* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nomenclature Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
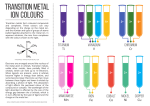
Things you should already know how to do so we won’t go over them again: Nomenclature Chemistry 11 Honours • Count protons, electrons and neutrons from atomic symbols • Count the number of atoms in a formula • Identify compounds as ionic or molecular (covalent) • Name ionic compounds • with polyatomic ions and multivalent ions • Name covalent compounds • using prefixes Writing Dissociation Equations: (comes up again in Chem 12) • When ionic compounds are put in water, they dissociate (a.k.a. dissolve - split into their ions) • Knowing the ions that make up a compound can help you name it! • An aqueous solution is formed containing the ions that made up the ionic salt • Example: NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Common Names for Ionic Compounds: (these don’t follow the rules) • Old way of naming compounds with multivalent ions • multivalent ions are named according to their Latin names, rather than using Roman numerals • Name the Latin root for the ion, then change the ending • The lower charge ion ends in “ous” • The higher charge ion ends in “ic” • Ex. FeCl2 = ferrous chloride = iron(II) chloride FeCl3 = ferric chloride = iron(III) chloride 1 Naming Acids: Naming Binary Acids: • How do you know if the compound is an acid? • • the formula has an “H” at the front • One exception we worry about… CH3COOH or C2H4O2 = acetic acid • the name ends in “acid” • • • Hydro_________ic acid ex. HCl Second ion = Cl- = Chloride Acid name = hydrochloric acid • 3 types of acids to name: • binary acids – contain ions ending in “ide” • acids containing polyatomic ions ending in “ate” • acids containing polyatomic ions ending in “ite” Naming Acids with Polyatomic Ions Ending in “ate”: • ____________ic acid • ex. HNO3 • polyatomic ion = NO3- = Nitrate • Acid name = Nitric acid Naming Acids with Polyatomic Ions Ending in “ite”: • ____________ous acid • ex. HNO2 • polyatomic ion = NO2- = Nitrite • Acid name = Nitrous acid 2 Writing Formulas for Acids: • The hydrogen always is written first (except in acetic acid – CH3COOH) ex. Hydrochloric acid • • • • Hydrochloric = chloride = ClNeed 1 H+ to match up the charges Formula = HCl • Example #1: Naming Hydrates: • Hydrate: an ionic salt that has water associated with it (incorporated into the crystal lattice structure) • Named just like ionic compounds, except… • the Greek prefixes are added at the end with the word “hydrate” to show how many water molecules are present • A dot is added between the formula of the salt and the formula of the water The “Weirdo’s” • iron(III) phosphate octahydrate • iron(III) = Fe3+ phosphate = PO43• octahydrate = 8H2O • ∴ FePO4 · 8H2O • Example #2: • Na2SO4 · 10H2O • Na+ = sodium SO42- = sulphate • 10 H2O = decahydrate • ∴ sodium sulphate decahydrate • Unlike other metals, transition metals show great similarities within a given period and group. 3 • Exhibit the following characteristics: • Form more than one oxidation state/charge. • The cations are often complex ions. • The transition metal is surrounded by a certain number of ligands (molecules or ions that bond to a metal ion). [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 K3[Fe(CN)6] • Most compounds are coloured. Coordination Compounds • Formed by transition metal ions. • Consists of a complex ion (a transition metal with its attached ligands, NH3 and Cl-) and counterions (ions to balance out charge). • For Example: [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 Co3+ • When these compounds dissolve in water, they usually produce coloured solutions that act as ionic compounds: [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2(s)→Co(NH3)5Cl2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) Coordination Number: • The number of bonds formed by metal ions to ligands varies from two to eight. • Depends upon the size, charge, and electron configuration of the transition metal ion 4 Ligands: • Each coordination number will produce a different geometry (we’ll talk more about this later in course). • A neutral molecule or ion having a lone electron pair that can be used to form a bond to a metal ion. • Monodentate Ligand: • Also called unidentate ligand. • Can form one bond to a metal ion. • Bidentate Ligand: • Can form two bonds to a metal ion. • Chelating Ligand or Chelates: • More than one atom with a lone pair that can bond to a metal ion. Nomenclature for coordination Compounds 1. To name a coordination compound, no matter whether the complex ion is the cation or the anion, always name the cation before the anion. 