* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diagram of circuit
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
12 in 1 electrical experiment set in English
Manual for teachers
www.magicblock.co.kr
Introduction
12 in 1 electrical experiment set in English
An interest of science through experiments
A familiarity with science English
Science context in English is easy if students learn scientific words.
Students have the confidence, not only in science but also in
English, which is the base of their study in school.
www.magicblock.co.kr
This package offers these features
Features
Engaging and comprehensive science content
Experimental process design
Practice skill for the experimental activity
Final report in English
The English publication makes students be familiar with science English.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Contents & schedule
Chapter
Contents
Class
1
How to use this book
2
What is an atom?
3
A brief history of atomic theory
4
Periodic table of the elements
5
The basic theories of electricity
6
“12 in 1 electrical experiment set” activity guide
7
Activity 1. Static electricity
8
Activity 2. Conductors and insulators
9
Activity 3. Make a fan
5
10
Activity 4. Resistor
6
11
Activity 5. Diode
7
12
Activity 6. Make a light
13
Activity 7. Morse code machine
14
Activity 8. Light control alarm
9
15
Activity 9. Make a bell
10
16
Activity 10. Make a electromagnet
12
17
Activity 11. Make a motor
11
18
Activity 12. Solar power cell
12
www.magicblock.co.kr
1
2,3
4
8
Chapter 1. How to use this book
12 in 1 electrical experiment set in English
Set up the scientific method
Design procedures
Study the related theories
Final report
Science English will be a valuable study for students to be global leaders.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 1. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 2. What is an atom?
The smallest unit of matter is called an atom.
Atom
Nucleus = Proton + Neutron
Electrons
www.magicblock.co.kr
Model of a carbon atom
Chapter 2. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 3. A brief history of atomic theory
1913 : Niels Bohr (Danish physicis)
Electrons move in different orbits, or energy levels, around
the nucleus like planets orbit the sun.
Each energy level is located a specific distance from the
nucleus and contains a certain number of electrons.
Current atomic model
It is based on the Bohr model, except that electrons
orbit the nucleus in random paths. The regions where
they are most likely to be found are called "electron
clouds".
www.magicblock.co.kr
Solar system
Pluto
From its discovery in 1930 until 2006, Pluto was
considered the solar system's ninth planet.
However, many objects similar to Pluto which
orbits in irregular path were discovered in the
outer solar system in the late 20th and early 21st.
On August 24, 2006 the IAU (International Astronomical Union) excluded Pluto from
the solar system. As result, there are 8 planets in the solar system now.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 3. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 4. Periodic table of the elements
Periodic table
Name of element
Atomic symbol
Atomic number
Atomic mass
Number of electrons
In 1869, Russian chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev organized all the known elements into
a chart according to their properties.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Periodic table
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 4. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 5. The basic theories of electricity
History of electricity
Thales in BC 600 found static electricity by rubbing amber with cat's fur.
English physician, William Gilbert, in 1646 made a careful study of electricity
He named the electricity, in English word from [elektron] in Greek word
("of amber" or "like amber").
www.magicblock.co.kr
Definition of electricity
Electricity is a form of energy that can be carried by wires and is used for
heating and lighting, and to provide energy for machines.
www.magicblock.co.kr
AC & DC
AC
An alternating current (AC) is an electric current
whose direction reverses cyclically (+ - + -……).
The usual waveform of an AC is a sine wave.
It is the most efficient transmission of energy.
DC
Direct current (DC) is the constant flow of electric
charge. It is used mostly in the circuit to work.
Direct current is obtained from an alternating
current through a rectifier that allow current to
flow only in one direction.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Speed of electricity
The speed of electricity is much faster because the electrons moves as below
illustration.
The speed of electricity in a copper conductor is about 99.9% of the speed of light.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Circuit
Circuit is an electrical network which is an interconnection of electrical elements
such as resistors, condensers, transmission lines, voltage sources, and switches.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Conductor / Insulator
Conductor
A material contains movable
electric charges. Copper has
a high conductivity.
