* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System ppt
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
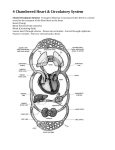
Circulatory and Respiratory System Honors Biology Powerpoint #4 Unit 8 – Chapter 37 Circulatory System Cute circulatory video Pantology of Cantrell Circulatory System • Structures: o Heart, Blood vessels, blood • Functions: o Brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells o Fights infection o Regulates body temperature. Heart • Made of cardiac muscle • Beats on average 6585 beats per minute • Pumps to circulate blood throughout the body Take your heart Rate Blood Vessels: • • • Carry blood to cells Lined with smooth muscle tissue Three kinds: 1. Arteries 2. Capillaries 3. Veins Fun Fact • If all arteries, veins, and capillaries of the human circulatory system were laid end to end, the total length would be 60,000 miles. That's nearly 2 ½ times around the Earth! • Your body has about 5.6 liters and circulates through the body 3 times/min. In one day, the blood travels a total of 12,000 miles- that's four times the distance across the U.S. from coast to coast. Arteries (carries blood away from heart) • Carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. • Thick, elastic walls Capillaries • Branch off of the Arteries • The smallest of the blood vessels o some have diameters as small as 1 red blood cell • Takes blood to cells where nutrients/gases diffuse Veins • Takes deoxygenated blood from the capillaries back to the heart Comparing arteries and veins Veins • Have valves to prevent backflow because not receiving pressure from heart • Muscles help pump blood back to heart through the veins Current Articles • http://www.livescience.com/44882-earreattachment-leeches.html Varicose veins Treatment for varicose/spider veins • Sclerotherapy. doctor injects the veins with a solution that scars and closes those veins, causing the blood to reroute through healthier veins. • Vein ligation/vein striping • Laser surgery. Laser surgery works by sending strong bursts of light into the vein that make the vein slowly fade and disappear. No incisions or needles are used. The treatment is often less effective than sclerotherapy. Blood • The human body has 4-6 liters of blood • Blood: o 45% of blood is Cells o 55% of blood is plasma Blood Cells: 3 kinds • Red Blood Cells: transports oxygen, contain hemoglobin (gives them color) • White Blood Cells (leukocytes): attack foreign substances or organisms. • Platelets: stick to broken blood vessels to stop bleeding when you are cut Plasma • 90% water • 10% other materials: o Dissolved gases o Salts o Nutrients o Enzymes o Hormones o Waste products Upper body Blood Flow in the Heart Cool Facts about the circulatory system The Heart • The human heart has four chambers oLeft and right ventricle oLeft and right atrium • The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body • The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs Valves Intraventricular Septum Left Atrium Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Ventricle 1) The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava. 2) The right atrium pumps blood through the tricuspid (AV) valve and into the right ventricle 3) Right Ventricle Contracts and pushes blood through pulmonary valve towards lungs 4) Blood is pushed through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs to receive oxygen 5) Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium from the lungs through the pulmonary veins 6) Blood passes through the bicuspid (mitral) valve into the left ventricle. 7) Contraction of Left ventricle pumps blood through aortic valve to the aorta 8)Blood travels through aorta and then to all regions of the body where it feeds cells with oxygen picked up from the lungs and nutrients from the digestive tract. Semilunar (pulmonary & Aortic) Valves Atrioventricular valves Blood Pressure • Blood pressure is a measure of the force exerted by the blood on the wall of the arteries. o An example is 120/80 (systolic pressure/diastolic pressure. • Systolic pressure is the result of the contraction of the ventricles (normal 110-140) • Diastolic pressure is during the ventricle relaxation (normal 70-90) Disorders of the Circulatory System: Coronary artery disease – Atherosclerosis • Plaque buildup blocks arteries, reducing, or even stopping blood flow • Plaques can break off, causing heart attack or stroke Cause: Damaged arteries are ‘invaded’ by bad LDL cholesterol. White blood cells try to digest the LDL. Ultimately, a jumble of cholesterol and cells is accumulated. Risk Factors: Smoking, high blood pressure, high LDL cholesterol, diabetes Treatments • Lifestyle changes: Follow healthy diet, maintain healthy weight, exercise, quit smoking, manage stress • Medicine: lowers cholesterol, helps prevent platelets from sticking and clotting (aspirin), helps harden plaque so lowers chance of breaking off • Surgeries: o Angioplasty (Coronary Stent) o Coronary artery bypass o Carotoid endartectomy Disorders of the Circulatory System • Heart Attack– Myocardial Infarction (MI) = Death of cardiac muscle cells Cause: Plaque dislodges, blocking an artery to the heart muscle. Cardiac muscle cells are starved for oxygen and die. After, scar tissue forms where cells died, reducing function of heart. Severity of a heart attack depends on size and area supplied by the artery. Risk Factors: Smoking, high blood pressure, high LDL cholesterol, diabetes Bypass surgery Disorders of the Circulatory System • Stroke=Death of cells in the brain. Cause: A blood vessel in the brain is blocked (by dislodged plaque, or bursts, starving the cells of oxygen) A stroke can have many different symptoms, including: numbness, vision changes, speech changes, or confusion. Risk Factors: Smoking, high blood pressure, high LDL cholesterol, diabetes Disorders of the Circulatory System • Arrhythmia= Irregular / skipped heart beat Cause: The heart uses electrical signals created in the SA node in the right atria, to begin a heartbeat. The conduction of these signals, or irregular firing of the SA node, can cause arrhythmias. Atrial arrhythmias are less dangerous than ventricular arrhythmias. Risk Factors: Generally random, but factors are stimulants (such as caffeine), fevers, stress, or genetic disorders. AFIB Oblation Heart Murmurs • Aortic Valve Replacement Disorders of the Circulatory System • High blood pressure - Hypertension Diastolic pressure over 90 Why it is dangerous: Excessive pressure can cause the arteries to thicken, and blood vessels to weaken and rupture. This can lead to heart failure, stroke, kidney failure, loss of sight when vessels in eyes burst. Risk Factors: Genetics, overweight, limited physical activity, smoking, alcohol consumption, certain medications Virtual Cardiology Lab