* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Correlation between molecular biology and mechanics in liver cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
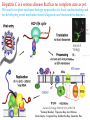
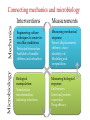
Correlation between molecular biology and mechanics in liver cells with viral infections G.K. Ananthasuresh Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India [email protected] Saumitra Das Professor Dept. of Microbiology and Cell Biology Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India [email protected] Both professors are associated with BioSystems Science and Engineering (BSSE) and have collaborated and co-advised a BSSE PhD student for five years. Hepatitis C is a serious disease that has no complete cure as yet. We want to explore mechano-biology approaches for basic understanding and for developing novel mechanics-based diagnosis and treatment techniques. HCV-lifecycle Journal of Virology (2008) 82 (23), p11927-38 1 Mondal, Upasana Ray, Asit Manna, Romi Gupta , Swagata Roy, Siddhartha Roy, Saumitra Das 1Tanmoy Microbiology Mechanics Connecting mechanics and microbiology Interventions Measurements Engineering culture techniques to create invivo like conditions: Perfusion bioreactors Scaffolds of tunable stiffness and actuation. Measuring mechanical response: Forces, displacements, stiffness, viscoelasticity, etc. Modeling and computation. Biological manipulation: Transfection, transformation, inducing infections. Measuring biological response: Cell sensors Gene and protein expression Drug efficacy Accomplishments of the Ananthasuresh-Das collaboration • • • • • • • • Miniature perfusion-bioreactors Bio-micro-manipulation Stiffness measurement Inverse problems to estimate interior properties Active scaffolds High-resolution imaging of cells and organelle during culture. Effect of viral infection on the organelles of liver cells including their morphology, permeability, and rigidity. Effect of mechanical stimuli and responses on the gene expression. Micromanipulation station An objective • Microfluidic platform for in-vivo culture of hepatocytes to study the effects of chronic Hepatitis C Virus infection Most studies of HCV have focussed on short term infection (2-3 days) in traditional Petri dish cultures. But HCV is a chronic infection and it takes years for the disease to manifest itself. The primary reason for short term studies is because of the unavailability of platforms for in-vivo like long term cultures for hepatocytes and the difficulty of designing, validating and standardizing such systems. This project aims at making a platform which mimics the organisation of cells in the liver. The important aspects of liver physiology like multiple cell types – hepatocytes, endothelial and Kupfer cells, and shear stress due to flow will be realised on the platform. This platform will be used to study the long-term effects of HCV infection on hepatocytes. The platform will contain micro-fabricated structures (mostly for the flow channels) and different cell types will be paZerned on the micro-fabricated structures to obtain the liver sinusoids. The cells will be grown under constant flow of the culture medium. The platform will be established as a viable, long – term, in-vivo like system of the liver invitro. Further many liver diseases such as drug induced hepatitis and viral hepatitis can be studied using this platform to understand the mechanism of disease progression. An alternate objective • Mechano-biology of hepatocytes in the context of HCV infection Changes in chromatin organisation and gene expression due to the alteration in nuclear mechanics induced by HCV infection. The changes in chromatin organisation due to the reduction of stiffness of the nuclei in HCV infection will be studied. The changes in chromatin organisation under mechanical stimuli – shear stress due to flow, and stretching and stiffening of the substrate will be explored. Required background • Strong expertise either in mechanics or microbiology with conviction to learn the other field (adequate training will be provided). • Modeling skills and adequate familiarity with engineering mathematics (or will to acquire them). • Inclination towards interdisciplinary research. Further reading • S. Balakrishnan, M. S. Suma, S. R. Raju, S. D. B. Bhargav, S. Arunima, S. Das and G. K. Ananthasuresh, "A Scalable Perfusion Culture System with Miniature Peristaltic Pumps for Live-Cell Imaging Assays with Provision for Microfabricated Scaffolds", BioResearch Open Access, 2015, 4(1), 343–357. DOI: 10.1089/biores.2015.0024 • hZp://mcbl.iisc.ernet.in/Saumitra • hZp://www.mecheng.iisc.ernet.in/~suresh