Insulator
A material resists the flow of
electric current. Materials
such as PET or Teflon are
very good electrical insulators.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Semiconductor
Semiconductor is a solid material that has electrical conductivity in between
a conductor and an insulator.
It can vary over that wide range either permanently or dynamically by
adding certain material.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Ohm’s law
All conductors contain electric charges which will move when an electric potential
difference (measured in volts) is applied across separate points on the material.
The rate of current is proportional to the voltage. (Ohm's law)
I
=
V
R
or
V = IR
I is the current, measured in amperes
V is the potential difference, measured in volts
R is the resistance, measured in ohms
www.magicblock.co.kr
Electric current
Electric current is the flow of electric charges. The electric charges may be either
electrons or ions. The SI unit of electric current intensity is the ampere.
For an electric current of 1 ampere, 1 coulomb of electric charge (which consists
of about 6.242×1018 electrons) drifts every second.
I (A) = Q / T
Q : the electric charge in coulombs
T : the time in seconds
www.magicblock.co.kr
Voltage
Voltage is the difference of electrical potential between two points of an electrical
or electronic circuit, expressed in volts (SI unit).
One volt is defined as the potential difference across a conductor when
a current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power.
The unit of SI is kg·m2·A-1·s-3, which can be equally represented as
one joule of energy per a coulomb of charges, J/C.
V = W / A = J / C = N ×m / A × s
= kg × m2 / A × s3
J = N × m = kg × m2 / s2,
where N is kg × m / s2
and
C=A×s
www.magicblock.co.kr
Watt, Joule
The watt (symbol: W) is the SI unit of energy, equal to one joule of energy per
second. Work is done at a rate of one watt when one ampere flows through a
potential difference of one volt.
1W = 1J / 1s
1W = 1A × 1V
1V = 1W / 1A = 1 J / 1A × 1s
One joule is the work done by a force of one Newton moving one
meter along the direction of the force.
This quantity is also denoted as a Newton meter with the symbol N·m.
1J = 1N × 1m = 1kg × m2 / s2
(see Newton's second law in the chapter 17)
Automobile engine : 25,000 watts (approximately 33.5 horsepower)
Incandescent light bulb : 25 to 100 watts
Fluorescent light : 5 to 30 watts
www.magicblock.co.kr
Electrical Resistance
The electrical resistance R of a material is given by ;
R=ρ
l
A
R is the electrical resistance of a specimen of the material.
(measured in ohms, Ω)
ρ is the electrical resistivity.
(measured in ohm meters, Ω·m)
l is the length of the piece of material.
(measured in meters, m)
A is the cross-sectional area of the
specimen .
(measured in square meters, m²)
www.magicblock.co.kr
Multiple prefix for science
www.magicblock.co.kr
The electric shock
The electric shock is happened when the current flows into your body.
Your body generally has about 400-2,000ohm(Ω),
1.5V of a battery : No damage.
220V of electricity : Dangerous
If AC 220V electric shock with
about 400 ohm at your wet
condition makes you very
dangerous from below calculation ;
I = V / R = 220 / 400 =
0.55A = 550mA
(very dangerous to you)
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 5. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 6. 12 in 1 electrical experiment set activity guide
www.magicblock.co.kr
12 kinds electrical experiments
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 7. Act(1) Static electricity
If two things have different charges, they attract, or pull toward each other.
If two things have the same charges, they repel, or push away from each other.
Rubbing the plastic plate with the cloth moved electrons from the cloth to the plate.
The plate had a negative static charge.
The neutral tissue paper was attracted to it.
When they touched, electrons slowly moved from the plastic plate to the paper.
Both objects had the same
negative charges, and the
paper was repelled.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Lightning
Lightning is a natural example of static discharge.
The initial charge separation is thought
to be associated with contact between
ice particles within storm clouds.
Visual phenomenon : flash
Audio phenomenon : thunder
The flash occurs because the air in the discharge channel is heated to such a high
temperature that it emits light.
