* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Short Communication Highly sensitive detection of cancer cells
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
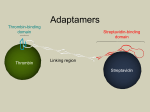
Short Communication Highly sensitive detection of cancer cells based on the DNA barcode assay and micro-capillary electrophoretic analysis Soyi Chung, Minkyung Cho, Jae Hwan Jung, and Tae Seok Seo* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (BK21 Program), Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701, Republic of Korea * Correspondence: Professor Tae Seok Seo, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (BK21 Program), Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), 291 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 305-701, Korea, E-mail: [email protected], Fax: +82-42-350-3933 Reagents DMEM, leibovitz’s (L-15 medium), 0.25% trypsin-EDTA, fetal bovine serum (FBS), and penicillin streptomycin were obtained from Gibco by Life Technologies (Grand Island, NY, USA). Magnetic particles (Dynabeads® MyOne™ Streptavidin T1, diameter 1 μm and Dynabeads® M-280 Tosylactivated, diameter 2.8 μm) were purchased from Invitrogen™ by Life Technologies (Oslo, Norway). Polystyrene particle (ProActive® Streptavidin Coated Microspheres, diameter 1 μm) was supplied by Bangs Laboratories, Inc. (Fishers, IN, USA). EZ-Link™ Sulfo-NHS-LC Biotinylation kit was obtained from Thermo Scientific (Rockford, IL, USA) to label monoclonal antibodies with biotins. Monoclonal epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) antibody and biotinylated polyclonal EpCAM antibody were purchased from Millipore Corporation (#MAB4444, Temecula, CA, USA) and R&D systems (BAF960, Minneapolis, MN, USA), respectively. Biotinylated polyclonal CDX2 was purchased from Bioss Inc. (bs-1620R-Biotin, Boston, MA, USA). Oligonucleotides were synthesized by Bioneer Corporation (Seoul, Korea) or Neoprobe (Daejeon, Korea). PBS powder and boric acid were supplied by Sigma Aldrich (St.Louis, MO, USA) and hydroxyl PEG Biotin (BiotinPEB-OH) with 2000 molecular weight was obtained from Nanocs Inc. (Boston, MA, USA). Cell culture Breast carcinoma cell lines MCF-7, and colorectal carcinoma cell lines SW620 were used as replacement of circulating tumor cells. All cell lines were purchased from Korean Cell Line Bank (KCLB, Seoul, Korea). MCF-7 was cultured using DMEM while SW620 was cultured in leibovitz’s (L-15 medium). Culture media were supplemented with 10% FBS, and 1% penicillin streptomycin. The cell lines were grown as an adherent monolayer in a T75 culture flask and incubated at 37°C under 5 % CO2 and 90% humidity conditions. We changed cell media for every 2 to 3 days. The cell lines were washed by a PBS solution and detached by 2 mL of 0.25% trypsin-EDTA at 37°C and 5 % CO2 incubation for 3 min, followed by centrifugation of 1300 rpm for 3 min. The cells were resuspended in the culture media and used for the cell detection experiment. Synthesis of magnetic particle probes Two types of magnetic particle probes were synthesized; anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibody labeled MMPs (anti-EpCAM MMPs) and 15 bp and 45 bp bracket ladder DNA labeled MMPs (15 bp MMPs and 45 bp MMPs). Anti-EpCAM MMPs were synthesized by covering the monoclonal antibody on the surface of the streptavidin coated magnetic particles. To prepare anti-EpCAM MMPs, monoclonal EpCAM antibodies were first biotinylated using a biotinylation kit according to manufacturer’s protocol. Then, the biotinylated monoclonal antibodies were linked to the streptavidin coated magnetic particles (Dynabeads® MyOne™ Streptavidin T1) using a recommended protocol. Briefly, 100 μL of the micro-magnetic particle (MMP) solution containing about 7 to 10 108 beads (approximately 1 mg) was washed three times with a 0.01 M PBS buffer. The tube containing the magnetic particle solution was placed in a magnet holder for 2 min and the supernatant was discarded. The resulting magnetic pellet was resupended with 20 μg of biotinylated monoclonal antibodies in a 0.01 M PBS buffer for 30 min at room temperature using a Dynabeads® Sample Mixer. After the incubation, the antibody conjugated MMPs were placed on an external magnet and washed two times. Subsequently, the MMPs were incubated for 30 min in a 0.032 mg/mL hydroxyl PEG Biotin (Biotin-PEG-OH) solution to block the non-specific binding of biomolecules on the surface of MMPs. The magnetic separation step was repeated twice to remove the unreacted Biotin-PEG-OH. Finally, the