* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
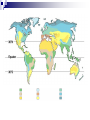
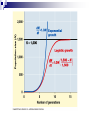
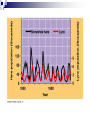
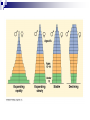
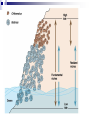
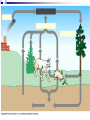
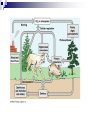
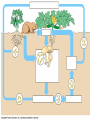
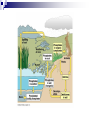
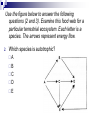
Ecology Biomes Behavior Populations Community Symbiosis Competition Succession Ecosystems Density dependant inhibition Density independent inhibition R selected species K selected species 4. If a meteor impact or volcanic eruption injected a lot of dust into the atmosphere and reduced sunlight reaching Earth's surface by 70% for one year, all of the following marine communities would be greatly affected except a deep-sea vent community. coral reef community. benthic community. pelagic community. estuary community. 2. As N approaches K for a certain population, which of the following is predicted by the logistic equation? The growth rate will not change. The growth rate will approach zero. The population will show an Allee effect. The population will increase exponentially. The carrying capacity of the environment will increase. 3. In which of the following habitats would you expect to find the largest number of Kselected individuals? an abandoned field in Ohio the sand dunes south of Lake Michigan the rain forests of Brazil south Florida after a hurricane a newly emergent volcanic island The following question refers to the figure below, which depicts the age structure of three populations 4. Assuming these age structure diagrams describe human populations, in which population is unemployment likely to be most severe in the future? I II III No differences in the magnitude of future unemployment would be expected among these populations. It is not possible to infer anything about future social conditions from age structure diagrams. 5. Which of the following variables is (are) important in contributing to the rapid growth of human populations? the high percentage of young people the average age to first give birth carrying capacity of the environment only A and B A, B, and C Clear-cutting tropical forests yields agricultural land with limited productivity because it is too hot in the tropics for most food crops. the tropical forest regrows rapidly and chokes out agricultural crops. few of the ecosystem’s nutrients are stored in the soil; most are in the forest trees. phosphorus, not nitrogen, is the limiting nutrient in those soils. decomposition rates are high but primary production is low in the tropics. Use the figure below to answer the following questions (2 and 3). Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem. Each letter is a species. The arrows represent energy flow. 2. Which species is autotrophic? A B C D E 3. Species C makes its predators sick. Which species is most likely to benefit from being a mimic of C? * A B C D E 6. If the flow of energy in an Arctic ecosystem goes through a simple food chain from seaweeds to fish to seals to polar bears, then which of the following is true? Polar bears can provide more food for Eskimos than seals can. The total energy content of the seaweeds is lower than that of the seals. Polar bear meat probably contains the highest concentrations of fat-soluble toxins. Seals are more numerous than fish. The carnivores can provide more food for the Eskimos than the herbivores can. AP Labs and Essays Lab 12 Lab 11 1997, # 1 1997, # 3 (lab) 1998, # 4 2002, # 2 2003, # 3 Symbiotic Relationships Parasitism Mutualism Commensualism 3. Which of the following is true about imprinting? a. b. c. d. e. It may be triggered by visual or chemical stimuli. It happens to many adult animals, but not to their young. It is a type of learning involving no innate behavior. It occurs only in birds. It causes behaviors that last for only a short time (the critical period). 4. Every morning at the same time John went into the den to feed his new tropical fish. After a few weeks John noticed that the fish would rise to the top of the tank as soon as he would enter the room. This is a good example of 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. habituation. imprinting. classical conditioning. operant conditioning. maturation. 5. A dog learns that it will get a treat when it barks. Which of the following might you use to describe this behavior? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The dog is displaying an instinctive fixed action pattern. The dog is performing a social behavior. The dog is trying to protect its territory. The dog has been classically conditioned. The dog's behavior is a result of operant conditioning. 6. The presence of altruistic behavior in animals is most likely due to kin selection, a theory that maintains that 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. aggression between sexes promotes the survival of the fittest individuals. genes enhance survival of copies of themselves by directing organisms to assist others who share those genes. companionship is advantageous to animals because in the future they can help each other. critical thinking abilities are normal traits for animals and they have arisen, like other traits, through natural selection. natural selection has generally favored the evolution of exaggerated aggressive and submissive behaviors to resolve conflict without grave harm to participants. 2. As N approaches K for a certain population, which of the following is predicted by the logistic equation? a. b. c. d. e. The growth rate will not change. The growth rate will approach zero. The population will show an Allee effect. The population will increase exponentially. The carrying capacity of the environment will increase. 