The clap of thunder is the result of the shockwave created as the superheated air
rapidly expands.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 7. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
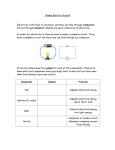
Chapter 8. Act(2) Conductors and insulators
A gap exists between spring connector ① and ② and will be connected to make
electricity flow in the circuit.
Conductor : Make circuit to flow electricity.
Insulator : Make circuit not to flow electricity.
Diagram of circuit
①
②
www.magicblock.co.kr
My experimental test
Conductor
They allow electricity to pass through easily.
Paperclip, cutting knife etc.
Insulator
Materials do not allow electricity to pass through easily.
Plastic plate, paper etc.
Test with other objects and fill out in the table below.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 8. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 9. Act(3) Make a fan (선풍기 만들기)
The main component of a fan is the
electric motor.
The motor begins to spin under the
interaction of the electric current
and magnetic field inside.
The fan blade attached to the
motor shaft converts this spinning
motion into airflow.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Diagram of circuit
Magnetic field
In physics, a magnetic field is a vector field that permeates space and which can
exert a magnetic force on moving electric charges and on magnetic dipoles.
The lines of magnetic
field can be seen
when iron filings are
in the presence of a
magnet.
The ends of magnet have the strong magnetic force.
자석의 양 끝단이 가장 강한 자석의 세기를 가진다.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Fleming’s left hand rule
Fleming's left hand rule for a electric motor shows the direction of the force
(motion) on a conductor carrying a current in a magnetic field.
The left hand is held with the thumb, index finger and middle finger mutually at
right angles as left figure.
The index finger represents the
direction of the magnetic field.
The middle finger represents the
direction of the current.
The thumb represents the direction
of the force or motion.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Fleming’s right hand rule
If you like to find the direction of force on the generator, you can use the
Fleming's right hand rule because it is reverse process.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Simple DC motor
STEP 1
When the coil is powered, a magnetic field is generated around the armature.
The left side of the armature is pushed away from the left magnet and drawn
toward the right, causing rotation.
STEP 2
The armature continues to rotate.
STEP 3
When the armature becomes
horizontally aligned, the
commutator reverses the
direction of current through the
coil, reversing the magnetic field.
The process then repeats.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 9. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 10. Act(4) Resistor
The fan spins faster without the resistor because a resistor "resists" the flow of
electric current.
The higher value of resistance (measured in ohms), the lower the current will be.
Diagram of circuit
www.magicblock.co.kr
Series and parallel resistors
Resistors in a parallel configuration,
each of them has the same potential
difference (voltage). To find their total
equivalent resistance (R):
The current through resistors in series
stays the same, but the voltage across
each resistor can be different.
To find their total resistance:
A resistor network that is a combination
of parallel and series can be calculated
for the total resistance:
www.magicblock.co.kr
Marking of resistor
Four-band identification is the most commonly used color-coding scheme on resistors.
The first two significant digits : the resistance value
The third : a power-of-ten multiplier (number of zeroes)
The fourth : the tolerance accuracy
The first band (green) : a value of 5
The second band (blue) : a value of 6,
and is counted as 56.
The third band (yellow) : a value of 104
The end band (red) : ± 2% tolerance accuracy.
It shows 560,000Ω ± 2% or 560kΩ ± 2%.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 10. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 11. Act(5) Diode
The diode has the property allowing the current to flow only in one direction,
Forward biased
The current can flow through the diode from its positive
side (called anode) to its negative side (called cathode).
Reverse biased
When the diode is connected in the opposite direction,
current can't flow through and the fan does not spin.
Diagram of circuit
Reverse biased
Forward biased
www.magicblock.co.kr
Diode
The directionality of current flow most diodes exhibit is sometime called the
rectifying property.
The most common function of a diode is to allow an electric current to pass in one
direction (the forward biased condition) and to block it in the opposite direction
(the reverse biased condition).
Polarity of diode
The line mark shows the cathode of diode.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Why is FM radio sound clear than AM radio sound?
