* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title: STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY Grade Level(s): 11th -12th
Inductive probability wikipedia , lookup
Bootstrapping (statistics) wikipedia , lookup
Confidence interval wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of statistics wikipedia , lookup
History of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs sampling wikipedia , lookup
Statistical inference wikipedia , lookup
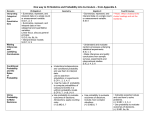
Title: STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY Grade Level(s): 11th -12th Objectives ● ● ● Analyze data to detech important characteristics such as: ○ shape ○ location ○ variability ○ unusual values Plan and conduct well-designed surveys and experiments, including: ○ using appropriate sampling methods ○ identifying sources of bias and confounding Use probability to anticipate Essential Questions ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● How do I construct and interpret graphical displays of univariate data? How do I describe the shape, center, and spread of a distribution? How do outliers affect a distribution? How do I summarize distributions of univariate data? What is the effect of changing units on summary measures? How do I compare center and spread? How do I compare clusters and gaps? How do I compare outliers? How do I compare shapes of distributions? How do I analyze patterns in scatterplots? What are correlation and linearity? How do I construct a least squares regression line? How do I construct a residual plot? How do I apply transformations to achieve linearity? How do I construct bar charts? How do I find marginal and joint frequencies for two-way tables? How do I find conditional relative frequencies and association? How do I compare distributions using bar charts? What are the various methods for data collection? What are the characteristics of a well-designed and well-conducted survey? What are populations and samples? What are sources of bias in sampling and surveys? What are the various sampling methods? What are the characteristics of a well-designed and well-conducted experiment? What are sources of confounding? What is block design? What types of conclusions can be drawn from observational studies? What is a sampling distribution? How does sample size influence a sampling distribution? What are discrete and continuous variables? How do I quantify the uncertainty in an estimator? How do I construct a confidence interval (CI)? ● ● How do I determine whether the results of an experiment are significant? How do I perform tests of significance (hypothesis tests)? Standards Content (Students will know) CC.2.4.HS.B.1 Summarize, represent, and interpret data on a single count or measurement variable. A1.2.2.1.2 A1.2.3.1.1 A1.2.3.2.1 A1.2.3.2.2 A1.2.3.2.3 Performance (Students will do) Activities/Assessments Describe the center (mean, median, and mode) of a distribution. “Student Height” activity. “MPG” activity. Describe the spread (range, interquartile range, standard deviation) of a distribution. “Univariate Data” assessment. Describe position (quartiles, percentiles, z-scores. Summarize data using boxplots. Describe the effect of changing units on summary measures. Compare shape, center, spread, and outliers. CC.2.4.HS.B.2 Summarize, represent, and interpret data on two categorical and quantitative variables. A1.2.1.1.1 A1.2.1.1.2 A1.2.1.1.3 A1.2.1.2.1 A1.2.1.2.2 A1.2.2.2.1 A2.2.1.1.1 A2.2.3.1.1 A2.2.3.1.2 Analyze patterns in scatterplots. “Height vs. Shoe Size” activity #1. Interpret correlation and linearity. Find the least squares regression line. Construct residual plots. “MPG vs. Vehicle Weight” activity #1. “Bivariate Data” assessment. Find outliers and influence points. Apply transformation to achieve linearity (logarithmic and power transformations). Construct frequency tables and bar charts. Determine marginal and joint frequencies for two-way tables. Determine conditional relative frequencies and association. Differentiate between independent and dependent random variables. Differentiate between discreet and continuous random variables. Calculate the mean and standard deviation for sums and differences of independent random variables. CC.2.4.HS.B.3 Analyze linear models to make interpretations based on the data. Assess the line of best fit. Use the least squares regression line to predict a y-hat for xs “Height vs. Shoe Size” activity #2. A1.2.2.2.1 A1.2.3.1.1 A1.2.3.2.1 A1.2.3.2.2 A1.2.3.2.3 A2.2.3.1.1 