* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart - IWS2.collin.edu
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
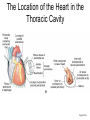
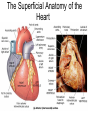
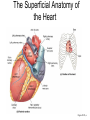
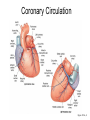
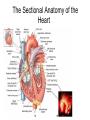
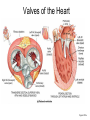
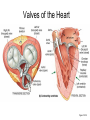
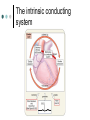
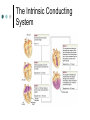
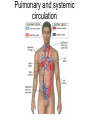
Exercise 35 Anatomy of the Heart Gross anatomy of the heart Localized in the mediastinum It has a pointed apex At the level of the 5th intercostal space And a broad base Beneath the 2nd rib Is the site of emerging of the great vessels The pericardium Pericardial cavity Visceral pericardium or epicardium Parietal pericardium Pericardial fluid Pericardial sac (fibrous) Stabilizes the heart and its vessels Pericarditis The Location of the Heart in the Thoracic Cavity Figure 20.2c Gross anatomy of the heart Myocardium Muscle wall of the heart Fibrous skeleton of the heart Endocardium Superficial Anatomy of the Heart The heart consists of four chambers Two atria • Two auricles Two ventricles Major blood vessels of the heart include Inferior and superior vena cavae Aorta, pulmonary trunk and pulmonary veins The Superficial Anatomy of the Heart The Superficial Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20.3b, c The superficial Anatomy of the heart Atria Thin walled upper chambers that receive blood from the vena cava Ventricles Thick walled lower chambers separated from the atria by AV valves External anatomy of the heart and blood flow Right atrium (RA) Receives blood coming from the body via superior, inferior vena cava and coronary sinus auricle Right ventricle (RV) Receives blood from the RA and pumps it into the pulmonary trunk Pulmonary trunk Left and right pulmonary arteries External anatomy of the heart and blood flow Lungs Pulmonary veins 2 rights and 2 lefts Left atrium (LA) Receives blood from the pulmonary veins Auricle External anatomy of the heart and blood flow Left ventricle (LV) Pumps blood into the aorta Aorta Ascending, arch, descending Ligamentum arteriosum Remnant of the ductus arteriosus Between pulmonary artery and aorta Blood supply to the heart Coronary arteries and coronary sulcus Right • Posterior interventricular artery • Marginal • Supplies posterior part of the ventricles and lateral part of the right heart Blood supply to the heart Left coronary • Anterior interventricular artery • Circumflex • Supplies the anterior part of the ventricles and laterodorsal part of the heart Anterior and posterior interventricular sulci Blood Supply to the Heart veins Veins that empty into the coronary sinus Great cardiac vein (anterior interventricular) , Middle cardiac vein (posterior interventricular), Small cardiac vein Coronary Circulation Figure 20.9a, b The Sectional Anatomy of the Heart Internal anatomy of the heart Right atrium Fossa ovalis • Foramen ovale Openings of the superior and inferior vena cavas Pectinate muscle SA and AV nodes Interatrial septum • Wall between atria Internal anatomy of the heart Right ventricle Tricuspid valve Chordae tedineae Papillary muscles Trabeculae carneae – muscular ridges Interventricular septum • Wall between ventricles Internal anatomy of the heart Moderator band (septomarginal band) • Horizontal muscular ridge • Brings the impulse to the papillary muscles • Only present in the RV Conus arteriosus • Conical pouch from which the pulmonary artery arises Internal anatomy of the heart Left atrium Principal cavity (sinus) Pectinate muscles on the auricle only Openings of the pulmonary veins Internal anatomy of the heart Left ventricle Bicuspid valve Trabeculae carneae Papillary muscles Chordae tendineae Valves of the Heart Figure 20.8a Valves of the Heart Figure 20.8b Valves of the heart Bicuspid or mitral or left AV Tricuspid or right AV Aortic semilunar Pulmonary semilunar The intrinsic conducting system Functional syncytium Gap junctions The intrinsic conducting system The intrinsic conducting system Controlling system over the heart Autonomic nervous system • Sympathetic • Parasympathetic Intrinsic conducting system or nodal system • Specialized myocardial tissue • Initiates the heart beat The Intrinsic Conducting System The conducting system includes: Sinoatrial (SA) node (80-100 bpm) • Contain the pacemaker cells • Located in the right atrium Atrioventricular (AV) node (40-60 bpm) • Located in the atrium septum at the junction of the atria and ventricles The Intrinsic Conducting System AV bundle or bundle of His • Located in the interventricular septum Right and Left bundle branches • Located in the interventricular septum Purkinje fibers • Located in the myocardium • Larger in the left ventricle Steps for the heart beat SA node begins the action potential Stimulus spreads across the atria Stimulus spreads to the AV node Atrial contraction Impulse then travels through the AV bundle Impulse reaches right and left bundle branches Steps for the heart beat Then it reaches the Purkinje fibers Impulse reaches the papillary muscles (via moderator band on the right side) Impulse is spread to the ventricles Ventricular contraction The Intrinsic Conducting System Pulmonary and systemic circulation Pulmonary circulation Pulmonary arteries Leave the RV Carry blood rich in CO2 Blood flows to the lungs Pulmonary veins Leave the lung Blood rich in O2 Blood flows to the LA Systemic circulation Aorta Leaves the LV Blood rich in O2 Blood flows to the body Vena cava Superior brings blood from head, neck, arms and superior trunk Inferior brings blood from the rest of the body Blood rich in CO2 Blood flows to the RA Microscopic anatomy of the heart Involuntary Cardiac cells Intercalated discs Branching Central nucleus Striations Identify these structure on the fresh heart RA Auricle Pectinate muscles Superior and inferior vena cavas Coronary sinus Tricuspid valve Identify these structure on the fresh heart RV Papillary muscles Chrodae tendineae Trabeculi carneae Moderator band Pulmonary trunk and its semilunar valve Identify these structure on the fresh heart LA Auricle Pectinate muscles Identify these structure on the fresh heart LV Myocardium Papillary muscles Chordae tendineae Mitral valve Trabeculi carneae Interventricular septum Aorta and its semilunar valve Coronary arteries