AM radio uses Amplitude Modulation,
- Use Medium Frequency (MF: 0.3MHz to 3 MHz) radio spectrum.
- Transmissions are affected by interference from other sources of radio.
FM radio uses Frequency Modulation,
- FM is transmitted in the Very High Frequency (VHF: 30MHz to 300MHz).
- FM signal is not subject to interference in the same way as AM signals.
- VHF radio waves act more like light, traveling in straight lines,
hence the reception range is generally limited to about 70~150kms.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Frequency
Frequency is defined as a number of cycles, or periods, per unit time. In SI units,
the unit of frequency is hertz (Hz), named after German physicist, Heinrich Hertz.,
1Hz means that an event repeats once per second, 2Hz is twice per second.
Heart rate and musical tempo are measured in beats per minute (bpm).
Frequency of rotation is expressed as a number of revolutions per minute (rpm).
The period is usually denoted as T, and
is the reciprocal of the frequency f:
f = 1/T
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 11. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 12. Act(6) Make a light
LED (Light Emitting Diode) is an electronic device which emits light when
electric current passes through it.
- It has the same property as the diode that it allows current to pass
through in one direction only.
- It uses much less electricity than an ordinary light bulb.
- The color of the LED will depend on the type of material (semi-conductor)
used to make it.
Diagram of circuit
www.magicblock.co.kr
LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor diode that emits light when an
electric current is applied in the forward direction of the device,
-The color of the emitted light depends on the composition and condition
of the semiconducting material used.
- LED can be infrared, visible, or ultraviolet.
- Besides lighting, interesting applications include using UV-LEDs for
sterilization of water and disinfection of devices.
Polarity of LED
www.magicblock.co.kr
Wavelength of light
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 12. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 13. Act(7) Morse code machine
In 1836, Samuel Morse demonstrated the ability of a telegraph system to transmit
information over wires.
- The information was sent as series of electrical signals.
- Short signals are referred to as dits (represented as dots).
- Long signals are referred to as dahs (represented as dashes).
- With the advent of radio communications, an international version of
Morse code became widely used.
Typical Morse machine
Diagram of circuit
www.magicblock.co.kr
Morse Code Characters
www.magicblock.co.kr
Practice of Morse code
The most well-known usage of Morse code is for sending the distress signal: SOS.
The SOS signal is sent as:
--S
___
O
--S
Morse code relies on precise intervals of time between dits and dahs, between
letters, and between words. Here's a chart that shows these relations.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 13. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 14. Act(8) Light control alarm
The light sensor is an electronic component which changes its resistance with the
amount of light illuminated on it.
- When the light is bright, its resistance decreases and vice versa.
- Many electrical appliances and lighting make use of this component to function.
- For example, a street light will turn on automatically in the evening when the
street gets dark.
Diagram of circuit
www.magicblock.co.kr
Light
The speed of light in a vacuum is presently defined to be exactly 299,792,458m/s
(about 3×108m/s). The speed of light depends upon the nature of the medium in
which it is traveling. Its speed is lower in a transparent substance than in a vacuum.
- The modern theory that explains the nature of light includes the notion of "waveparticle duality" described by Albert Einstein in the early 1900s.
- Einstein asserted that the energy of a photon is proportional to its frequency.
- This theory states that light has both a particle nature and a wave nature.
- Einstein received the Nobel Prize in 1921 for his work, "the wave-particle duality
on photons".
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 14. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 15. Act(9) Make a bell
When the switch is pressed, the circuit closed and the current begins to flow
through the wire around the spool (solenoid).
- The metal rod gets magnetized and attracts the metal hammer arm.
Due to the movement of the arm, the hammer moves and strikes the bell and the
bell rings.
- The movement of the arm breaks the contact and the current stops flowing.
The electromagnet loses its magnetism and the arm returns back to its original
position.
- This completes the circuit once again and the action is repeated. As a result, the
hammer vibrates and the bell continues to ring as long as the switch is pressed.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Diagram of bell system
Diagram of circuit
www.magicblock.co.kr
The principle of maglev
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 15. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 16. Act(10) Make a electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is induced by the
flow of an electric current through a coil of wire.