2. In naming the complex ion: a) Name the ligands first, in alphabetical order, then the metal atom or ion. The metal atom or ion is written before the ligands in the chemical formula. b) See the table on next slide for names of some common ligands. 5 • Anionic ligands end in "-o”. • Anions that end in "-ide"(e.g. chloride), "-ate" (e.g. sulfate, nitrate), and "-ite" (e.g. nirite), change the endings as follows: • For neutral ligands, the common name of the molecule is used. • For example: H2NCH2CH2NH2 (ethylenediamine). • Important exceptions: -ide -ate -ite • • • • -o -ato -ito • Greek prefixes are used to designate the number of each type of ligand in the complex ion. • If the ligand already contains a Greek prefix (e.g. ethylenediamine) or if it is a polydentate ligand, the prefixes bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, pentakis-, are used instead. Water is called ‘aqua’. Ammonia is called ‘ammine’. Carbon monoxide is called ‘carbonyl’. N2 and O2 are called ‘dinitrogen’ and ‘dioxygen’. Number Prefix Number 1 mono 5 2 di (bis) 6 3 tri (tris) 7 4 tetra (tetrakis) 8 Prefix Number Prefix 9 nona (ennea) 10 deca hepta 11 undeca octa 12 dodeca penta (pentakis) hexa (hexakis) 6 • After naming the ligands, name the central metal. • If the complex ion is a cation, the metal is named the same as the element. • If the complex ion is an anion, the name of the metal ends with the suffix –ate. Name of Metal Name in an Anionic Complex Iron Ferrate Copper Cuprate Lead Plumbate Silver Argenate Gold Aurate Tin Stannate • Co in a complex anion is called Cobaltate and Pt is called Platinate. • For some metals, the Latin names are used in the complex anions. • Fe is called Ferrate (not ironate). • Following the name of the metal, the oxidation state of the metal in the complex is given as a Roman numeral in parentheses Example time…(hope these help) • Name the following coordination compounds: • [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3]Cl3 triamminetriaquachromium(III) chloride • • • • The complex ion is inside the parentheses, which is a cation. The ammine ligands are named before the aqua ligands according to alphabetical order. Since there are three chlorides binding with the complex ion, the charge on the complex ion must be +3 ( since the compound is electrically neutral). From the charge on the complex ion and the charge on the ligands, we can calculate the oxidation number (charge) of the metal. In this example, all the ligands are neutral molecules. Therefore, the oxidation number of chromium must be same as the charge of the complex ion, +3. • [Pt(NH3)5Cl]Br3 pentaamminechloroplatinum(IV) bromide • • • The complex ion is a cation, the counter anion is the 3 bromides. The charge of the complex ion must be +3 since it bonds with 3 bromides. The NH3 are neutral molecules while the chloride carries - 1 charge. Therefore, the oxidation number of platinum must be +4. • [Pt(H2NCH2CH2NH2)2Cl2]Cl2 dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)platinum(IV) chloride • ethylenediamine is a bidentate ligand, the bis- prefix is used instead of di-. • [Co(H2NCH2CH2NH2)3]2(SO4)3 tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) sulfate • • The sulfate is the counter anion in this molecule. Since it takes 3 sulfates to bond with two complex cations, the charge on each complex cation must be +3. Since ethylenediamine is a neutral molecule, the oxidation number of cobalt in the complex ion must be +3. • K4[Fe(CN)6] potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) • • • Potassium is the cation and the complex ion is the anion. Since there are 4 K+ binding with a complex ion, the charge on the complex ion must be - 4. Since each ligand carries –1 charge, the oxidation number of Fe must be +2. • Na2[NiCl4] sodium tetrachloronickelate(II) • The complex ion is the anion so we have to add the suffix –ate in the name of the metal. 7 • Write the formulas for the following: • Hexaammineiron(III) nitrate [Fe(NH3)6](NO3)3 • Ammonium tetrachlorocuprate(II) (NH4)2[CuCl4] • Sodium chloropentacyanoferrate(III) Na3[Fe(CN)5Cl] • Potassium hexafluorocobaltate(III) K3[CoF6] Homework: • Nomenclature Worksheet • Study for quiz 8










![Coordination Compounds [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000678035_1-c20c75fd4abb97d3ba4a0b0fce26e10b-150x150.png)