* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polio
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Anthrax vaccine adsorbed wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
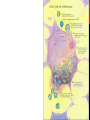
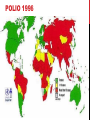
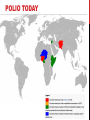
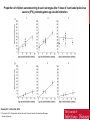
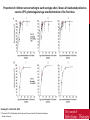
YESHA PATEL GENERAL • What is it? • Highly contagious viral infection that can lead to paralysis • What causes it? • poliomyelitis virus that targets motor neurons • Who gets it? • Young and vulnerable • Clinically suspected in those with • Acute onset of flaccid paralysis • Absent tendon reflexes CLASSIFICATION • Symptomatic • Nonparalytic polio • Paralytic polio (~0.1 – 2% of case) • • • Spinal polio Bulbar polio Bulbospinal polio • Asymptomatic (~95% of cases) SYMPTOMS General • • • • • Headache Sore throat Fever Vomiting General discomfort Non-paralytic • • • • Abnormal reflexes Difficulty swallowing Joint stiffness Muscle tenderness Paralytic • • • • • Loss of reflexes Severe spasms and muscle pain Floppy limbs Sudden paralysis Deformed limbs TREATMENT • No cure for polio • Goal of treatment: relieve symptoms • Antibiotics • Analgesics • Long term rehabilitation • Occupational and physical therapy • Corrective braces, shoes • Surgery TRANSMISSION • Highly contagious • Primarily spreads via the fecal-oral route. • Occasionally oral-oral route • Most infectious 7-10 days before and after appearance of symptoms • Immune deficiency, malnutrition, and injury increase risk of transmission and infection • Can cross maternal-fetal barrier PREVENTION • Passive immunization • Purified gamma globulin from survivors • Vaccines • 3 types • • Inactivated poliovirus vaccine • Salk Vaccine Live and attenuated poliovirus vaccine • Sabin Vaccine • Oral polio vaccine POLIO 1996 POLIO TODAY Proportion of children seroconverting to each serotype after 1 dose of inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV), plotted against age at administration. Grassly N C J Infect Dis. 2014 © The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Proportion of children seroconverting to each serotype after 2 doses of inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV), plotted against age at administration of the first dose. Grassly N C J Infect Dis. 2014 © The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. REFERENCES • Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Global Health – Polio. Web. Accessed 20 March 2014. http://www.cdc.gov/polio/ • Grassly N C J Infect Dis. 2014 • Johnson, Shannon. Polio. Healthline 2012. Web. Accessed 20 March 2014. • Poliomyelitis (2011). PubMed Health. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002375/ • Smithsonian. How the Poliovirus Works. Web. Accessed 26 March 2014. http://amhistory.si.edu/polio/virusvaccine/how.htm • World Health Organizaiton. Health Topics – Poliomyelitis (Polio). Web. Accessed 20 March 2014. http://www.who.int/topics/poliomyelitis/en/