- The strength of the electromagnet depends on the amount of electric current
and the number of turns of the coil.
- The higher the current and the more number of turns will make the
electromagnet more powerful.
- The magnetic field disappears when the flow of electricity is stopped.
Diagram of circuit
www.magicblock.co.kr
Permanent magnet and electromagnet
The difference between permanent magnet and electromagnet
www.magicblock.co.kr
Solenoid
The right hand grip rule is a physics principle applied to electric current passing
through a solenoid, resulting in a magnetic field.
When you wrap your right hand around the solenoid with your fingers in the
direction of the conventional current, your thumb points in the direction of the
magnetic north pole. (Fig. A)
Electricity passing through a straight wire:
The thumb points in the direction of the
conventional current (from positive to negative),
The other fingers point in the direction of the
magnetic field from north to south.(Fig. B)
Fig. A
www.magicblock.co.kr
Fig. B
Chapter 16. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 17. Act(11) Make a motor
When electric current passes through the coil (called "armature" of the motor), it
becomes an electromagnet.
When the red and black wires reach the stripped part of the coil, current flows,
forming an electromagnet.
- Since magnet pole of the same type
repels each other, the north of the
electromagnet is repelled by the north of
the magnet.
- This gives the coil a push, and it spins to
a position where the wires and the coil
breaks off, and the current ceases to flow.
- Inertia carries it around until the stripped
portion makes contact again.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Diagram of circuit
Newton’s laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws which provide relationships
between the forces acting on a body and the motion of the body.
The laws form the basis for classical physics and mechanics.
- Newton’s first law
(The principle of inertia)
- Newton’s second law
(F = ma)
- Newton’s third law
(action-reaction's principle)
www.magicblock.co.kr
Newton’s first law
The term "inertia" is more properly understood as a shorthand for "the principle of
inertia" as described by Newton in Newton's first law of motion,
"An object that is not subject
to any outside forces (friction
force etc.) moves at a
constant velocity.“
In even simpler terms, inertia
means" A body in motion
tends to remain in motion, a
body at rest tends to remain
at rest.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Newton’s second law
Mass as related to "inertia" of a body can be defined also by the formula:
F = ma
According to this formula, the greater the mass, the less the acceleration under
given force.
The Newton (N) is the unit of force derived in the SI system;
It is equal to the amount of force required to give a mass of one kilogram an
acceleration of one meter per second squared.
kg x m
1N
=
S2
1 N is the force of earth's gravity on an object with a mass of about
102g (1/9.8kg) (such as a small apple).
1kg on the surface of the earth weighs 9.8N. (1kg×9.8 m/s2=9.8 N)
www.magicblock.co.kr
Newton’s third law
Whenever a particle A exerts a force on another particle B,
B simultaneously exerts a force on A with the same magnitude in the opposite
direction, both forces acting along the same line.
This law is often simplified into the
sentence, "Every action has an equal
and opposite reaction.“
It is called
"action-reaction's principle“.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 17. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 18. Act(12) Solar power cell
Most solar cells in the solar panels are made from a crystalline substance called
silicon, one of the Earth's most common materials.
Solar cells are typically made by slicing a large crystal of silicon into thin wafers and
putting two separate wafers with different electrical properties together, along with
wires to enable electrons to travel between layers.
Diagram of circuit
When sunlight hits the wafers, electrons
naturally travel from one layer to the other
because of the different properties of each
layer, resulting in the release of electricity.
www.magicblock.co.kr
Photoelectric effect
The photoelectric effect is a quantum electronic phenomenon in which electrons are
emitted from matter after the absorption of energy from electromagnetic radiation
such as x-rays or visible light.
Diagram of circuit
Study of the photoelectric effect led to
important steps in understanding the
quantum nature of light and influenced the
formation of the concept of
"wave-particle duality".
www.magicblock.co.kr
Chapter 18. Science English Expression to Learn and Science English Tips
www.magicblock.co.kr