* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
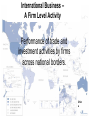
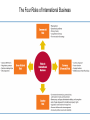
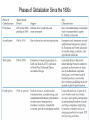
1.Introduction to International Business International Business Strategy Management & the New Realities by Cavusgil, Knight and Riesenberger FM : Anis Gunawan,MM [email protected] International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities 5. Functional Area excellence 4. Entering and operating in International Markets. 3.Strategy and opportunity assessment 2. The environment of International Business 1. Foundation concepts of International business International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities International Business – A Firm Level Activity Performance of trade and investment activities by firms across national borders. Chin a The Nature of International Business 1. All value-adding activities including sourcing, manufacturing, and marketing, can be performed in international locations 2. The subject of cross-border trade can be products, services, capital, technology, know how, and labor 3. Firms internationalize through exporting, foreign direct investment, licensing, franchising, and collaborative ventures International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Nafta International Trade Exchange of products and services across national borders; typically through exporting and importing. I&Evideos\Indo ex International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Exporting Sale of products or services to customers located abroad, from a base in the home country or a third country. Export International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Importing or Global Sourcing Procurement of products or services from suppliers located abroad for consumption in the home country or a third country. International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Comparing the Growth Rates of World GDP and World Exports • • • • Dramatic Growth of FDI Since the 1980s September 11, 2001 interrupted FDI inflows with the worldwide panic that ensued following the terrorist attacks in the United States. Developed economies = Australia, Canada, Japan, the United States, and most countries in Western Europe. Developing economies = Parts of Africa, Asia, and Latin America. Of particular significance is the growth of FDI into developing economies despite widespread poverty and less investment capital than advanced economies. The improved lives of billions are directly linked to world trade and investment. International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Inflows into World Regions (in Billions of U.S. Dollars per Year) Leading Countries in International Services Trade Service Industry Sectors That Are Rapidly Internationalizing The Four Risks of International Business Geographic Location of Multinational Enterprises, 2006 Globalization of Markets and the Internationalization of the Firm International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Globalization of Markets: A Macro Concept • Two mega trends have altered the international business landscape: the globalization of markets or economies and technological advances. • Market globalization is a broad term referring to the interconnectedness of national economies and the growing interdependence of buyers, producers, suppliers, and governments in different countries. • Globalization allows firms to view the world as one large marketplace for goods, services, capital, labor, and knowledge. International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Phases of Globalization 1st Phase: 1830, peaking around 1880 Aided by railroads, ocean transport; resulting in the rise of manufacturing and trading companies 2nd Phase: 1900, peaking late 1920s Fueled by electricity and steel; early MNEs 3rd Phase: 1948, peaking around 1970 GATT, end of WW II, Marshall Plan; gradual reduction of barriers to trade 4th Phase: 1980, peaking around 1997 Fueled by Internet and other technologies: rapid liberalization in Emerging Markets… Phases of Globalization Since the 1800s The Death of Distance International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Airbus 380 The Drivers and Consequences of Market Globalization Information Technology • The cost of computer processing fell by 30 percent per year during the past two decades, and continues to fall. • The remarkable performance of the U.S. economy in the 1990s was due in large part to aggressive integration of IT into firms’ value-chain activities, which accounted for 45 percent of total business investments at the time. • IT alters industry structure, changes the rules of competition, and creates new ways to outperform rivals, thus forming the basis for competitive advantage. • Data, information, and experience can be readily shared via collaboration software within a multinational company. • Smaller firms can leverage IT to design and produce customized products that can be targeted to narrow, cross-national niches. • The impact of IT on our daily lives has been profound- cell phones, Google, Yahoo, etc. International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities Declining Cost of Global Communication and Growing Number of Internet Users Examples of How Firms Value Chain Activities Can Be Internationalized Chevy