* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Exchange System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
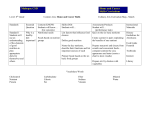
Module 2.5 Food Composition & The Exchange Lists By Jennifer Turley and Joan Thompson © 2013 Cengage Presentation Overview 1. Food Composition a. Chemical composition of food b. Use in diet planning & evaluation 2. Exchange List system a. Purpose b. Exchange Lists c. Use in diet planning & evaluation d. Sample diets Food Composition Food composition tables & databases provide the chemical composition of foods We will use the USDA nutrient databank for food composition values: http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/search/ Information on the chemical composition of foods can be attained by using the online search option or by downloading the free software database The Nutrient Data Laboratory There you can see a search option and an option to download software option. Food Composition Tables The chemical nutrient values are provided given a certain serving size of specific foods Chemical values in the USDA nutrient databank include: 1. Calories 2. Protein, Carbs & Fat (total and type of fatty acid) 3. Fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E & K) 4. Water soluble vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, folate, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, vitamin C) 5. Major minerals (Na, K, Cl, Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus) 6. Trace minerals (iron, zinc, iodine, selenium, etc) Chemical values are also given in some cases the types of amino acids and for phytochemicals (plant chemicals that are not essential nutrients but have many beneficial physiological effects in the human body when consumed from a variety of plant foods). Exchange List System Excellent tool for: 1. Meal planning 2. Calorie control 3. Meeting AMDRs and DRIs Exchange List System Created for diabetic diet/ meal planning Dietary carbohydrates levels can be planned to be compatible with insulin prescription Diet prescription meets standard dietary goals for health Exchange List System Portion sizes are based on: Grams of protein Grams of carbohydrate Grams of fat Total number of Calories (not nutrient content) The Exchange Lists 1. Starch (grains, cereals, pasta, breads, crackers, some snacks, starchy vegetables, dried beans, peas, and lentils) 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Fruit Non-starchy vegetables Milk Meat and meat substitutes Fat Other carbohydrates Free foods Combination foods The Exchange Lists Exchange Lists The detailed exchange lists provide the consumer with an idea of which foods in which quantities count for an exchange The prescribed exchanges are used up throughout the day Please see the detailed exchange lists appendix Example list Exchange Lists Example list Exchange Lists Example list Exchange Lists Summary Food Composition tables & database Show the chemical composition of food based on a specified food portion. Are used in diet planning & analysis Exchange Lists Are used in diet planning and evaluation Are based on grams of carbohydrate, protein & fat, as well as total Calories provided per food exchange References for this presentation are the same as those for this topic found in module 1 of the textbook