* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MatterCycles
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Total organic carbon wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
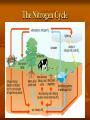
Matter Cycles Objective 3 Chapter 3-3 The Water Cycle 1. 2. 3. 4. Water evaporates (or transpirates from plants) into the atmosphere. Water condenses (clouds), and then precipitates (rains) back down to the Earth. Water runs into streams and rivers (runoff) or is absorbed into the ground (seepage) to become ground water. Water is taken up by the roots of plants or it makes its way to the oceans, flowing above ground or below ground. The Water Cycle cont. The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and decomposition take up and release Carbon and Oxygen. Volcanic eruptions and erosion release Carbon Dioxide into the atmosphere and oceans Burial and decomposition of dead organisms store Carbon underground (coal & oil). Human activities, such as cutting and burning forests, and burning fossil fuels, release Carbon Dioxide into the atmosphere. Global Warming… The Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Fixation changes the nitrogen in the air into nitrogen life can use in the soil. Lightning, bacteria fertilizer Once Nitrogen has been fixed in the soil it is then taken up by producers (plants). The Nitrogen Cycle Phosphorus It is not abundant in the atmosphere, so it follows a simple cycle. soil producer herbivore carnivore decomposer back to soil The Phosphorus Cycle Limiting Nutrient Each ecosystem has at least 1 important nutrient that limits it’s growth Desert = Water Rainforest = Nitrogen Ocean = Phosphorus The limiting nutrient determines the ecosystems carrying capacity Carrying capacity = the maximum amount of life an ecosystem can support