* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download List the ways that diseases are transmitted from one person to
History of biological warfare wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
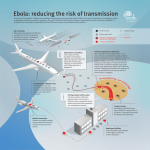
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Lesson 2.3 Infectious Spread Simulation Worksheet ID# _________________________________________________ Date: ______ Sec: ______ Infectious Disease Simulation Introduction: An infectious disease is any disease caused by microbes that can be spread from one person to another. Microbes include bacteria viruses, and other agents such as parasites. This activity will simulate the spread of an infectious disease. A simulation is a simplified demonstration of a real biological process. Our simulation will show how an infectious disease can spread from one infected person to other people, who in turn infect others. Procedure: 1. Your teacher will give everyone a container filled with a clear solution. This solution represents your bodily fluids. Only one person in the class will have a cup that has been “infected”. 2. In this part of the activity, you will interact with THREE other students. Watch teacher for instructions. List in order the three people you interacted with: 1st : ______________________ 2nd: ____________________ 3rd: ___________________ Estimate how many people you think will be infected in the class. ________ 3. Your teacher will come around and put an “infection indicator” in your container. If you have exchanged solutions with the original infected person or someone else after they became infected, you are now infected and your solution will turn pink. If you have not exchanged solutions with anyone who was infected, your solution will not turn color. Next, your teacher will ask everyone who is infected to raise their hand. How many people were infected? ________ 4. All infected individuals should their name and the three people that they interacted with write on the board in order to determine whom they contracted the infection from. As a class decide if you can tell who started this epidemic. Lesson 2.3 Infectious Spread Simulation Worksheet ID# _________________________________________________ Date: ______ Sec: ______ Infectious Disease Simulation Analysis: 1. In the space provided below complete a patient zero tree. Can you tell who started the spread of ‘infection’ within your class? Your name 1st interaction 2nd interaction 3rd interaction 2. The spread of the disease in our simulation was very rapid. Multiple people were infected within a few minutes. In real life, infections do not spread as rapidly as in this simulation. Why is the spread of infections slower in real life? Lesson 2.3 Infectious Spread Simulation Worksheet 3. In addition to exposure to microbes, what other factors might influence your risk of getting an infectious disease; for example, what defensive barriers might your body use to prevent infection? 4. Lets say that the spread activity is depicting the Flu (H1N1). How would giving half of the class a flu vaccine change the rate of spread? Estimate the number of people that would be infected. Why?