* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Producing offspring by the joining of sex cells.
Survey
Document related concepts
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
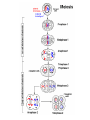
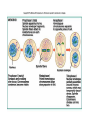
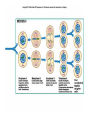
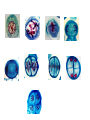
Differences • Plant: Plant cell mitosis is similar to animal cell mitosis, but there are differences. – Plant cells form spindle fibers during mitosis but do not have centrioles. – A structure called a cell plate forms between the two new nuclei. • New cell walls forms along the cell plate, then, a new cell membrane develops inside the cell walls. Living Things Reproduce All living things reproduce in one of the following ways: Asexual reproduction - Producing offspring without the use of gametes. BOP: Give two examplesSexual reproduction - Producing offspring by the joining of sex cells. • Fertilization: is a type of sexual reproduction where there is a fusion of male (sperm) and female (egg) sex cells. • Gene: A gene is a segment of DNA that controls the protein production and the cell cycle. Meiosis The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells-egg & sperm. Meiosis takes place in 5 stages, stages 2 & 4 have 4 phases during each stage. Stage 1: Interphase Stage 2: Meiosis I Stage 3: Cytokinesis I Stage 4: Meiosis II Stage 5: Cytokinesis II Stage 1: Interphase The cell grows to its mature size. The DNA in the cell makes a copy of itself. 2 cylindrical structures called centrioles are also copied. • Stage 2: Meiosis I (there are four phases) – Prophase I: • Chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form 23 chromosome pairs. • Centrioles move to opposite sides of the nucleus. • Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell. • Nuclear envelope breaks down. – Metaphase I: • Chromosome pairs line up across the center of the cell. • Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers. – Anaphase I: • • • • Centromere’s split. The chromosome pairs separate in half. Each chromosome pair is pulled into different half of cell. Cell stretches out as the opposite ends are pushed apart. – Telophase I: • • • • Cytoplasm divides. Cell splits. A new cell membrane forms around the newly created cells. At the end of Telophase I, 2 cells have been created. • Stage 3: Cytokinesis I – The cell divides into 2 new cells. • Stage 4: Meiosis II – Prophase II: • Centrioles move to opposite sides of the nucleus. • Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell. – Metaphase II: • Chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. • Each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere. – Anaphase II: • The centromere split. • The 2 chromatids separate. – Chromatid: ½ of a chromosome • 1 chromatid is drawn by its spindle fiber to 1 end of the cell. • The other chromatid moves to the opposite end. • Cell stretches out as the opposite ends are pushed apart. – Telophase II • Chromosomes begin to stretch out & lose their rod like appearance. • A new nuclear envelope forms around each region of chromosomes. • Stage 5: Cytokinesis II • The cytoplasm divides. • 4 new cell membranes form around the 4 new cells. • The new cells have ½ of the chromosomes found in regular body cells. Video: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sites/dl/free/0072437316/120074/bi o19.swf::Stages%20of%20Meiosis References: CMAPP http://www.citruscollege.edu/lc/archive/biology/Pages/Chapter09-Rabitoy.aspx