* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download white blood cells - LAHS | Life Science
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
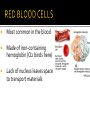
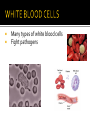
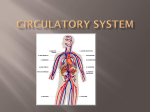
pp 940-942 • The average adult has about FIVE liters of blood inside of their body, which makes up 7-8% of their body weight. • There are about one billion red blood cells in two to three drops of blood. • For every 600 red blood cells, there are about 40 platelets and one white cell. Transports nutrients, O2, CO2, & waste Defends the body against disease plasma: liquid medium red blood cells (erythrocytes): transport CO2 and O2 gas For every 600 red blood cells, there are about 40 platelets and one white blood cell. white blood cells (leukocytes): defend against disease platelets: form blood clots For every 600 red blood cells, there are about 40 platelets and one white blood cell. Made of 90% water, sugar, salts, amino acids, vitamins, minerals Most common in the blood Made of iron-containing hemoglobin (O2 binds here) Lack of nucleus leaves space to transport materials Transports O2 to cells in body and picks up CO2 waste Average lifespan 100 – 120 days Many types of white blood cells Fight pathogens Partial cells formed in bone marrow Stimulate blood clotting Steps to blood clotting Platelets congregate at damaged site 2. Clotting factors are released from platelets 3. Factors create chemical reaction that releases fibrin (long, stick, protein chain) 4. Creates Clot (net traps red blood cells and hardens to create a scab) 1.