* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
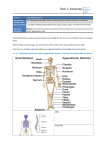
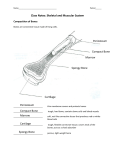
Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |1 Body Planes Name and describe the following body planes. Name : Name: 2. 1. Definition: 4. Describe anatomical position and why we have it. Name: 3. Definition: Definition: Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |2 Directional Terms Match the following directional terms to their definition. Directional Term _____5. Anterior _____6. Posterior _____7. Superior _____8. Inferior _____9. Lateral _____10. Medial _____11. Proximal _____12. Distal _____13. Palmar _____14. Dorsal _____15. Plantar _____16. Cranial _____17. Caudal _____18. Superficial _____19. Deep _____20. Supine _____21. Prone a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. q. Definition Sole of the foot Top of the foot or back of the hand Facing upward Toward the back or rear Nearest to the midline of the body Toward the head Facing downward Located in or on the palm Toward the feet Further away from the midline of the body Closer to the surface of the body closer to the torso further away from the torso situated under or beneath before or in front of situated higher or above further away from the surface of the body Body Quadrants Place the letter of the following organs in the quadrant(s) where they are located. a. e. i. m. q. Right lobe of liver Large intestine Right spermatic cord Left lobe of liver Left kidney b. f. j. n. Gallbladder Appendix Left spermatic cord Stomach c. g. k. o. Right kidney Right ovary Right ureter Pancreas d. h. l. p. Small intestine Left ovary Left ureter Spleen 22. Upper Right 23. Upper Left 24. Lower Right 25. Lower Left Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |3 Bones 26. What are the five functions of bones? 1. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. ____________________________________________________________________________________ Types of Bones Write the name of the correct bone type under the pictures below. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |4 Parts of Long Bones Label and describe the parts of long bones. a. Epiphysis 39. b. Diaphysis 40. c. Metaphysis 41. d. Articular cartilage 42. e. Medullary cavity 43. f. Periosteum 44. g. Endosteum 45. 46. What is a joint? What does the word articulation mean? Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |5 Types of Joints Match the following types of joints to their definitions as well as an example. Joint _____47. Definition Example Fibrous a. bones connected with cartilage; immovable/partly movable d. _____48. Cartilaginous b. bones are connected with fibrous tissue; mainly immovable e. _____49. Synovial c. bones that are connected with ligaments; enclosed in a joint capsule; freely movable f. Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |6 Classification of Synovial Joints Match each type of synovial joint to its definition and example. Synovial Joint _____50. Plane Joint Definition a. Example rounded end of one bone protrudes into a sleeve or ring composed of bone of another; rotation is only motion allowed _____51. Hinge Joint g. b. cylindrical projection of one bone fits into a trough-shaped surface on another; motion is along single plane; only flexion and extension allowed _____52. Pivot Joint h. c. resemble condyloid joints, but allow greater freedom of movement; both articular surfaces are concave and convex _____53. Condyloid Joint i. d. the spherical or hemispherical head of one bone articulates with the cuplike socket of another; most freely moving joints _____54. Saddle Joint j. e. articular surfaces are flat and only allow short gliding or translational movements k. _____55. Joint Ball and Socket f. oval articular surface of one bone fits into a complementary depression in another; bone articular surfaces are oval; permit all angular motions l. Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |7 Joint Movements Match each joint movement to its definition and example. Joint Movement Definition _____56. Flexion Example a. p. _____57. Extension b. q. _____58. Abduction c. r. _____59. Adduction d. s. _____60. Dorsiflexion e. t. _____61. Plantarflexion f. u. _____62. Supination g. v. Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |8 _____63. Pronation h. w. _____64. Internal i. Rotation x. _____65. External j. Rotation y. _____66. Opposition k. z. _____67. Circumduction l. aa. _____68. Inversion m. bb. _____69. Eversion n. cc. _____70. Rotation o. dd. Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page |9 Types of Muscle Tissue Describe the three types of muscle tissue. 71. found in/on: interesting info: voluntary/involuntary? striations? y/n 72. found in/on: interesting info: voluntary/involuntary? striations? y/n 73. found in/on: interesting info: voluntary/involuntary? striations? y/n Characteristics of Muscle Tissue Match each characteristic to its definition. Characteristic Definition _____74. Excitability a. Ability of a muscle fiber to recoil and resume its resting length after being _____75. Contractility _____76. Extensibility b. Ability to shorten forcibly when adequately stimulated _____77. Elasticity c. Ability to receive and respond to a stimulus stretched d. Ability to be stretched or extended beyond resting length Functions of Muscle 78. What are the four functions of muscle? 1. _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________________________________ 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ Name ________________________ Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide Page | 10 Skeletal Muscle Terminology Match each term with its definition. Term Definition _____79. Agonist a. The more stable attachment site of a muscle _____80. Antagonist b. The fibrous tissue that surrounds muscles, groups of muscles, blood vessels, _____81. Synergist _____82. Fixator _____83. Origin _____84. Insertion d. Muscles that oppose or reverse a particular movement _____85. Action e. The fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone _____86. Nerve innervation f. _____87. Fascia g. The less stable attachment site of a muscle _____88. Tendon h. The muscle that provides the major force for producing a specific movement and nerves c. Muscles that immobilize a bone or a muscle’s origin so that only the desired movements occur The body movement that results from the contraction of a muscle i. Additional muscles that help agonists j. The nerve that supplies the stimulus for contraction of a muscle Fiber Arrangement Write the name of each muscle fiber arrangement below its image.