* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 9 Chordates - Jamestown Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
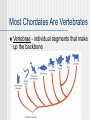
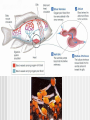
Unit 9 Chordates Ch. 30 Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, & Amphibians What Is a Chordate? A chordate is an animal that has, for at least some stage of its life, a dorsal, hollow nerve cord; a notochord; pharyngeal pouches; & a tail that extends beyond the anus What Is a Chordate? Notochord - a long supporting rod that runs through the body just below the nerve cord Pharyngeal pouches - paired structures in the throat region, used to help in gas exchange Most Chordates Are Vertebrates Vertebrae - individual segments that make up the backbone Nonvertebrate Chordates The 2 groups of nonvertebrate chordates are tunicates & lancelets Both are soft-bodied marine organisms Tunicates are often called sea squirts because of the stream of water they eject Nonvertebrate Chordates Lancelets are small nonvertebrate chordates that often live with their bodies 1/2 buried in sand What Is a Fish? Fishes are aquatic vertebrates; most fishes have paired fins, scales, & gills Evolution of Fishes The evolution of jaws & the evolution of paired fins were important developments during the rise of fishes Form & Function in Fishes Adaptations to aquatic life include various modes of feeding, specialized structures for gas exchange, & paired fins for locomotion Groups of Fishes When you consider their basic internal structure, all living fishes can be classified into 3 groups: jawless fishes, cartilaginous fishes, & bony fishes Diversity of Ray-Finned Fishes Ecology of Fishes Fishes are important source of food for many organisms What Is an Amphibian? An amphibian is a vertebrate that, typically, lives in water as a larva & on land as an adult, breathes with lungs as an adult, has moist skin that contains mucous glands, & lacks scales & claws Evolution of Amphibians Early amphibians evolved several adaptations that helped them live at least part of their lives out of water Bones in the limbs of amphibians became stronger, permitting more efficient movement Evolution of Amphibians Lungs & breathing tubes enabled them to breathe air The sternum, or breastbone, formed a bony shield to support & protect internal organs, especially the lungs Form & Function in Amphibians Tadpoles are filter feeders, adult amphibians are almost entirely carnivorous Form & Function in Amphibians An amphibian’s heart has 3 chambers, 2 atria & 1 ventricle Some wastes diffuse across the skin, but kidneys remove most wastes from bloodstream Form & Function in Amphibians An amphibian typically begins its life in water, then moves on land as an adult Groups of Amphibians The 3 groups of amphibians alive today are salamanders, frogs & toads, & caecilians Diversity of Amphibians Ecology of Amphibians Some amphibians that release toxins have brightly colored bodies The colors & patterns serve as a warning to potential predators