* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.E.4B.1 Our Solar System
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Near-Earth object wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
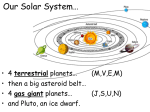
8.E.4B.1 Our Solar System p. 1 8.E.4B.1 Obtain and communicate information to model and compare the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Our solar system is composed of eight planets in the following order from the Sun out: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Celestial objects in our solar system include the eight planets that orbit the Sun, the moons that orbit the eight planets, and many asteroids, comets, and meteors. Objects found in the solar system have characteristics based on surface features and atmosphere (if there is one). These objects move via orbit/revolution and/or rotation. Examples of celestial objects include: Planets Planets may have either a terrestrial/rocky surface or a gaseous surface. Gaseous planets are considerably larger than terrestrial planets. Planets may have rings or other unique surface characteristics. Movement of planets is based on revolution around the Sun and rotation on the planet’s axis. Moons Moons are studied in relation to the planet they orbit. Not all planets have moons. Most are rocky bodies covered with craters, but some have unique characteristics. Movement of moons is based on revolution around their planets and rotation on their axis. 1 8.E.4B.1 Our Solar System (continued) p. 2 8.E.4B.1 Obtain and communicate information to model and compare the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Asteroids Most asteroids are rocky bodies that orbit in a region in the solar system known as the Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter. They vary in size and shape. Movement is based on their revolution around the Sun. Some asteroids outside the asteroid belt have orbits that cross Earth’s orbit, which require scientists to monitor their positions. Comets Comets have a main body or head (ice, methane and ammonia and dust) and a tail that emerges as the comet gets closer to the Sun during its orbit. The effects of the solar winds result in the tail always pointing away from the Sun. Comets have long, narrow, elliptical orbits that cause them to cross paths with other objects in the solar system. Most comets originate from regions of the solar system that lie beyond the orbit of Neptune. Meteors Meteors are chunks of rock that burn upon entering a planet’s atmosphere. Prior to entering the atmosphere, chunks of rock move about within the solar system and are known as meteoroids. When a chunk of rock strikes the surface of a planet or moon, it is known as a meteorite. 2 2 2