* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History of Astronomy
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Galileo affair wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
International Year of Astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Patronage in astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
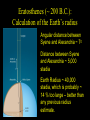
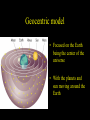
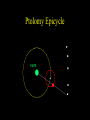
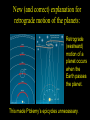
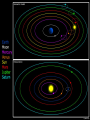
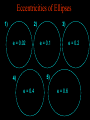
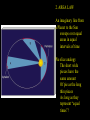
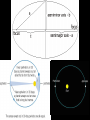
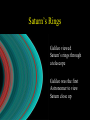
Historical Astronomy Ancient World • Early Humans questioned their existence • The Sun and moon played huge roles in early Astronomy • Actually closer to Astrology Early Astronomy • Dominated by religious reasoning • Mostly the Earth, Moon, and Sun • Gave most occurrences religious reasoning instead of facts Stonehenge • Found in England • Huge slabs of rocks in a circle • Used for summer and winter solstice ceremonies • Still not sure who made Stonehenge Stonehenge • Constructed 3000 – 1800 B.C. • Alignments with locations of sunset, sunrise, moonset and moonrise at summer and winter solstices • Probably used as calendar. Mayan Civilization • Stars played a huge role in the civilization • Created massive observatories • Made their own calendar Mayan Calendar • Ends December 21st 2012 Not the end of the world Signifies a new era “the golden era” Mayan Observatories Caracol (Maya culture, approx. A.D. 1000) Classical Astronomy Catholic Church • Dominated Science during Europe’s early formation • Regulated what Astronomers studied Pythagoras • First recorded Greek to believe that the Earth was round • Thought the sphere was the most godly shape Aristotle • Aristotle’s universe was Geocentric – Geocentric means “Earth-centered” • The Earth is at rest – At the center of the Universe • It is surrounded by 56 spheres – rotating, perfect, concentric, crystalline – 55 spheres for the Planets, Sun, Moon – 1 sphere for the Stars Aristotle • Famous for his “Round Earth” Theory • EVIDENCE- During a lunar eclipse he saw Earth’s circular shadow Eratosthenes • Famous Egyptian Experiment • Measured the circumference of Earth • Was within 200 miles Eratosthenes (~ 200 B.C.): Calculation of the Earth’s radius Angular distance between Syene and Alexandria ~ 70 Distance between Syene and Alexandria ~ 5,000 stadia Earth Radius ~ 40,000 stadia, which is probably ~ 14 % too large – better than any previous radius estimate. Theories of the Solar System Geocentric model • Focused on the Earth being the center of the universe • With the planets and sun moving around the Earth Ptolomy • Believed the planets moved around the Earth in Epicycles • Geocentric theory Ptolomy Epicycle Ptolomy’s epicycle theory Epicycles helped Ptolomy explain retrograde motion Heliocentric model Copernicus • First Astronomer to theorize that Earth was revolving around the sun = heliocentric • Was not accepted until after his death • First book published on the day of his Death The Copernican Revolution Nicolaus Copernicus (1473 – 1543): Heliocentric Universe (Sun in the Center) New (and correct) explanation for retrograde motion of the planets: Retrograde (westward) motion of a planet occurs when the Earth passes the planet. This made Ptolemy’s epicycles unnecessary. Tycho Brahe • Flamboyant and rich Dutch astronomer • Best planetary observations • Observed as a king’s astronomer Johannes Kepler • Studied under Tycho Brahe • Used Tycho’s observations to create “The Laws of Planetary Motion” after Tycho’s death Kepler’s 1st law • All planets orbit around the sun in an elliptical shape with the sun at one foci Eccentricities of Ellipses 1) 2) e = 0.02 3) e = 0.1 e = 0.2 5) 4) e = 0.4 e = 0.6 Kepler’s Equal Area Law • States that each planet covers an equal area during the same amount of time • Regardless of their speed 2. AREA LAW An imaginary line from a Planet to the Sun sweeps over equal areas in equal intervals of time Pie slice analogy The short wide pieces have the same amount Of pie as the long thin pieces As long as they represent “equal times”! Semimajor Axis F1 Center F2 T=0d T=10d T=0d T=10d Equal Areas in Equal Times Kepler’s 3rd Law • The period of time it takes for a planet to orbit the sun is directly related to its distance from the sun. » • P= period • A= semi major axis 2 P 3 = A Giordano Bruno • First to consider stars as other suns (exoplanets) Burned at the stake for heresy in 1600 Galileo Galilei • First Astronomer to use a telescope • Telescope was invented by Hans Lippershey in 1600 • Went blind later in life, due to staring at the sun through a telescope for too long • Church wasn’t happy with him Galileo Galilei • Huge contributions to Astronomy: • • • • Jupiter’s moons Moon features Rings of Saturn Sun Spots • Strange experiments Jupiter’s Moons • First Astronomer to view extraterrestrial moons • Able to see four moons Saturn’s Rings • Galileo viewed Saturn’s rings through a telescope • Galileo was the first Astronomer to view Saturn close up Major discoveries of Galileo: • Moons of Jupiter (4 Galilean moons) (What he really saw) • Rings of Saturn (What he really saw) Major discoveries of Galileo (III): • Sun spots (proving that the sun is not perfect!) Major discoveries of Galileo (IV): • Phases of Venus, proving that Venus orbits the sun, not the Earth! Moon’s features • Identified craters on the moon • Proposed that the moon’s surface is changing Galileo’s finger • On display at Institute and Museum of History of Science Florence, Italy Isaac Newton • Arguably the best contributor to modern science • Defined the Laws of Physics The Apple Story • Legend has it: • As a young lad Newton sat under an apple tree and observed an apple fall, beginning his theories of Physics Contemporaries Charles Messier (June 26, 1730 – April 12, 1817) was a French astronomer, who published a catalogue of 110 deep sky objects such as nebulae, galaxies, and star clusters. M1 M31 Messier Catalogue – of space objects Albert Einstein • German scientist • Modern Science Genius, with very complex theories Einstein • Developed theory of relativity • E = mc 2 • Universe shape Theory Stephen Hawkings • Today’s foremost Astrophysics thinker • Teaches at Cambridge University in England • He is expanding on Einstein’s theories Soak it all in!