Package `compute.es`
... ## 1. Computations to Calculate Effect Sizes: # For example, suppose the primary study reported a t-test # value for differences between 2 groups. Then, running: tes(t=1.74, n.1=30, n.2=31) # Or, more simply: tes(1.74, 30, 31) ...
... ## 1. Computations to Calculate Effect Sizes: # For example, suppose the primary study reported a t-test # value for differences between 2 groups. Then, running: tes(t=1.74, n.1=30, n.2=31) # Or, more simply: tes(1.74, 30, 31) ...
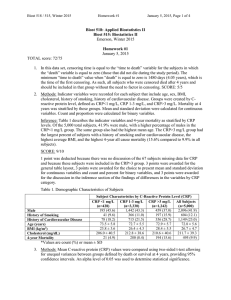
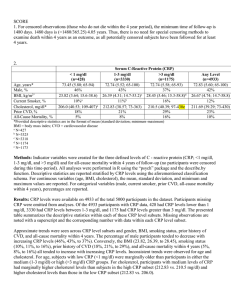
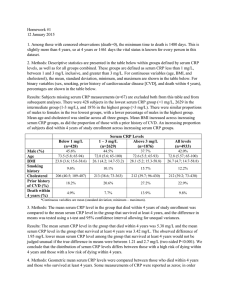
Homework Activities
... e. The vast majority of this class (more than 80%) feel that statistics is important to society. In fact, more than 65% of the class feel that statistics is very important to society. About 14% of the class are neutral about the importance of statistics and only 1 of the 35 students in this group be ...
... e. The vast majority of this class (more than 80%) feel that statistics is important to society. In fact, more than 65% of the class feel that statistics is very important to society. About 14% of the class are neutral about the importance of statistics and only 1 of the 35 students in this group be ...
The Interplay of Bayesian and Frequentist Analysis ∗
... This version of the frequentist principle is actually a joint frequentist/Bayesian principle. Suppose, for instance, that we decide it is relevant to statistical practice to repeatedly use a particular statistical model and procedure – for instance, a 95% classical confidence interval for a normal m ...
... This version of the frequentist principle is actually a joint frequentist/Bayesian principle. Suppose, for instance, that we decide it is relevant to statistical practice to repeatedly use a particular statistical model and procedure – for instance, a 95% classical confidence interval for a normal m ...
Statistical Inference with SCILAB
... population. The consequent action and decision-making are called hypothesis testing. The process consist on taking a random sample from the population and making a statistical hypothesis about the population. If the observations do not support the model or theory postulated, the hypothesis is reject ...
... population. The consequent action and decision-making are called hypothesis testing. The process consist on taking a random sample from the population and making a statistical hypothesis about the population. If the observations do not support the model or theory postulated, the hypothesis is reject ...
Inferential Statistics Unit
... second question is called a numerical data set. This is the case because the data is comprised of numbers, specifically different amounts of money. There are two types of numerical data; discrete and continuous. Numerical data is discrete if the possible values are isolated points on a number line. ...
... second question is called a numerical data set. This is the case because the data is comprised of numbers, specifically different amounts of money. There are two types of numerical data; discrete and continuous. Numerical data is discrete if the possible values are isolated points on a number line. ...
Power point review
... select 100to you may able randomly chosen members question the validity of B. Divide a population by gender and select 50 individuals answer (C) randomly from each group C. Select individuals randomly and place into gender groups until you have the same proportion as in the population D. Select five ...
... select 100to you may able randomly chosen members question the validity of B. Divide a population by gender and select 50 individuals answer (C) randomly from each group C. Select individuals randomly and place into gender groups until you have the same proportion as in the population D. Select five ...