* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System: Organization and Tissues
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
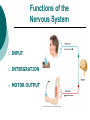
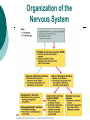
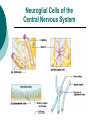
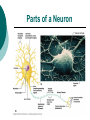
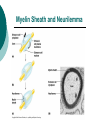
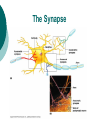
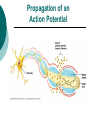
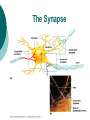
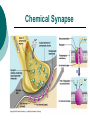
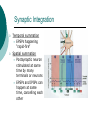
The Nervous System: Organization and Tissues Chapter 11 Functions of the Nervous System INPUT INTERGRATION MOTOR OUTPUT Organization of the Nervous System Histology of the Nervous System Neuroglial cells Neurons Neuroglial Cells of the Central Nervous System Neuroglial Cells of the Peripheral Nervous System Neurons Characteristics Excitable Longevity High Metabolic Rate Sometimes Large Amitotic May Regenerate Parts of a Neuron Myelin Sheath and Neurilemma Structural Classification of Neurons Functional Classification of Neurons Neurophysiology Electrical currents correspond to the flow ions across cellular membranes Ion channels allow the flow of ions into and out of the cell Passive, or leakage, channels Active, or gated, channels Gated Ion Channels Resting Membrane Potential The Synapse Generating an Nerve Impulse Generating an Nerve Impulse Propagation of an Action Potential Propagation of an Action Potential The Synapse Electrical Synapse Chemical Synapse Postsynaptic Potentials Exciatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) Chemically gated, bring neuron closer to AP threshhold Used to stimulate axon hillock Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP) Hyperpolarizes, reduces ability to generate AP Synaptic Integration Temporal summation EPSPs happening “rapid-fire” Spatial summation Postsynaptic neuron stimulated at same time by many terminals or neurons EPSPs and IPSPs can happen at same time, cancelling each other Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Biogenic Amines Dopamine Norepinephrine Epinephrine Serotonin Histamine ATP Dissolved Gases Amino Acids GABA Glutamate Glycine Aspartate Peptides Endorphins Somatostatin Cholecystokinin