3. In which of the following habitats would you expect to find the largest number of Kselected individuals? an abandoned field in Ohio b. the sand dunes south of Lake Michigan c. the rain forests of Brazil d. south Florida after a hurricane e. a newly emergent volcanic island a. The following question refers to the figure below, which depicts the age structure of three populations 4. Assuming these age structure diagrams describe human populations, in which population is unemployment likely to be most severe in the future? a. b. c. d. e. I II III No differences in the magnitude of future unemployment would be expected among these populations. It is not possible to infer anything about future social conditions from age structure diagrams. Why do most food chains consist of only three to five links? * 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. There are only five trophic levels: producers; primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers; and decomposers. Most communities are controlled bottom-up by mineral nutrient supply, and few communities have enough nutrients to support more links. The dominant species in most communities consumes the majority of prey; thus, not enough food is left to support higher predators. According to the energetic hypothesis, the inefficiency of energy transfer from one trophic level to the next limits the number of links that can exist. According to the trophic cascade model, increasing the biomass of top trophic levels causes a decrease in the biomass of lower levels, so that the top levels can no longer be supported. 3. Two barnacles, Balanus and Chthamalus, can both survive on the lower rocks just above the low tide line on the Scottish coast, but only Balanus actually does so, with Chthamalus adopting a higher zone. Which of the following best accounts for this niche separation? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. competitive exclusion predation of Chthamalus by Balanus cooperative displacement primary succession mutualism The following questions refer to the diagram in Figure 53.2 of five islands formed at about the same time near a particular mainland. 6. Island with the greatest number of species A B C D E 7. Island with the lowest extinction rate A B C D E Use the figure below to answer the following questions (2 and 3). Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem. Each letter is a species. The arrows represent energy flow. 2. Which species is autotrophic? A B C D E 3. Species C makes its predators sick. Which species is most likely to benefit from being a mimic of C? * A B C D E Refer to the figure below,, a diagram of a food web, for the following questions (4 and 5). Arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species. 6. If the flow of energy in an Arctic ecosystem goes through a simple food chain from seaweeds to fish to seals to polar bears, then which of the following is true? a. Polar bears can provide more food for Eskimos than seals can. b. The total energy content of the seaweeds is lower than that of the seals. c. Polar bear meat probably contains the highest concentrations of fat-soluble toxins. d. Seals are more numerous than fish. e. The carnivores can provide more food for the Eskimos than the herbivores can. Behavioral Ecology Innate Behavior FAP Learning – critical period Associative learning Imprinting Classical conditioning (pavlov) Operant conditioning Play Animal Cognition (percieption and processing) Taxis Kinesis Migration Social Behavior Hierarchy Agonistic Territoriality Courtship rituals When, during a field trip, the instructor touched the body of a moth that was sitting on a tree trunk, the moth raised its forewings to reveal large eye-spots on its hind wings. The instructor asked the class why the moth lifted its wings. One student said that certain sensory receptors had fired and triggered a neuronal reflex culminating in the contraction of certain muscles. A second student responded that the behavior might frighten would-be predators. (cont.) What can you say about the explanations of these two students? * The first response is correct, while the second is incorrect. The first response answers a proximate question, while the second answers an ultimate question. The first response is biological, while the second is philosophical. The first explanation is testable as a scientific hypothesis, while the second is not. Both explanations are reasonable and simply represent a difference of opinion. 2. A cage with male mosquitoes in it has a small earphone placed on top, through which the sound of a female mosquito is played. All the males immediately fly to the earphone and thrust their abdomens through the fabric of the cage. 2. (cont.) Which of the following best describes this? The males learn to associate the sound with a female and are thus attracted to it. Copulation is a fixed action pattern, and the female flight sound is a sign stimulus that initiates it. The sound from the earphone irritated the male mosquitoes, causing them to attempt to sting it. The reproductive drive is so strong that when males are deprived of females, they will attempt to mate with anything that has even the slightest female characteristic. Through classical conditioning, the male mosquitoes have associated the inappropriate stimulus from the earphone with the normal response of copulation. 3. Which of the following is true about imprinting? It may be triggered by visual or chemical stimuli. It happens to many adult animals, but not to their young. It is a type of learning involving no innate behavior. It occurs only in birds. It causes behaviors that last for only a short time (the critical period). 4. Every morning at the same time John went into the den to feed his new tropical fish. After a few weeks John noticed that the fish would rise to the top of the tank as soon as he would enter the room. This is a good example of habituation. imprinting. classical conditioning. operant conditioning. maturation. 5. A dog learns that it will get a treat when it barks. Which of the following might you use to describe this behavior? The dog is displaying an instinctive fixed action pattern. The dog is performing a social behavior. The dog is trying to protect its territory. The dog has been classically conditioned. The dog's behavior is a result of operant conditioning.