* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - MRS. ANTILLA`S ROOM
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
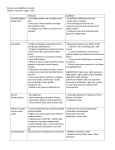
Introduction to Hinduism and Buddhism Hinduism Beginnings. Initially Aryans and non-Aryans followed separate religions Eventual blending of worship resulted in Thousands of common gods Made people question the world, their place in it, and basic injustices Hindu practices develop over a long time span Marriage next to a sacred fire, reciting the Vedas Scholars tried to organize Hinduism many times but there is no one founder or set of beliefs 3 Origins of Hinduism Hindus common world view includes liberating the soul from illusions, disappointments, and mistakes. Basic Beliefs Teachers make distinctions between the atman (individual soul) and the Brahman (the world collective soul) Moksha - a state of perfect understanding of all things After you fully understand the relationship you can be released from life in this world Idea of reincarnation (reborn until Moksha is achieved) Karma Karma determines the caste you are reborn into depending on good or bad deeds in your life If good you could be a Brahmin, warrior or merchant. If bad a woman, a laborer, or an untouchable. 6 Changes in Hinduism Brahman is sometimes seen as having the personality of 3 gods: Brahma the creator, Vishnu the protector, and Shiva the destroyer Brahma faded away a bit ad a great mother goddess grew in popularity Free to choose the deity they worship Often follows family lines Also free to choose the right path to achieve Moksha; right thinking, right action, or religious devotion Beginnings of Buddhism Siddhartha Guatama, the founder of Buddhism, born in the foothills of the Himalayas Quest to see outside world As a baby he depicted the marks of a great man Saw old age, sickness, death, and a peaceful religious man Went on a spiritual journey to try to end suffering (sought enlightenment) Spent 49 days fasting before he determined where life’s suffering originated from Four Noble Truths 1. Everything in life is suffering and sorrow 2. The cause of all suffering is people’s selfish desire for temporary pleasures of this world 3. The way to end all suffering is to end all desire 4. The way to end desire and attain enlightenment is to follow the eightfold path a middle way between desire and selfdenial The Eightfold Path Those seeking enlightenment had to master each step one at a time The only way to achieve nirvana Belief in reincarnation, and also that the world is created and destroyed repeatedly Rejected many Hindu gods and the caste system Religious Community Because of the rejection of the caste system many early followers were lower class people Monks and nuns took vows of poverty and could not marry as they did missionary work