* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Closed and Open Loop Gain
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
PID controller wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
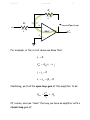
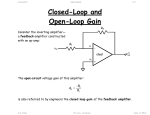
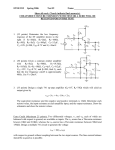
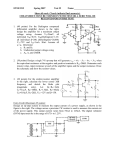
4/29/2017 840942916 1/4 Closed-Loop and Open-Loop Gain Consider the inverting amplifier—a feedback amplifier constructed with an op-amp: R2 vin R1 v- ideal v+ oc vout + The open-circuit voltage gain of this amplifier: Avo R2 R1 is also referred to by engineers the closed loop gain of the feedback amplifier. 4/29/2017 840942916 2/4 Q: Closed loop? What does that mean? A: The term “closed loop” refers to loop formed by the feed-forward path and the feed-back (i.e., feedback) path of the amplifier. In this case, the feed-forward path is formed by the op-amp, while the feed-back path is formed by the feedback resistor R2. R2 vin R1 Feed-back Path v- - Closed-Loop ideal v+ + oc vout Feed-forward Path If the loop is broken, then we say the loop is “open”. The gain (vo vi ) for the open loop case is referred to as the open-loop gain. 4/29/2017 840942916 3/4 R2 i2 R1 vin v- Open-Loop - i1 ideal v+ oc vout + For example, in the circuit above we know that: v 0 oc vout Aop v v i1 i2 0 v vin i1R1 0 Combining, we find the open-loop gain of this amplifier to be: Aopen oc vout Aop vin Of course, once we “close” the loop, we have an amplifier with a closed-loop gain of: 4/29/2017 840942916 Aclosed 4/4 oc vout R 2 vin R1 which of course is the open-circuit voltage gain of this inverting amplifier. Note that the closed-loop gain ( R2 R1 ) does not explicitly involve the op-amp gain Aop. * The closed-loop gain is determined by two resistor values, which typically are selected to provide significant gain ( Avo 1 ), albeit not so large that the amplifier is easily saturated. * Conversely, the open-loop gain (-Aop) obviously does involve the op-amp gain. Moreover, as in this case, the open-loop gain of a feedback amplifier often only involves the op-amp gain! * As a result, the op-amp gain is often alternatively referred to as the open-loop gain. Note that closing the feedback loop turns a generally useless amplifier (the gain is too high!) into a very useful one (the gain is just right)!