* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The World Wide Web
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
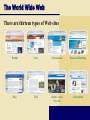
The Internet and World Wide Web Communications What are computer communications? Process in which two or more computers or devices transfer data, instructions, and information p. 460 Fig. 9-1 Networks What is a network? Collection of computers and devices connected via communications devices and transmission media p. 469 Fig. 9-9 The Internet What are some services found on the Internet? p. 68-69 Fig. 2-1 The Internet The Internet is a worldwide collection of networks that links millions of businesses, government agencies, educational institutions, and individuals History of the Internet How did the Internet originate? ARPANET Goal: To allow scientists at different locations to share information p. 69 Networking project by Pentagon’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) Became functional September 1969 Goal: To function if part of network were disabled History of the Internet How has the Internet grown? Today More than one billion host nodes 1984 More than 1,000 host nodes 1969 Four host nodes p. 69 Internet Hosts History of the Internet Who controls the Internet? No one — it is a public, cooperative, and independent network Several organizations set standards c c World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Oversees research, sets standards and guidelines Mission is to contribute to the growth of the Web Nearly 400 organizations around the world are members of the W3C Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 2, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click W3C below Chapter 2 p. 70 t Uses of Computer Communications What are wireless Internet access points and cybercafés? Wireless Internet access point allows wireless connection to Internet in public location 3G network Cybercafé is coffee house that provides computers with Internet access p. 464-465 Fig. 9-4 How the Internet Works What is a domain name? Text version of Internet protocol (IP) address Number that uniquely identifies each computer or device connected to Internet p. 73 - 74 Figs. 2-4 – 2-5 The World Wide Web What is the World Wide Web (WWW)? A worldwide collection of electronic documents Also called the Web Each electronic document is called a Web page Can contain text, graphics, audio, video, and built-in connections A Web site is a collection of related Web pages p. 75 The World Wide Web What is a Web browser? Program that allows you to view Web pages Microsoft Internet Explorer Opera p. 75 Firefox Netscape Safari The World Wide Web What is a search engine? Program used to find Web sites and Web pages by entering words or phrases called search text Also called a keyword p. 78 – 80 Fig. 2-10 The World Wide Web There are thirteen types of Web sites Portal News Informational Business/Marketing Blog Wiki Online Social Network Educational The World Wide Web Entertainment Advocacy Content Aggregator Web Application Personal The World Wide Web What are the guidelines for evaluating the value of a Web site? Affiliation Audience Currency p. 84 Fig. 2-15 Authority Design Content Objectivity t Netiquette What is netiquette? Code of acceptable behaviors users should follow while on the Internet Golden Rule: Treat others as you would like them to treat you. p. 100 First Web Page