magnetic probes were resuspended in a 1 mL 0.01 M PBS buffer and stored at 4 °C prior to use. The coupling efficiency was calculated to be 90% based on the UV absorbance at 280 nm before and after the conjugation reaction. In addition, 15 bp MMPs and 45 bp MMPs were synthesized to conjugate the double strand DNA over the surface of tosyl magnetic particles. Tosyl-activated magnetic beads (Dynabeads® M-280 Tosyl-activated) were linked to the amine-functionalized double stranded bracket ladder DNAs (15 bp and 45 bp) according to the previously reported protocol. [1] 100 μL of a tosyl micro-magnetic particle (tosyl MMP) solution (2 108 beads, ~3 mg) were washed three times with 1 mL of a 0.1 M borate buffer. The resulting solution was resuspended with the double stranded DNA solution. Complementary single stranded DNAs (see Table S1) were hybridized by denaturing at 95 °C for 1 min followed by gradient cooling of 0.1 °C/s down to 25 °C. The conjugation of the amino-functional group of the double stranded DNA to the tosyl group of the tosyl MMPs was carried out at 37 °C for 48 h under vortex. The double stranded DNA conjugated tosyl MMPs were then washed twice time with a 0.01 M PBS. Then, the tosyl MMPs were passivated by adding 1 mL of a 0.5 % BSA solution at 37 °C for 4 h. The tosyl MMPs were magnetically separated and washed with a 0.01 M twice. Eventually, the tosyl MMPs were resuspended in 1 mL of a 0.01 M PBS buffer and stored at 4 °C prior to use. Synthesis of polystyrene particle probes In order to prepare anti-EpCAM polyclonal antibody and 20 bp barcode DNA labeled polystyrene microparticles (anti-EpCAM & 20 bp PMPs) and anti-CDX2 polyclonal antibody and 30 bp barcode DNA labeled PMPs (anti-CDX2 & 30 bp PMPs), coupling chemistry between streptavidin and biotin was employed. 200 μL of an aqueous streptavidin coated PMP (about 2 mg) solution was washed by 1 mL of a 0.01 M PBS buffer under the centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 3 min and the supernatant was removed. The resulting polystyrene pellet was resuspended with 60 μg of biotinylated polyclonal antibodies in a 0.01 M PBS buffer at room temperature for 30 min using a Dynabeads® Sample Mixer. After the incubation, a washing step was repeated three times with 1 mL of a 0.01 M PBS solution and the resulting pellet was resuspended with a double stranded biobarcode DNA solution. FAM labeled single stranded DNAs were hybridized with biotin labeled DNAs (see Table S1), to form the FAM and biotin labeled double stranded DNAs. Hybridization was conducted by denaturing at 95 °C for 1 min followed by gradient cooling of 0.1 °C/s down to 25 °C. The DNA solution was incubated with the polyclonal antibody coated PMPs for 30 min to conjugate the double stranded biobarcode DNAs to the PMPs. Conjugation efficiency was almost 100% due to the rapid and strong biotin and streptavidin interaction. The antibody and DNA modified PMPs were washed twice under the centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 3 min. The synthesized anti-EpCAM & 20 bp PMPs and anti-CDX2 & 30 bp PMPs were passivated by adding 1 mL of a 0.032 mg/mL PEG solution, followed by the washing step using the centrifugation at 13000 rpm for 3 min. Finally, the produced PMPs were resuspended in 1 mL of a 0.01 M PBS buffer and stored at 4 °C in a dark container to reduce photobleaching of the fluorophore. Table S1. Information of DNA biobarcode sequences Sequence (5’ 3’) Name Amine – ACGTGGGGCACACAG 15bp FAM – CTGTGTGCCCCACGT Biotin – GAGGTACATCGAGGTAAGCA 20bp FAM – TGCTTACCTCGATGTACCTC Biotin - ATAAGAAACAACTAATACCACATCATCCAT 30bp 45bp FAM - ATGGATGATGTGGTATTAGTTGTTTCTTAT Amine - TTAATTACAAATTCATACAATTTTTCAATACTAATTAACATATCG FAM - CGATATGTTAATTAGTATTGAAAAATTGTATGAATTTGTAATTAA Table S2. Calculation of relative elution time ratio of barcode DNAs 15 bp 20 bp 30 bp 45 bp Absolute elution time (Top panel) 109.394 s 113.574 s 123.456 s 134.883 s * Relative elution time ratio 0.000 0.164 0.552 1.000 Absolute elution time (Middle panel) 99.932 s 103.707 s 123.284 s * Relative elution time ratio 0.000 0.162 1.000 Absolute elution time (Bottom panel) 95.664 s 107.850 s 117.887 s * Relative elution time ratio 0.000 0.549 1.000 * Calculation = ( Elution time between a sample and a 15 bp peak) / ( Elution time between a 45 bp peak and a 15 bp peak) References : [1] Hill, H.D. and C.A. Mirkin, Nat Protoc 2006, 1, 324-336.










![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008791587_1-e65c6aed4cb40504aeeddda921f62bfc-150x150.png)