* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download survey of biochemistry - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
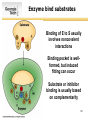
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
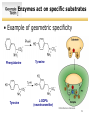
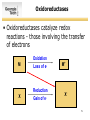
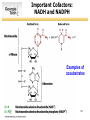
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Enzyme Catalysis 1 General Properties of Enzymes • High reaction rates – 106 to 1012 times faster than uncatalyzed reaction • Mild reaction conditions – Temp < 100°C – Atmospheric Pressure – pH near 7 • High reaction specificity • Capacity for regulation 2 Enzymes act on specific substrates • Example of geometric specificity Phenylalanine Tyrosine Tyrosine L-DOPA (neurotransmitter) 3 Classification of Enzymes 4 Oxidoreductases • Oxidoreductases catalyze redox reactions - those involving the transfer of electrons Oxidation M X Loss of e- Reduction Gain of e- M+ X- 5 Oxidoreductases 6 Transferases • Transferases catalyze the transfer of a specific group from one molecule to another. 7 Hydrolases • Hydrolases break down chemicals through the use of water. 8 Lyases • Cleave C-C, C-O, C-N, and other bonds by elimination, leaving double bonds or rings 9 Isomerases • Catalyze geometric or structural changes within a molecule 10 Ligases • Catalyze the joining of 2 molecules coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP or some similar triphosphate. 11 Enzyme bind substrates Binding of E to S usually involves noncovalent interactions Binding pocket is wellformed, but induced fitting can occur Substrate or inhibitor binding is usually based on complementarity 12 Types of Cofactors Holoenzyme: protein + its cofactor Apoenzyme: protein without its cofactor Prosthetic group: tightly bound cofactor that does not dissociate from the enzyme 13 Important Cofactors: NADH and NADPH Examples of cosubstrates 14 Thermodynamics: Energy for Reaction Chemistry 15 Thermodynamics: Energy for Reaction Chemistry 16 PRS 17 PRS • A chemical reaction can occur spontaneously if ∆G is: 1. 2. 3. 4. Positive Negative 0 ∆G does not relate to reaction spontaneity 18 PRS • Which best describes heme? 1. 2. 3. 4. Oxidoreductase Apoenzyme Prosthetic group Holoenzyme 19 Reminders • No office hours today - Mon, Jun 9 • Exams to be returned on Wed • Read Chapter 11 • Practice drawing structures – All 20 amino acids – All 5 nucleotides (A, T, G, C, U) – NADH and NADPH 20