* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Vocab
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
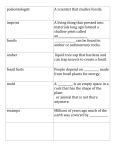
Evolution Evolution: a change with in a population of a species over time. Biological evolution: the change over time of living organisms. Charles Darwin: was a naturalist who proposed and provided scientific evidence that all species of life have evolved over time from common ancestors through the process he called natural selection. Selection Artificial selection: the breeding of plants and animals with desired traits to attempt to produce off spring with these same traits. Natural selection: survival of the fittest organisms that are the best adapted to their environment and the ones that will live long enough to reproduce and pass on their favorable adaptations. Selection Cont… Adaptation: a trait that increases the chances that an organism will survive and reproduce. Mutation: a random change to a gene that results in a new trait. Fossils Fossil: evidence of past life preserved in rock. Fossil record: the complete body of fossils that shows how species and ecosystems change over time. Extinction: The evolutionary termination of a species caused by the failure to reproduce and the death of all remaining members of the species; the natural failure to adapt to environmental change. Types of Fossils Trace fossil: a type of fossil that provides evidence of the activities of an organisms but not actual remains. Cast: a fossil that is a copy of an organisms shape, formed when minerals seep into a mold. Carbon Film: a type of fossil consisting of an extremely thin coating of carbon on a rock. Mold: a fossil formed when an organism buried in sediment dissolves leaving a hollow area. Index Fossils Index fossil: a fossil found in a narrow time range but widely distributed around the earth; used to date rock layers. Trilobite: a marine organism that is an example of an index fossil.