* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download J Gruv - Nutrientspart1
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
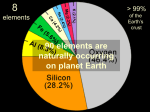
Nutrient management for organic vegetable production in NC Part I http://compost.tamu.edu/demos/palopinto/compost.jpg Average rates (lbs/acre) of N, P2O5 and K2O applied to vegetable crops in the US Nitrogen Phosphorus Potassium Why are these rates so high ? http://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/sb969/sb969c.pdf Most growers believe that high rates of nutrients are needed to produce high yields of high quality vegetables Jalapeno pepper production in Fresno County, California Total cost of production: $4392 Total fertilizer costs: $170 Fertilizer costs = 4% of total costs ~ 16 elements have been identified as essential for the growth of all plants Soil C OH air & water N K Ca Mg P S Cl Fe Mn Zn B Cu Mo macronutrients micronutrients V Co Ni Needed by some plants Na Si Micronutrients are critical components of enzymes minerals Soil solids contain nutrients organic matter H20 Soil water contains nutrients H 20 K+ H 20 +2 Ca - -H 20 Mg+2 H20 - - Humus H+ H20 exchangeable ions H 20 Clay -- H20 H 20 - Na Ca+2 H 20 H20 + K+ H20 H 20 H20 Soil soup H20 H20 H20 What’s in the soil soup ?? Cu+3 DOM Ca+2 NO3- Ca+2 +2 NO3- Mg +2 H PO 2 4 Ca Zn+2 DOM + K - NO3 K+ +2 Ca+2 Mg Mg+2 Fe NO 3 +3 DOM SO4-2 Ca+2 Adapted from Brady and Weil (2002) Which forms of nutrients are available to plants ? solution exchangeable “active” OM passive “OM” weatherable minerals Re-seasoning the soup Modified from Havlin et al. (1999) …… Crop yield Deficiency Symptoms Nutrient availability http://www.extension.umn.edu/distribution/horticulture/components/M1190fig1.htm Understanding nutrient uptake H 20 Root exudates activate soil microbes Transpirational stream H 20 Root growth Feed the soil vs. Feed the crop ? Both strategies are important ! Healthy roots need available nutrients ! Unhealthy roots use nutrients inefficiently… ? Chronic root malfunction Acute root disease The acid infertility complex Nutrient availability varies with pH Understanding aluminum toxicity Toxic forms Aluminum of Al are toxicity is bioavailable at lowminimal pHs above pH 5.5 http://www2.ctahr.hawaii.edu/tpss/research_extension/rxsoil/alroot.gif 100% Percentage of maximum cation exchange capacity 75% 50% 25% Exchangeable Al+3 0% Brady and Weil (2002) Micronutrient deficiencies frequently occur when naturally acid soils are over-limed http://www.fftc.agnet.org/library/image/bc51002p7.html Avoid over-liming !! http://hubcap.clemson.edu/~blpprt/acid2-chart1.gif