A2.2.3.1.2 within the observed range of x-values. CC.2.4.HS.B.4 Recognize and evaluate random processes underlying statistical experiments. A1.2.3.3.1 A2.2.3.2.1 A2.2.3.2.2 A2.2.3.2.3 Design and carry out statistical experiments (census, survey, experiment, observational study). “MPG vs. Vehicle Weight” activity #1. “Linear Models” assessment. Use appropriate probability distributions (normal, binomial, t, chi-squared, F) to determine the probability of obtaining a particular sample statistic. Design, carry out, and interpret the results of a statistical survey. Design, carry out, and interpret the results of a statistical experiment. Understand and apply the Central Limit Theorem (CLT). Design, carry out, and interpret the results of a statistical observational study. CC.2.4.HS.B.5 Make inferences and justify conclusions based on sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies. A1.2.3.2.1 A1.2.3.2.2 A1.2.3.2.3 A2.2.3.2.1 A2.2.3.2.2 A2.2.3.2.3 Name the characteristics of a well-designed and wellconducted survey. “Ice Cream and Drownings” activity. Identify sources of bias in sampling surveys. “Do Pirates Cause Global Warming?” activity. Determine the appropriate sampling method (simple random sample, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling). Name the characteristics of a well-designed and wellconducted experiment. “Surveys, Studies, and Experiments” assessment. Understand the components of an experiment, including: treatments, control groups, experimental units, random assignments and replication. Identify sources of bias and confounding, including placebo effect and blinding. Understand completely randomized design and randomized block design, including matched pairs design. CC.2.4.HS.B.5 Construct confidence intervals (CI) for population parameters at various levels of confidence. A1.2.3.2.1 A1.2.3.2.2 A1.2.3.2.3 Estimate population parameters and margins of error. “Dice Simulation” activity. Understand properties of point estimators, including unbiasedness and variability. “Human Body Temperature” activity. Interpret confidence intervals. “Ruler” activity. A2.2.3.2.1 A2.2.3.2.2 A2.2.3.2.3 Construct a confidence interval for a mean. Construct a confidence interval for a proportion. Construct a confidence interval for a difference between two means. Construct a confidence interval for a difference between two proportions. Construct a confidence interval for the slope of a least squares regression line. CC.2.4.HS.B.5 Perform hypothesis tests and interpret their results at various levels of significance. A1.2.3.2.1 A1.2.3.2.2 A1.2.3.2.3 A2.2.3.2.1 A2.2.3.2.2 A2.2.3.2.3 Perform a t-test (one- and two-tailed) for a sample mean. Perform a z-test (one- and two-tailed) for a sample proportion. “Do Calculators Help?” activity. “Does Music Improve Performance?” activity. Perform a t-test (one- and two-tailed) for a difference between two sample means (independent samples). “Accounting Firm” activity Perform a matched pairs t-test (one- and two-tailed) for a “State Department of difference between two sample means (dependent samples). Education” activity. Perform a z-test (one- and two-tailed) for a difference between two sample proportions (unequal variances). Perform a pooled z-test (one- and two-tailed) for a difference between two sample proportions (equal variances). Perform a chi-squared test for independence. Perform a chi-squared test for goodness of fit (GOF). Perform a chi-squared test for homogeneity of proportions. Perform an analysis of variance (ANOVA). CC.2.4.HS.B.6 Use the concepts of independence and conditional probability to interpret data. A2.2.3.2.1 A2.2.3.2.2 A2.2.3.2.3 Interpret probability, including long-run relative frequency interpretation. Apply the “Law of Large Numbers.” “Coin Flipping” activities. “Can You Find the Fake Data?” activity. Use the addition rule and multiplication rule. “Basketball Free Throws” activity. Use discrete random variables and their probability distributions (binomial, geometric). “Probability” assessment. Simulate random behavior and probability distributions. Use the properties of the normal distribution. Use tables of the normal distribution. Use the normal distribution as a model for measurements. CC.2.4.HS.B.7 Apply the rules of probability to compute probabilities of compound events in a uniform probability model. A1.2.3.3.1 A2.2.3.2.1 A2.2.3.2.2 A2.2.3.2.3 Calculate the probability of compound events. “Two Way Table” activities. “Playing Card” activities. “Probability” assessment.