DNA molecules is the long-term storage of information. DNA is often compared to a set of blueprints or a recipe, since it contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells, such as proteins and RNA molecules. • The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in regulating the use of this genetic information. What is Biosafety? • Biosafety is a term used to describe efforts to reduce and eliminate the potential risks resulting from biotechnology and its products. What are Living Modified Organisms (LMO’s)? • The Organisms resulting from the use of modern biotechnological techniques are commonly referred to as genetically modified organisms (GMO’s) or living modified organisms (LMO’s). • LMO’s include a variety of food crops that have been genetically modified to possess the desired traits for benefits such as increased nutritional productivity and resistance to pests or diseases. Common examples of modified crops include tomatoes, cassava, corn and soybeans. Cloning • This is the process of producing a genetically identical copy. Genes can be cloned, as well as cells and whole organisms. Many plants clone themselves naturally to reproduce. Plants can also be cloned by simply taking a cutting a twig or stem and planting it. This is called vegetative propagation. What are some potential benefits of biotechnology? • Advances in medicine, agriculture and other fields, e.g. new medical treatments & vaccines, new industrial products & improved fibres & fuels. • Increase in food security • Increased yield in marginal lands • Reduced use of water in agriculture Potential benefits (cont’d) Develop species which may be :• Pest Resistance • Herbicide tolerance • Disease resistance • Cold tolerance • Drought tolerance/salinity tolerance • Enhanced nutrition • Pharmaceuticals What are some potential risks of biotechnology? • Adverse effects on biological diversity • Risks to human health (e.g. Allergies, resistance to antibiotics etc.) • Development of super weeds • The instability of inserted genes • Insect resistance (Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)) • Negative impact on non-targets: • Terminator technology (suicide gene) or the GURT Technology: Genetic Use Restriction Technologies (GURTs) Examples of crops that have been genetically modified: Sugar Beet Oilseed Rape Carnation Chicory Cotton Maize Melon Papaya Potato Rice Soybean Sunflower Tomato Tobacco Wheat Lentil Plum Examples of animals that have been genetically modified • Pigs • Chickens • Mice Dogs Eggs Flies GloFish Monkey Fishes Labeling • Consumers have a right to know what is in their food -especially those products for which health and environmental concerns have not been satisfactorily resolved. • For religious or ethical reasons - persons may want to avoid eating animal products, including animal DNA • Mandatory labeling -will allow consumers to identify and avoid food products that may pose health risk e.g. allergic reaction.