* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resistance - XAMK Moodle
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Aluminum electrolytic capacitor wikipedia , lookup
Electrolytic capacitor wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor plague wikipedia , lookup
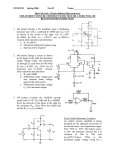
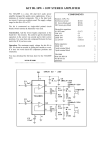
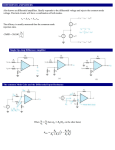
Resistance Natural feature of materials Metals are good conductors and non metal are insulators Voltage dependent resistors (VDR) Temperature dependent resistors (NTC or PTC resistors) l R A Typical resistivity Material Resistivity Material Resistivity Silver 1,64 E10-8 Nichrome 100E10-8 Copper 1,72E10-8 Silicon 2500 Aluminium 2,83E10-8 Paper 10E10 Iron 12,3E10-8 Mica 5E11 Constantan 49E10-8 Quarz 1E17 Rsistors in parallel and in series 1 1 1 1 ... Rtot R1 R2 R3 Rtot R1 R2 R3 ... Capacitors Component can store charge How much capacitor can store charge Capacitors ability to collect electrons Capacitance Voltage over the capacitor Q C V C 0 r A d Capacitors in parallel and in series Ctot C1 C2 C3 ... 1 Ctot 1 1 1 C1 C2 C3 ... Different types of capacitors Big electrolyte capacitors Tantalum caoacitors Signal conditioning capacitors made from plastic or ceramic Aluminium electrolyte capacitors Cylindrical shape and big size They are polarized Typical values 100 nF to 4700μF Typical maximum voltage value 12V,16V, 32V, 64V Made of long sheet of coated plastic film Insulating material is non conducting liquid Tantalum capacitors Low voltage devices Capacitance 1μF – 150μF Stable capacitance and very low impedance in low frequencies Dont like voltage spikes Can be exploded if connected wrong way into the circuit Plastic capacitors Typical materials polystyrene, polyester, polypropylene or teflon Capacitance 1 nF – 50μF Ceramic and mica capacitors Coils or Inductors The DC current through a coil forms an electric magnet Short circuit for DC, AC signal properties used in electronics Series and parallel connections are calculated like resistors di vL dt wL 1 2 Li 2 Transformers When two coils are put close to each otherby mutual inductance the energy is transferred from one coil to the other V1 N1 V2 N 2 I1 N1 I2 N2 RLC-circuits Material type Conductrors (resistivity about 10E-7 Ωm) Insulators Semi conductive materials (resistivity over 10E10Ωm) Germanium was the first Silicon has replace germanium Compaund semiconductors (GaAs) P-type semiconductors (holes are the majority carriers( N-type semiconductors (electrons are the majority carriers) Diodes P-type end is anode and n-type is cathode Voltage over zener-diode does not depend on the current passing the component Light emitting diodes (LED) NPN and PNP transistors Transistor is a current controlled current source The transistor can be used as a switch or as an amplifier Integrated circuits Include many integrated components (divided by the amount of transistors) SSI small (operational amplifiers, regulators) MSI medium LSI large scale (processors) VLSI Operational amplifiers Used to amplify signals instead of transistor amplifiers Filter circuits Integrators derivators Inverting amplifier Rf vout G vin R1 Noninverting amplifier Rf vout G 1 vin R1 Summing amplifier vout Rf R1 v1 Rf R2 v2 Rf R3 v3 ... Differential amplifier vout Rf R (v2 v1 ) Integrator Derivator