* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter One
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
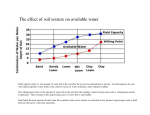
Chapter One The Importance of Soil Video The Importance of Soil Additional acreage is lost due to urbanization or degradation . Soil is a nonrenewable resource The Importance of Soil Most of the time we take soil for granted. Soil is a very thin and often fragile layer of life supporting material. The Importance of Soil What does living things need? – Proper temperature – Oxygen – Water – Carbon – Other nutrients – These factors are exchanged in the soil that allow elements to be recycled rather than lost The Importance of Soil Oxygen: – Plant roots need oxygen to grow. – Gases will pass in and out of the soil to supply the oxygen for the roots The Importance of Soil – Temperature Plants will grow best in certain soil temperature ranges. Most plants will root in temperature around 40-50 degrees F. Water: – Seldom stays in one place The Importance of Soil Carbon: – Plant leaves collect sunlight to use the energy in the process of photosynthesis. – Which involves converting atmosphere carbon to biological carbon – Atmosphere carbon = carbon dioxide – Biological carbon = simple sugars The Importance of Soil Nutrients : – Plant nutrients are chemicals a plant needs to grow. – There are two types of nutrients cycles Nitrogen cycle Mineral cycle The Importance of Soil Nitrogen: – Comes directly from the atmosphere where it occurs as a gas that plants cannot use. 4 Needs of Soil There are four needs of the soil – Anchorage – Water – Oxygen – Nutrients 4 Needs of Soil Anchorage: – This is where plants grow freely and are firmly supported or anchored so they can grow to reach the sunlight. – Water: – Soil will provide the plants with all the water the plant needs – Roots are the best water absorbing body . 4 Needs of Soil Oxygen: – All creature even plants need oxygen. Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis but consume it during respiration. 4 Needs of Soil Nutrients: – There are 16 nutrients usually considered to be needed for plants. – Plants obtain 13 of the 16 nutrients from the soil itself. – Other nutrients come from Air and water. Carbon Oxygen hydrogen 3 phase system What is soil Matrix? – It is the arrangement of solid particles and pore spaces which consists of three phases of solid , liquid, and gases. 3 phase system The ideal Soil Type: – 50% solid material 45 % mineral particles 5% organic matter – 25% water – 25% gases 3 phase system Root Growth: – Water reaches the root by two ways either water flows toward the root Or the root grows into moist soil Soil Particles Sand: .05-2mm Silt: .002-.05 mm Clay: <.002 mm Sand .05-2mm Sand drains easily = POOR ABILITY TO RETAIN MOISTURE Little chemical activity = LITTLE NUTRIENT BONDING Silt .002-.05mm Able to hold lots of water and gives water to plants easily Little chemical activity = LITTLE NUTRIENT BONDING May compact under heavy traffic = poor air and water movement Clay <.002mm Water adheres very well to clay = HIGH ABILITY TO RETAIN MOISTURE – But can hold water so tightly plants can’t get it Very chemically active = GOOD NUTRIENT BONDING Soil Texture Ribbon Test Used to determine what particles your soil is made up of Loam- a fertile soil of clay and sand containing humus. Ribbon test Video Soil Texture Triangle Video