* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Why People Buy: Consumer Behavior
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Communication in small groups wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
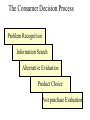
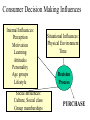
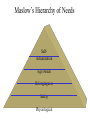
Why People Buy: Consumer Behavior Consumer Behavior • The process individuals and groups go through to select, purchase, or use goods, services, ideas, or experiences The Consumer Decision Process Problem Recognition Information Search Alternative Evaluation Product Choice Post purchase Evaluation Problem Recognition • Occurs whenever a consumer recognizes a difference between the current state and the ideal or desired state • Internal cues - consumers recognize state of discomfort • External cues - marketers may stimulate consumers to recognize problem Information Search • Consumer checks memory and surveys environment to identify what options are available • Sources might include personal experience and knowledge, friends, advertising, web sites, and magazines. Evaluation of Alternatives • Identify consideration set • Narrow list and compare pros and cons • Use evaluative criteria to decide among remaining choices Product Choice • People may ultimately make the choice based on heuristics • Heuristics represent rules of thumb – brand loyalty – country of origin – liking Post purchase Evaluation • How good a choice was it? • Customer satisfaction/dissatisfaction – “buyer’s remorse” • Ultimately affects future decisions and word of mouth communication Consumer Decision Making Influences Internal Influences: Perception Motivation Learning Attitudes Personality Age groups Lifestyle Social Influences: Culture, Social class Group memberships Situational Influences: Physical Environment Time Decision Process PURCHASE Internal Influences • • • • • • • Perception Motivation Learning Attitudes Personality Age Lifestyle Perception • Process by which people select, organize, and interpret information – Exposure: stimulus must be within sensory receptors to be noticed – Perceptual Selection: consumers will pay attention to some stimuli and not to others – Interpretation: consumers assign meaning to stimuli Motivation • An internal state that drives us to satisfy needs • Once we activate a need, a state of tension exists that drives the consumer to some goal that will reduce this tension and eliminate the need • Consequently, only unmet needs motivate Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs SelfActualization Ego Needs Belongingness Safety Physiological Learning • A change in behavior caused by information or experience • Behavior learning theories assume learning takes place as the result of connections formed between events • Cognitive learning occurs when consumers make a connection between ideas or by observing things in their environment Attitudes • A lasting evaluation of a person, object, or issue • 3 components of attitudes – affect – cognition – behavior Personality • The set of unique psychological characteristics that consistently influences the way a person responds to situations in the environment – Innovativeness – Self-confidence – Sociability Family Life Cycle • Related to age groups, our purchases also depend on our current position in the family life cycle – stages through which family members pass as they grow older Lifestyles • Pattern of living that determines how people choose to spend their time, money, energy and reflects their values, tastes, and preferences • Expressed through preferences for sports activities, music interests, and political opinions • Psychographics is the segmentation tool used to group consumers according to AIOs SRI’s VALS Descriptions Situational Influences • Physical Environment – arousal – pleasure • Time – time poverty Social Influences • • • • Culture and Subcultures Social Class Group Behavior and Reference Groups Opinion Leaders Cultures and Subcultures • Culture is the values, beliefs, customs, and tastes produced and valued by a group of people • A subculture is a group coexisting with other groups in a larger culture whose members share a distinctive set of beliefs or characteristics Social Class • Social class is the overall rank of people in a society • People in the same class tend to have similar occupations, similar income levels, share common tastes in clothes, decorating styles, and leisure activities. They may share political and religious beliefs. Reference Groups • A reference group is a set of people a consumer wants to please or imitate • The “group” can be composed of one person, a few people, or many people. They may be people you know or don’t know – Conformity is at work when people change as a reaction to real or imagined group pressure – Sex roles are society’s expectations regarding appropriate attitudes, behaviors, and appearances for men and women Opinion Leaders • A person who influences others’ attitudes or behaviors because they are perceived as possessing expertise about the product