* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurosis - sechenov.ru
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Conditioned place preference wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Impulsivity wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Memory disorder wikipedia , lookup
Munchausen by Internet wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorders and memory wikipedia , lookup
Claustrophobia wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
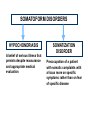
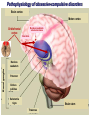
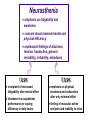
The State Education Institution of Higher Professional Training The First Sechenov Moscow State Medical University under Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Department of Pathophysiology Neurosis Lecture presentation Professor Pirozhkov S.V. 2015-2016 education year MODELING OF NEUROSIS WITH PREDOMINANCE OF INHIBITION ● Use of conditioned stimulus of extreme intensity ● Exposure to simultaneous effects of several strong stimuli ● Exposure to the effect of complex conditioned or unusual stimuli MODELING OF NEUROSIS WITH PREDOMINANCE OF EXCITATION ● Undue delays in providing food reinforcement ● Complex discrimination tasks ● The need to develop several different discriminations in one experimental session MODELING OF NEUROSIS WITH A PATHOLOGICAL LABILITY OF THE MAIN NERVOUS PROCESSES (EXCITATION AND INHIBITION) ● Sudden change in the meaning of the conditioned stimulus ● Abrupt change of the habitual environment ● Collision of different reflexes (for example, alimentary and defensive) Neurosis – ● typical form of disorder of the higher nervous functions ● that is potentially reversible ● caused by psychological stress and ● characterized by disorders of mood, emotions, behavior, mentation, and general decrease of well-being without degradation of a personality or loss of judgment ● often accompanied by autonomous symptoms and, in some types, by disorders of sensation and locomotion FACTORS THAT FOSTER INADEQUATE ADAPTATION IN NEUROTIC CONFLICT ● Faulty upbringing ● Negative experiences in early childhood or formative years of life ● Personal traits ● Hereditary predisposition ● Unfavourable circumstances, hard conditions of life THE CORRESPODENCE OF CLASSICAL NEUROSES TO MODERN NOSOLOGICAL FORMS ACCORDING TO ICD-10 F40. Phobic disorders (agoraphobia, social phobia etc.) Compulsion neurosis F42. Obsessive-compulsive disorders F44. Dissociative (conversion) disorders Hysteric neurosis F45. Somatoform disorders F48.0. Neurasthenia Neurasthenia DISSOCIATIVE (CONVERSION) DISORDERS Characteristic features: - sudden, temporary alteration in the integrative functions of consciousness - loss of memory or identity - deficit of voluntary motor and sensory function - these deficits are temporary, and not intentionally produced or simulated SOMATOFORM DISORDERS HYPOCHONDRIASIS A belief of serious illness that persists despite reassurance and appropriate medical evaluation SOMATIZATION DISORDER Preoccupation of a patient with somatic complaints with a focus more on specific symptoms rather than on fear of specific disease Common phobias: ● Fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia) ● Fear of blood ● Fear of flying ● Social phobia ● Agoraphobia Pathophysiology of obsessive-compulsive disorders Brain cortex Motor cortex Nucleus caudatum volume decrease Orbitofrontal cortex Alteration Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatum Putamen Globus pallidus Substantia nigra Brain stem Thalamus Neurasthenia ● emphasis on fatigability and weakness ● concern about lowered mental and physical efficiency ● unpleasant feelings of dizziness, tension, headaches, general instability, irritability, anhedonia I type: ● complaint of increased fatigability after mental effort ● decrease in occupational performance or coping efficiency in daily tasks II type: ● emphasis on physical weakness and exhaustion after only minimal effort ● feeling of muscular aches and pain and inability to relax